Mybatis中使用注解 or xml 文件?
注解使用姿势
下面以Select注解为例。
@Select 的本质还是 xml 文件的形式,有两种方式@Select注解和@SelectProvider。
以下使用@Select注解。
<pre>
public interface UserMapper {
Select("SELECT id, name FROM users WHERE id = #{id}")
User selectById(int id);
}
</pre>
@Select("<script>SELECT firstName <if test=\"includeLastName != null\">, lastName</if> FROM names WHERE lastName LIKE #{name}</script>")
List<Name> selectXmlWithMapper(Parameter p);
以下使用@SelectProvider注解。@SelectProvider注解也可以使用:String sql = new SQL().SELECT().FROM().WHERE().toString();
<pre>
public interface UserMapper {
SelectProvider(type = SqlProvider.class, method = "selectById")
User selectById(int id);
public static class SqlProvider {
public static String selectById() {
return "SELECT id, name FROM users WHERE id = #{id}";
}
}
}
</pre>
Xml使用方式
太常见,略。
是注解还是XML
个人觉得一个比较折中的方式是简单 SQL 可以用注解开发,如果是一些有诸如条件判断类的需求的 SQL 还是要写在 xml 文件中。不要为了拥抱注解,而完全摒弃了 xml 的形式。但这里需要特别注意,一个实体类只能使用xml或注解中的一种,不能一个实体类中一个方法使用注解,一个方法使用xml。
关于SelectOne方法
selectOne实质是使用的selectList。
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
关于SelectList的源码分析
下面以源码包中的LanguageTest测试类为例。代码如下。
@BeforeAll
static void setUp() throws Exception {
try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("org/apache/ibatis/submitted/language/MapperConfig.xml")) {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
}
BaseDataTest.runScript(sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment().getDataSource(),
"org/apache/ibatis/submitted/language/CreateDB.sql");
}
分为四个步骤:
- 读取配置文件。
- 新建sqlSessionFactory。
- 初始化数据库脚本。
- 执行selectList方法。
1. 读取配置文件

//LanguageTest.java
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("org/apache/ibatis/submitted/language/MapperConfig.xml")
//Resources.java
/**
* 返回类路径上的资源作为Reader对象
*
* @param resource The resource to find
* @return The resource
* @throws java.io.IOException If the resource cannot be found or read
*/
public static Reader getResourceAsReader(String resource) throws IOException {
Reader reader;
if (charset == null) {
//因没指定字符集,走这里
reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource));
} else {
reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource), charset);
}
return reader;
}
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource) throws IOException {
return getResourceAsStream(null, resource);
}
/**
* 返回类路径上的资源作为Stream对象
*
* @param loader The classloader used to fetch the resource
* @param resource The resource to find
* @return The resource
* @throws java.io.IOException If the resource cannot be found or read
*/
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(ClassLoader loader, String resource) throws IOException {
InputStream in = classLoaderWrapper.getResourceAsStream(resource, loader);
if (in == null) {
throw new IOException("Could not find resource " + resource);
}
return in;
}
//ClassLoaderWrapper.java
/**
* 从特定的类加载器开始,从类路径获取资源
*
* @param resource - the resource to find
* @param classLoader - the first class loader to try
* @return the stream or null
*/
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return getResourceAsStream(resource, getClassLoaders(classLoader));
}
// 将当前ClassLoader加入到ClassLoader集合
ClassLoader[] getClassLoaders(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return new ClassLoader[]{
classLoader,//当前classLoader,这里为空
defaultClassLoader,//默认的classLoader
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
getClass().getClassLoader(),
systemClassLoader};
}
/**
* 尝试从一组类加载器中获取资源
*
* @param resource - the resource to get
* @param classLoader - the classloaders to examine
* @return the resource or null
*/
InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader[] classLoader) {
for (ClassLoader cl : classLoader) {
if (null != cl) {
// try to find the resource as passed
InputStream returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// now, some class loaders want this leading "/", so we'll add it and try again if we didn't find the resource
if (null == returnValue) {
returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream("/" + resource);
}
if (null != returnValue) {
return returnValue;
}
}
}
return null;
}
// ClassLoader
/**
* Returns an input stream for reading the specified resource.
