目录
1 网站链接
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d8b6b4358f774294a89de2a6ac4d9337
2 题目
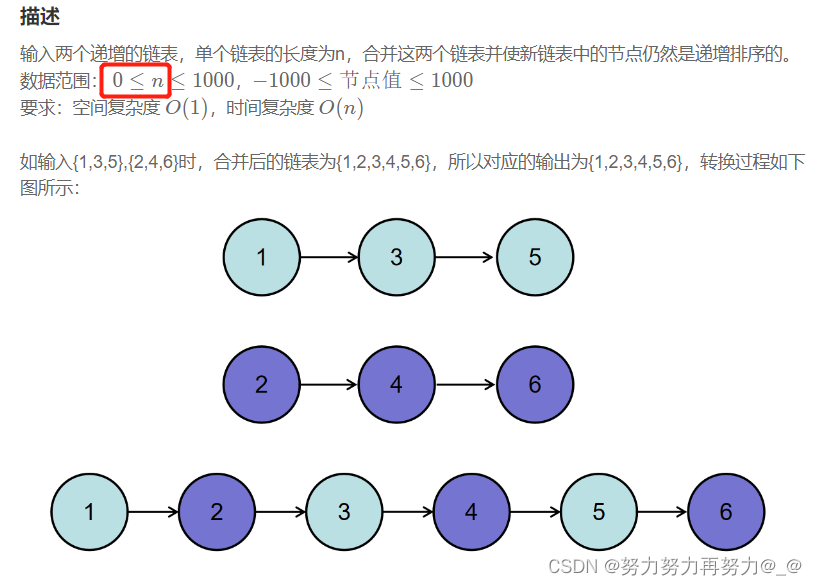
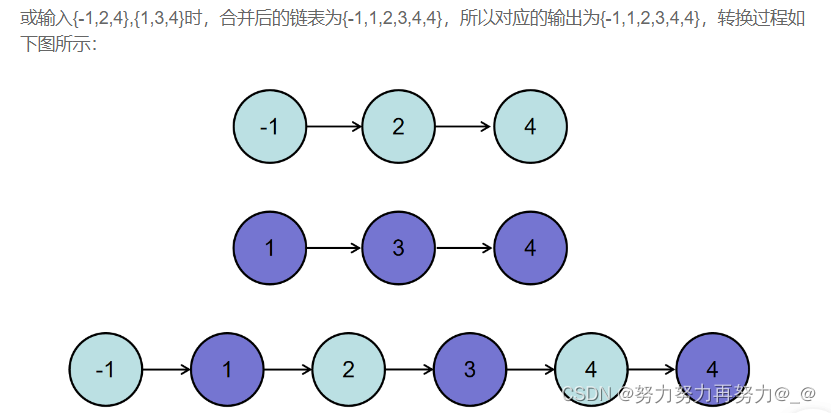
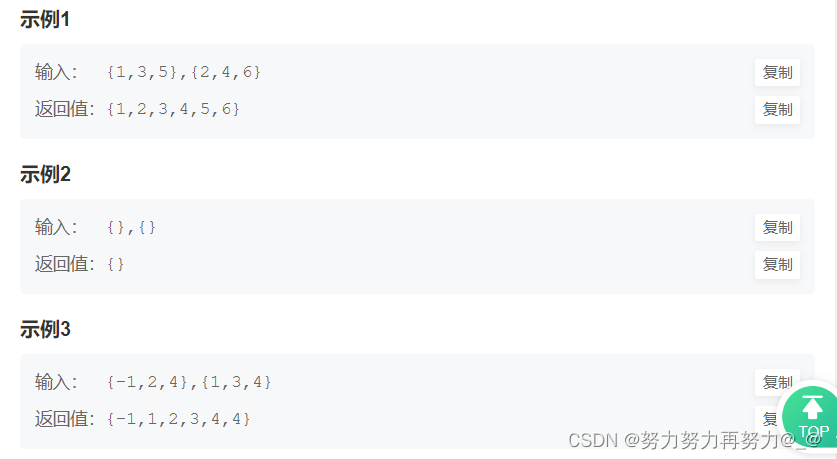
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
}
}
3 注意点
- 两个链表的长度可能是不一样的,题目中只说了单个链表的长度为n
- 我一开始看成两个链表长度为n,就以为两个链表长度一样了
- n的取值范围是0到1000,0和1000是可以取到的,所以链表的长度可能为0,即形参部分list1和list2可能为null
4 解题思路
由于两个链表的长度都可能为零,也就是传入的形参可能为null,所以将题目分为以下四种情况
- list1 = null,list2 != null(特殊情况)
- list1 != null,list2 = null(特殊情况)
- list1 = null,list2 = null(特殊情况)
- list1 != null,list2 != null(正常情况)
4.1 三种特殊情况
我们在一开始就进行判断,哪一个形参是null
- list1 = null && list2 != null ,则返回list2 ------(1)
- list1 != null && list2 = null ,则返回list1 ------(2)
- list1 = null && list2 = null ,则返回null -------(3)
(1)和(3)可以合并,只要list1=null,就返回list2
4.2 普通情况
4.2.1 方案一
按顺序遍历两个链表,依次比较两个链表中数值的大小,创建一个新链表
4.2.2 方案二
按顺序遍历两个链表,依次比较两个链表中数值的大小,在原有两个链表的基础上,修改next属性的值,将两个链表串联在一起
4.2.3 方案三
遍历两个链表,将链表中的值全部取出,放在ArrayList中,排序,再创建新的链表
5 答案
5.1 方案一代码(创建一个新链表)
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
//情况一:list1为空,list2不为空,返回list2
//情况二:list1为空,list2为空,返回null
//情况三:list1不为空,list2为空,返回list1
if (list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null){
return list1;
}
//情况四:list1不为空,list2不为空,顺序遍历,比较生成新链表
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode node = null;
ListNode head = null;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
//判断当前两个链表中的特定节点,哪个值更小,把更小的取出
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
node = new ListNode(list1.val);
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
node = new ListNode(list2.val);
list2 = list2.next;
}
//判断是否已经创建新链表
if (head == null) {
pre = node;
head = node;
} else {
pre.next = node;
pre = node;
}
}
//list2提前遍历完
if (list1 != null) {