*
* <p> The search order is described in the documentation for {@link
* #getResource(String)}. </p>
*
* @param name
* The resource name
*
* @return An input stream for reading the resource, or <tt>null</tt>
* if the resource could not be found
*
* @since 1.1
*/
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
return url != null ? url.openStream() : null;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Finds the resource with the given name. A resource is some data
* (images, audio, text, etc) that can be accessed by class code in a way
* that is independent of the location of the code.
*
* <p> The name of a resource is a '<tt>/</tt>'-separated path name that
* identifies the resource.
*
* <p> 该方法将首先在父类加载器中搜索*资源;如果父级为<tt> null </ tt>,
* 则会搜索虚拟机内置的类加载器的路径。如果失败,此方法将调用{@link #findResource(String)}来查找资源。 </p>
*
* @apiNote When overriding this method it is recommended that an
* implementation ensures that any delegation is consistent with the {@link
* #getResources(java.lang.String) getResources(String)} method.
*
* @param name
* The resource name
*
* @return A <tt>URL</tt> object for reading the resource, or
* <tt>null</tt> if the resource could not be found or the invoker
* doesn't have adequate privileges to get the resource.
*
* @since 1.1
*/
public URL getResource(String name) {
URL url;
if (parent != null) {
url = parent.getResource(name);
} else {
url = getBootstrapResource(name);
}
if (url == null) {
url = findResource(name);
}
return url;
}
/**
* 从VM的内置类加载器中查找资源。
*/
private static URL getBootstrapResource(String name) {
URLClassPath ucp = getBootstrapClassPath();
Resource res = ucp.getResource(name);
return res != null ? res.getURL() : null;
}
先加载JAVA_HOME的路径下的instrument.dll动态链接库。

加载指令动态链接库到本地动态链接库上下文中。


idea运行main方法之前的准备工作。

//InstrumentationImpl.java
private void loadClassAndCallPremain(String var1, String var2) throws Throwable {
this.loadClassAndStartAgent(var1, "premain", var2);
}
加载lib下的jar包,包括加载rt.jar内的2000多个常用类。

先尝试从jdk的相关路径进行获取。

即从URLClassPath获取。

然后再尝试从URL的路径进行获取。
//URLClassLoader.java
public URL findResource(final String name) {
/*
* The same restriction to finding classes applies to resources
*/
URL url = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<URL>() {
public URL run() {
return ucp.findResource(name, true);
}
}, acc);
return url != null ? ucp.checkURL(url) : null;
}
//URL.java
* <P>如果用于URL的协议(例如HTTP或JAR),则存在一个公共的,专门的URLConnection子类,该子类属于以下软件包之一或其子软件包之一:
* java.lang,java.io,java .util,java.net,
* 返回的连接将属于该子类。例如,对于HTTP,将返回HttpURLConnection,对于JAR,将返回JarURLConnection。</ P>
*
* @return a {@link java.net.URLConnection URLConnection} linking
* to the URL.
* @exception IOException if an I/O exception occurs.
* @see java.net.URL#URL(java.lang.String, java.lang.String,
* int, java.lang.String)
*/
public URLConnection openConnection() throws java.io.IOException {
return handler.openConnection(this);
}
//Handler.java
public synchronized URLConnection openConnection(URL var1, Proxy var2) throws IOException {
String var4 = var1.getFile();
String var5 = var1.getHost();
String var3 = ParseUtil.decode(var4);
var3 = var3.replace('/', '\\');
var3 = var3.replace('|', ':');
if (var5 != null && !var5.equals("") && !var5.equalsIgnoreCase("localhost") && !var5.equals("~")) {
var3 = "\\\\" + var5 + var3;
File var6 = new File(var3);
if (var6.exists()) {
return this.createFileURLConnection(var1, var6);
} else {
URLConnection var7;
try {
URL var8 = new URL("ftp", var5, var4 + (var1.getRef() == null ? "" : "#" + var1.getRef()));
if (var2 != null) {
var7 = var8.openConnection(var2);
} else {
var7 = var8.openConnection();
}
} catch (IOException var10) {
var7 = null;
}
if (var7 == null) {
throw new IOException("Unable to connect to: " + var1.toExternalForm());
} else {
return var7;
}
}
} else {
return this.createFileURLConnection(var1, new File(var3));
}
}
// URLClassLoader.java
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
if (url == null) {
return null;
}
URLConnection urlc = url.openConnection();
InputStream is = urlc.getInputStream();
if (urlc instanceof JarURLConnection) {
JarURLConnection juc = (JarURLConnection)urlc;
JarFile jar = juc.getJarFile();
synchronized (closeables) {
if (!closeables.containsKey(jar)) {
closeables.put(jar, null);
}
}
} else if (urlc instanceof sun.net.www.protocol.file.FileURLConnection) {
synchronized (closeables) {
closeables.put(is, null);
}
}
return is;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
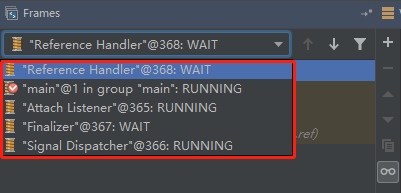
java启动后的线程有哪些?
从下图可以看到有ReferenceHanlder线程,有main线程组中的main线程,有Attach Listencer线程,有Finalizer线程,有Signal Dispatcher线程。可以通过以下方法得出。
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.lang.management.ThreadInfo;
import java.lang.management.ThreadMXBean;
public class MultiThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取java线程管理MXBean
ThreadMXBean threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();
ThreadInfo[] threadInfos = threadMXBean.dumpAllThreads(false, false);
// 遍历线程信息,仅打印线程ID和线程名称信息
for (ThreadInfo threadInfo : threadInfos) {
System.out.println("[" + threadInfo.getThreadId() + "] " + threadInfo.getThreadName());
}
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.version"));
}
}
ReferenceHandler线程:由Reference静态代码块中建立并且运行的线程,它的运行方法中依赖了比较多的本地(native)方法,ReferenceHandler线程的主要功能是处理pending链表中的引用对象。

// ReferenceHandler直接继承于Thread覆盖了run方法
private static class ReferenceHandler extends Thread {
// 静态工具方法用于确保对应的类型已经初始化
private static void ensureClassInitialized(Class<?> clazz) {
try {
Class.forName(clazz.getName(), true, clazz.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw (Error) new NoClassDefFoundError(e.getMessage()).initCause(e);
}
}
static {
// 确保Cleaner这个类已经初始化
// pre-load and initialize Cleaner class so that we don't
// get into trouble later in the run loop if there's
// memory shortage while loading/initializing it lazily.
ensureClassInitialized(Cleaner.class);
}
ReferenceHandler(ThreadGroup g, String name) {
super(g, null, name, 0, false);
}
// 注意run方法是一个死循环执行processPendingReferences
public void run() {
while (true) {
processPendingReferences();
}
}
}
/* 原子获取(后)并且清理VM中的pending引用链表
* Atomically get and clear (set to null) the VM's pending-Reference list.
*/
private static native Reference<Object> getAndClearReferencePendingList();
/* 检验VM中的pending引用对象链表是否有剩余元素
* Test whether the VM's pending-Reference list contains any entries.
*/
private static native boolean hasReferencePendingList();
/* 等待直到pending引用对象链表不为null,此方法阻塞的具体实现又VM实现
* Wait until the VM's pending-Reference list may be non-null.