pre.next = list1;
}
//list1提前遍历完
if (list2 != null) {
pre.next = list2;
}
return head;
}
}
5.2 方案二代码(改变两个链表的指针,将两个链表和成一个链表)
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
//情况一:list1为空,list2不为空,返回list2
//情况二:list1为空,list2为空,返回null
//情况三:list1不为空,list2为空,返回list1
if (list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null){
return list1;
}
//情况四:list1不为空,list2不为空,顺序遍历,比较生成新链表
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode node = head;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
//判断当前两个链表中的特定节点,哪个值更小,把更小的取出
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
node.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
node = node.next;
} else {
node.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
node = node.next;
}
}
//list2提前遍历完
if (list1 != null) {
node.next = list1;
}
//list1提前遍历完
if (list2 != null) {
node.next = list2;
}
return head.next;
}
}
图解
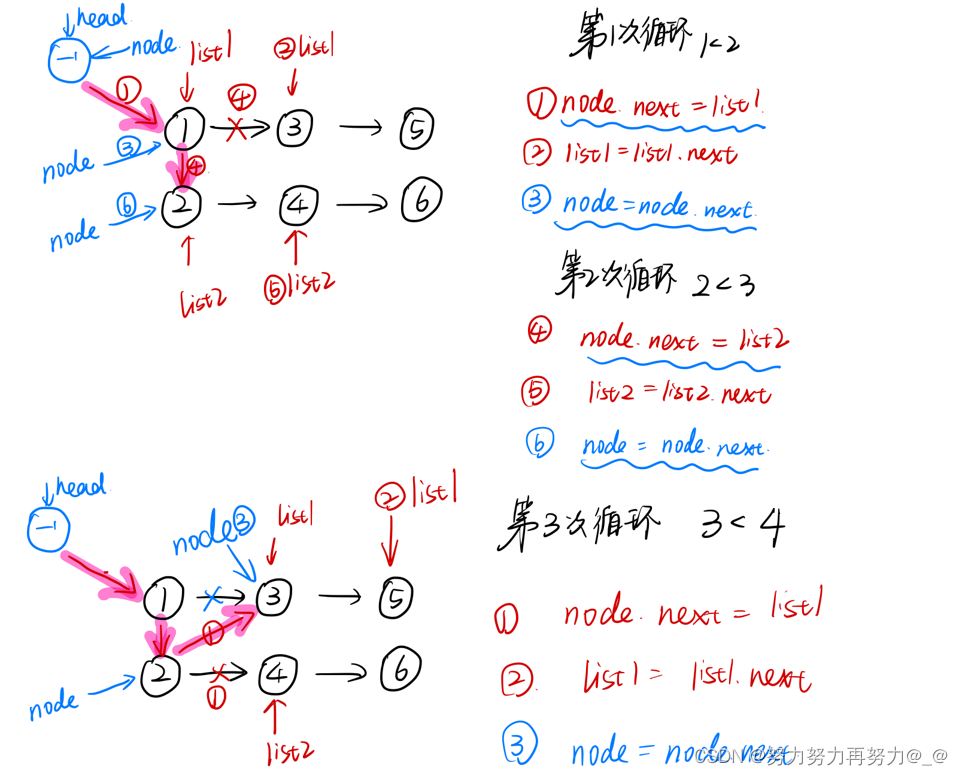
5.3 方案三代码(将链表数值全部取出,排序,创建一个新链表)
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
//情况一:list1为空,list2不为空,返回list2
//情况二:list1为空,list2为空,返回null
//情况三:list1不为空,list2为空,返回list1
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
//情况四:list1不为空,list2不为空,顺序遍历,比较生成新链表
while (list1 != null) {
list.add(list1.val);
list1 = list1.next;
}
while (list2 != null) {
list.add(list2.val);
list2 = list2.next;
}
list.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode node = null;
for (Integer i : list) {
node = new ListNode(i);
pre.next = node;
pre = node;
}
return head.next;
}
}
6 启发
在将两个链表合并时,若是用判断两个链表谁的第一个节点的数值较小,较小的那个成为新的头节点,这样处理起来比较繁琐,需要就list1的头节点较小还是list2的头节点较小写if-else判断。
可以先创建一个头节点head,然后指向两个链表中值较小的那个节点,最后在返回新链表的头结点的时候,直接返回head.next即可。























 371
371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