*/
private static native void waitForReferencePendingList();
// 锁对象,用于控制等待pending对象时候的加锁和开始处理这些对象时候的解锁
private static final Object processPendingLock = new Object();
// 正在处理pending对象的时候,这个变量会更新为true,处理完毕或者初始化状态为false,用于避免重复处理或者重复等待
private static boolean processPendingActive = false;
// 这个是死循环中的核心方法,功能是处理pending链表中的引用元素
private static void processPendingReferences() {
// Only the singleton reference processing thread calls
// waitForReferencePendingList() and getAndClearReferencePendingList().
// These are separate operations to avoid a race with other threads
// that are calling waitForReferenceProcessing().
// (1)等待
waitForReferencePendingList();
Reference<Object> pendingList;
synchronized (processPendingLock) {
// (2)获取并清理,标记处理中状态
pendingList = getAndClearReferencePendingList();
processPendingActive = true;
}
// (3)通过discovered(下一个元素)遍历pending链表进行处理
while (pendingList != null) {
Reference<Object> ref = pendingList;
pendingList = ref.discovered;
ref.discovered = null;
// 如果是Cleaner类型执行执行clean方法并且对锁对象processPendingLock进行唤醒所有阻塞的线程
if (ref instanceof Cleaner) {
((Cleaner)ref).clean();
// Notify any waiters that progress has been made.
// This improves latency for nio.Bits waiters, which
// are the only important ones.
synchronized (processPendingLock) {
processPendingLock.notifyAll();
}
} else {
// 非Cleaner类型并且引用队列不为ReferenceQueue.NULL则进行入队操作
ReferenceQueue<? super Object> q = ref.queue;
if (q != ReferenceQueue.NULL) q.enqueue(ref);
}
}
// (4)当次循环结束之前再次唤醒锁对象processPendingLock上阻塞的所有线程
// Notify any waiters of completion of current round.
synchronized (processPendingLock) {
processPendingActive = false;
processPendingLock.notifyAll();
}
}
ReferenceHandler线程启动的静态代码块如下:
static {
// ThreadGroup继承当前执行线程(一般是主线程)的线程组
ThreadGroup tg = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
for (ThreadGroup tgn = tg;
tgn != null;
tg = tgn, tgn = tg.getParent());
// 创建线程实例,命名为Reference Handler,配置最高优先级和后台运行(守护线程),然后启动
Thread handler = new ReferenceHandler(tg, "Reference Handler");
/* If there were a special system-only priority greater than
* MAX_PRIORITY, it would be used here
*/
handler.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
handler.setDaemon(true);
handler.start();
// 注意这里覆盖了全局的jdk.internal.misc.JavaLangRefAccess实现
// provide access in SharedSecrets
SharedSecrets.setJavaLangRefAccess(new JavaLangRefAccess() {
@Override
public boolean waitForReferenceProcessing()
throws InterruptedException{
return Reference.waitForReferenceProcessing();
}
@Override
public void runFinalization() {
Finalizer.runFinalization();
}
});
}
// 如果正在处理pending链表中的引用对象或者监测到VM中的pending链表中还有剩余元素则基于锁对象processPendingLock进行等待
private static boolean waitForReferenceProcessing()
throws InterruptedException{
synchronized (processPendingLock) {
if (processPendingActive || hasReferencePendingList()) {
// Wait for progress, not necessarily completion.
processPendingLock.wait();
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
由于ReferenceHandler线程是Reference的静态代码创建的,所以只要Reference这个父类被初始化,该线程就会创建和运行,由于它是守护线程,除非JVM进程终结,否则它会一直在后台运行(注意它的run()方法里面使用了死循环)。
Attach Listener线程:负责接收到外部的命令,对该命令进行执行然后把结果返回给发送者。
在Linux平台上,attach方法最终是使用了/proc和ptrace来读取目标VM中的数据,ptrace提供了一种使父进程可以监视和控制其它进程的方式,它还能够改变子进程中的寄存器和内核映像,因而可以实现断点调试和系统调用的跟踪(ptrace会使内核暂停当前进程并将控制权交给跟踪进程,使跟踪进程得以察看或者修改被跟踪进程的寄存器,待收集完跟踪信息以后会把控制权交回给当前进程让其继续运行)。
VirtualMachine.attach(Attach到Attach Listener线程后执行有限命令)
VirtualMachine.attach方法过程分析(linux):
(1)信号机制
JVM启动的时候并不会马上创建Attach Listener线程,而是通过另外一个线程Signal Dispatcher在接收到信号处理请求(如jstack,jmap等)时创建临时socket文件/tmp/.java_pid并创建Attach Listener线程(external process会先发送一个SIGQUIT信号给target VM process,target VM会创建一个Attach Listener线程);
(2)Unix domain socket
Attach Listener线程会通过Unix domain socket与external process建立连接,之后就可以基于这个socket进行通信了。
创建好的Attach Listener线程会负责执行这些命令(从队列里不断取AttachOperation,然后找到请求命令对应的方法进行执行,比如jstack命令,找到 { “threaddump”, thread_dump }的映射关系,然后执行thread_dump方法)并且把结果通过.java_pid文件返回给发送者。
整个过程中,会有两个文件被创建:
.attach_pid,external process会创建这个文件,为的是触发Attach Listener线程的创建,因为SIGQUIT信号不是只有external process才会发的,通过这个文件来告诉target VM,有attach请求过来了(如果.attach_pid创建好了,说明Attach Listener线程已经创建成功)。相关代码在LinuxVirtualMachine.java中;
.java_pid,target VM会创建这个文件,这个是因为Unix domain socket本身的实现机制需要去创建一个文件,通过这个文件来进行IPC。相关代码在attachListener_linux.cpp中。
其中的都是target VM的pid。
Signal Dispatcher线程:signal dispatcher 线程通过sem_wait会在等待,当进程接到信号SIGQUIT的时候,只有vm thread会被中断(见上面分析),而进入UserHandler 函数,通过调用 os::signal_notify 去通告signal dispatcher 线程,让 signal dispatch 线程去处理信号。
在信号设计里,因为信号中断是在内核态调用的,内核调用了线程注入了自己的信号函数,一般只允许在该函数里处理简单的事物,所以在java里面专门设计了处理信号后续的线程(signal dispatcher),接受到信号的线程通过信号函数notify到处理信号的线程(signal dispatcher ),最后由该线程做后续的事情。比如线程dump。
Finalizer线程:用于垃圾回收的线程。
private static class FinalizerThread extends Thread {
private volatile boolean running;
FinalizerThread(ThreadGroup g) {
super(g, "Finalizer");
}
public void run() {
// in case of recursive call to run()
if (running)
return;
// Finalizer thread starts before System.initializeSystemClass
// is called. Wait until JavaLangAccess is available
while (!VM.isBooted()) {
// delay until VM completes initialization
try {
VM.awaitBooted();
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
// ignore and continue
}
}
final JavaLangAccess jla = SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess();
running = true;
for (;;) {
try {
Finalizer f = (Finalizer)queue.remove();
f.runFinalizer(jla);
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
// ignore and continue
}
}
}
}
static {
ThreadGroup tg = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
for (ThreadGroup tgn = tg;
tgn != null;
tg = tgn, tgn = tg.getParent());
Thread finalizer = new FinalizerThread(tg);
finalizer.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY - 2);
finalizer.setDaemon(true);
finalizer.start();
}
2. 新建sqlSessionFactory

因遇到new 关键字,需要通过classLoader进行加载该类到内存。
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
// SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.java
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
return build(reader, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
//XMLConfigBuilder.java
public XMLConfigBuilder(Reader reader, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(reader, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
//XPathParser.java
public XPathParser(Reader reader, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver);
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(reader));
}
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setFeature(XMLConstants.FEATURE_SECURE_PROCESSING, true);
factory.setValidating(validation);
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver);
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {
@Override
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
// NOP
}
});
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
//DocumentBuilderImpl.java
public Document parse(InputSource is) throws SAXException, IOException {
if (is == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
DOMMessageFormatter.formatMessage(DOMMessageFormatter.DOM_DOMAIN,
"jaxp-null-input-source", null));
}
if (fSchemaValidator != null) {
if (fSchemaValidationManager != null) {
fSchemaValidationManager.reset();
fUnparsedEntityHandler.reset();
}
resetSchemaValidator();
}
domParser.parse(is);
Document doc = domParser.getDocument();
domParser.dropDocumentReferences();
return doc;
}
//DOMParser.java
/**
* parse
*
* @param inputSource
*
* @exception org.xml.sax.SAXException
* @exception java.io.IOException
*/
public void parse(InputSource inputSource)
throws SAXException, IOException {
// parse document
try {
XMLInputSource xmlInputSource =
new XMLInputSource(inputSource.getPublicId(),
inputSource.getSystemId(),
null);
xmlInputSource.setByteStream(inputSource.getByteStream());
xmlInputSource.setCharacterStream(inputSource.getCharacterStream());
xmlInputSource.setEncoding(inputSource.getEncoding());
parse(xmlInputSource);
}
// wrap XNI exceptions as SAX exceptions
catch (XMLParseException e) {
Exception ex = e.getException();
if (ex == null) {
// must be a parser exception; mine it for locator info and throw
// a SAXParseException
LocatorImpl locatorImpl = new LocatorImpl();
locatorImpl.setPublicId(e.getPublicId());
locatorImpl.setSystemId(e.getExpandedSystemId());
locatorImpl.setLineNumber(e.getLineNumber());
locatorImpl.setColumnNumber(e.getColumnNumber());
throw new SAXParseException(e.getMessage(), locatorImpl);
}
if (ex instanceof SAXException) {
// why did we create an XMLParseException?
throw (SAXException)ex;
}
if (ex instanceof IOException) {
throw (IOException)ex;
}
throw new SAXException(ex);
}
catch (XNIException e) {
Exception ex = e.getException();
if (ex == null) {
throw new SAXException(e.getMessage());
}
if (ex instanceof SAXException) {
throw (SAXException)ex;
}
if (ex instanceof IOException) {
throw (IOException)ex;
}
throw new SAXException(ex);
}
}
//XMLConfigBuilder.java
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));//获取最外层的configuration标签
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));//先解析properties属性
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));//解析settings属性
loadCustomVfs(settings);//VFS含义是虚拟文件系统;主要是通过程序能够方便读取本地文件系统、FTP文件系统等系统中的文件资源。Mybatis中提供了VFS这个配置,主要是通过该配置可以加载自定义的虚拟文件系统应用程序。
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));//保存类和别名的关系
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));//插件拦截器,其使用可参考https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html#plugins
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));//这个是我们最关心的mappers配置
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
xml配置文件
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="defaultScriptingLanguage" value="velocity"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="velocity" type="org.apache.ibatis.submitted.language.VelocityLanguageDriver"/>
<typeAlias alias="name" type="org.apache.ibatis.submitted.language.Name"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="" value=""/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="UNPOOLED">
<property name="driver" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:mem:language"/>
<property name="username" value="sa"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/apache/ibatis/submitted/language/Mapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
3. 初始化数据库脚本
//BaseDataTest.java
BaseDataTest.runScript(sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment().getDataSource(),
"org/apache/ibatis/submitted/language/CreateDB.sql");
public static void runScript(DataSource ds, String resource) throws IOException, SQLException {
try (Connection connection = ds.getConnection()) {
ScriptRunner runner = new ScriptRunner(connection);
runner.setAutoCommit(true);
runner.setStopOnError(false);
runner.setLogWriter(null);
runner.setErrorLogWriter(null);
runScript(runner, resource);
}
}
public static void runScript(ScriptRunner runner, String resource) throws IOException, SQLException {
try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource)) {
runner.runScript(reader);
}
}
/**
* 返回类路径上的资源作为Reader对象(同之前的读取配置文件)
*
* @param resource The resource to find
* @return The resource
* @throws java.io.IOException If the resource cannot be found or read
*/
public static Reader getResourceAsReader(String resource) throws IOException {
Reader reader;
if (charset == null) {
reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource));
} else {
reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource), charset);
}
return reader;
}
public void runScript(Reader reader) {
setAutoCommit();
try {
if (sendFullScript) {
executeFullScript(reader);
} else {
executeLineByLine(reader);
}
} finally {
rollbackConnection();
}
}
//ScriptRunner.java
private void handleLine(StringBuilder command, String line) throws SQLException {
String trimmedLine = line.trim();
if (lineIsComment(trimmedLine)) {
Matcher matcher = DELIMITER_PATTERN.matcher(trimmedLine);
if (matcher.find()) {
delimiter = matcher.group(5);
}
println(trimmedLine);
} else if (commandReadyToExecute(trimmedLine)) {
command.append(line, 0, line.lastIndexOf(delimiter));
command.append(LINE_SEPARATOR);
println(command);
executeStatement(command.toString());
command.setLength(0);
} else if (trimmedLine.length() > 0) {
command.append(line);
command.append(LINE_SEPARATOR);
}
}
private void executeStatement(String command) throws SQLException {
try (Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.setEscapeProcessing(escapeProcessing);
String sql = command;
if (removeCRs) {
sql = sql.replace("\r\n", "\n");
}
try {
boolean hasResults = statement.execute(sql);
while (!(!hasResults && statement.getUpdateCount() == -1)) {
checkWarnings(statement);
printResults(statement, hasResults);
hasResults = statement.getMoreResults();
}
} catch (SQLWarning e) {
throw e;
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (stopOnError) {
throw e;
} else {
String message = "Error executing: " + command + ". Cause: " + e;
printlnError(message);
}
}
}
}
4. 执行selectList方法
我们以testLangRaw测试方法为例。
@Test
void testLangRaw() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
Parameter p = new Parameter(true, "Fli%");
List<Name> answer = sqlSession.selectList("selectRaw", p);
assertEquals(3, answer.size());
for (Name n : answer) {
assertEquals("Flintstone", n.getLastName());
}
}
}
//DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
//JdbcTransactionFactory.java
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);
}
//DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
//DefaultSqlSession.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
//Configuration.java
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
if (validateIncompleteStatements) {
buildAllStatements();
}
return mappedStatements.get(id);
}
//ParamNameResolver.java
/**
* 如果对象是{@link Collection}或数组,则包装到{@link ParamMap}。
*
* @param object a parameter object
* @param actualParamName an actual parameter name
* (If specify a name, set an object to {@link ParamMap} with specified name)
* @return a {@link ParamMap}
* @since 3.5.5
*/
public static Object wrapToMapIfCollection(Object object, String actualParamName) {
if (object instanceof Collection) {
ParamMap<Object> map = new ParamMap<>();
map.put("collection", object);
if (object instanceof List) {
map.put("list", object);
}
Optional.ofNullable(actualParamName).ifPresent(name -> map.put(name, object));
return map;
} else if (object != null && object.getClass().isArray()) {
ParamMap<Object> map = new ParamMap<>();
map.put("array", object);
Optional.ofNullable(actualParamName).ifPresent(name -> map.put(name, object));
return map;
}
return object;
}
//CachingExecutor.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//MappedStatement.java
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
//RawSqlSource.java
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
//CachingExecutor.java
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
return delegate.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
//BaseExecutor.java
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
//CachingExecutor.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//BaseExecutor.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);//查询当前缓存
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
//SimpleExecutor.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
//PreparedStatementHandler.java
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
参考:
关于java启动后的线程有哪些?https://www.cnblogs.com/throwable/p/12271653.html
Attach机制:https://blog.csdn.net/fedorafrog/article/details/104537472
























 970
970











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








