实现思路
- 采用jieba进行数据处理
- 采用gensim构建主题模型
- 采用pyLDAvis可视化主题模型
包下载、引入
下载依赖包
pip install jieba
pip install gensim
pip install pyLDAvis
引入依赖包
import pyLDAvis.gensim_models
import jieba.posseg as jp,jieba
from gensim.models.coherencemodel import CoherenceModel
from gensim.models.ldamodel import LdaModel
from gensim.corpora.dictionary import Dictionary
jieba数据处理
打开两个文档,作为文档集
# 读取需要处理的文本
doc1=open('./data/text1.txt','rb').read()
doc2=open('./data/text2.txt','rb').read()
# 构建文本集
texts = [doc1,doc2]
# 词性标注条件
flags = ('n', 'nr', 'ns', 'nt', 'eng', 'v', 'd','vn','vd')
# 停用词表,打开一张停用词表
stopwords = open("./stop_words.txt","r",encoding='utf-8').read()
# 分词
words_ls = []
for text in texts:
# 采用jieba进行分词、词性筛选、去停用词
words = [word.word for word in jp.cut(text) if word.flag in flags and word.word not in stopwords]
words_ls.append(words)
LDA模型构建
# 构造词典
dictionary = Dictionary(words_ls)
# 基于词典,使【词】→【稀疏向量】,并将向量放入列表,形成【稀疏向量集】
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(words) for words in words_ls]
# lda模型,num_topics设置主题的个数
lda = LdaModel(corpus=corpus, id2word=dictionary, num_topics=3, random_state=100, iterations=50)
# U_Mass Coherence
ldaCM = CoherenceModel(model=lda, corpus=corpus, dictionary=dictionary, coherence='u_mass')
# 打印所有主题,每个主题显示10个词
for topic in lda.print_topics(num_words=10):
print(topic)
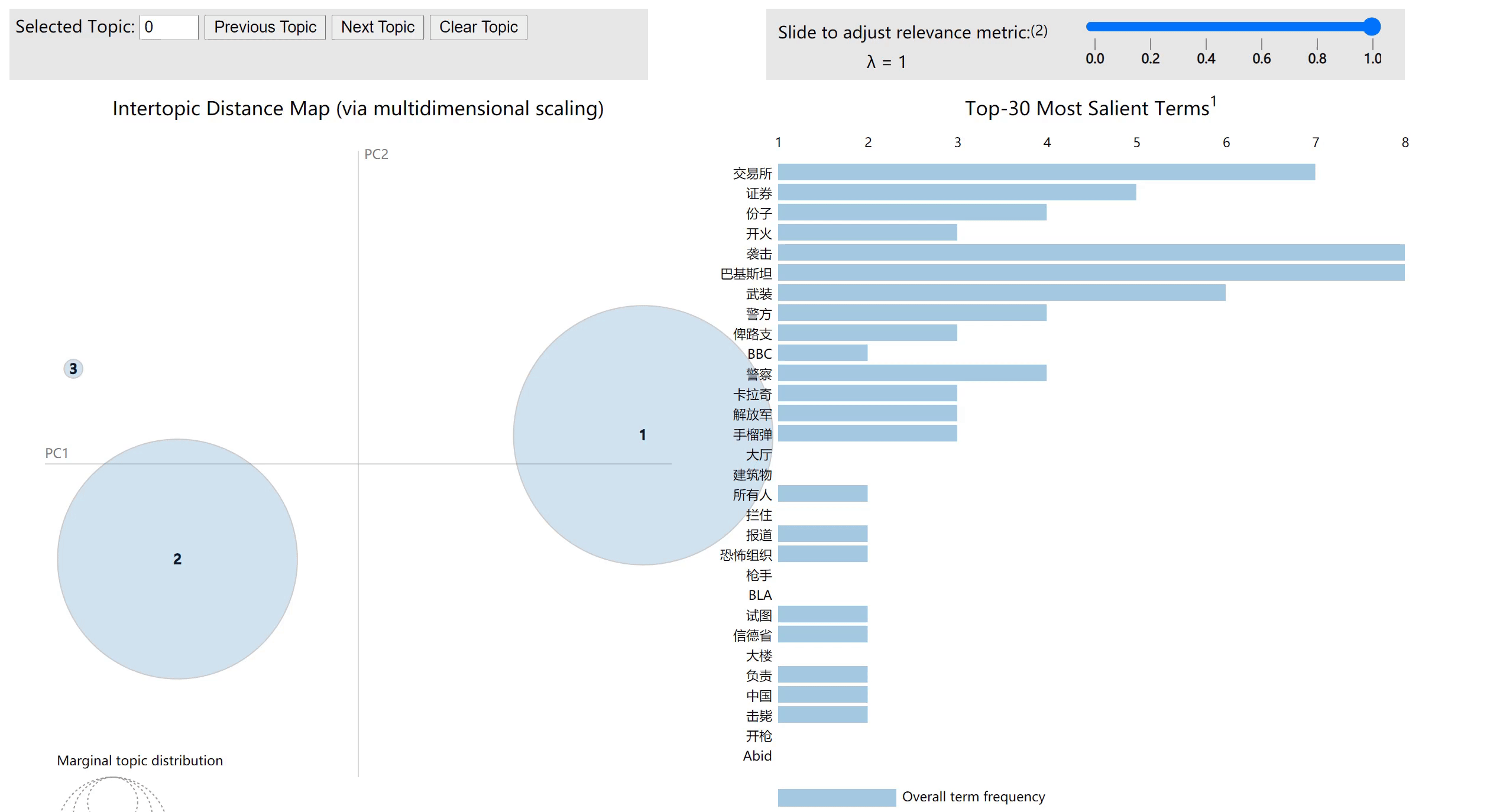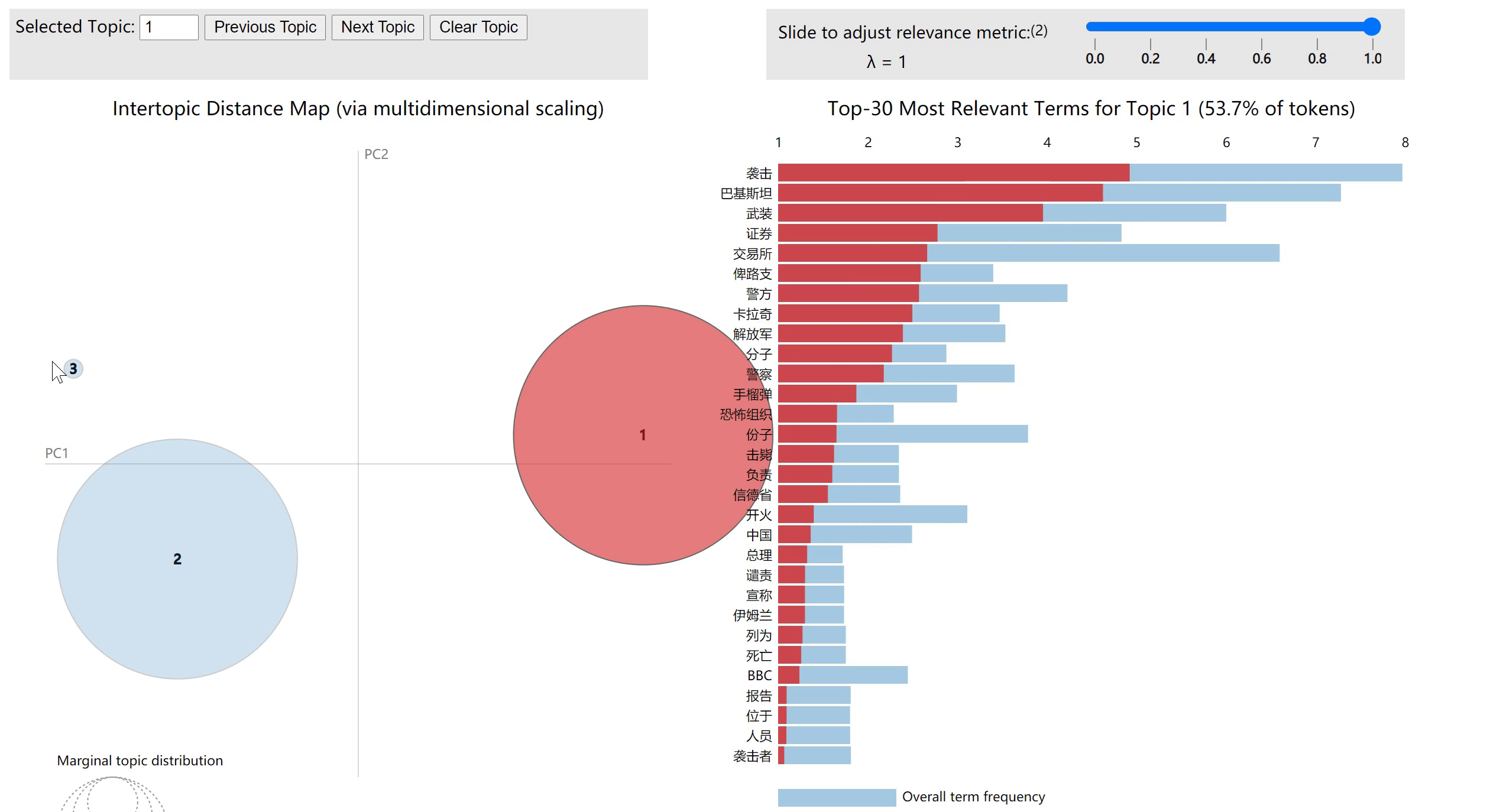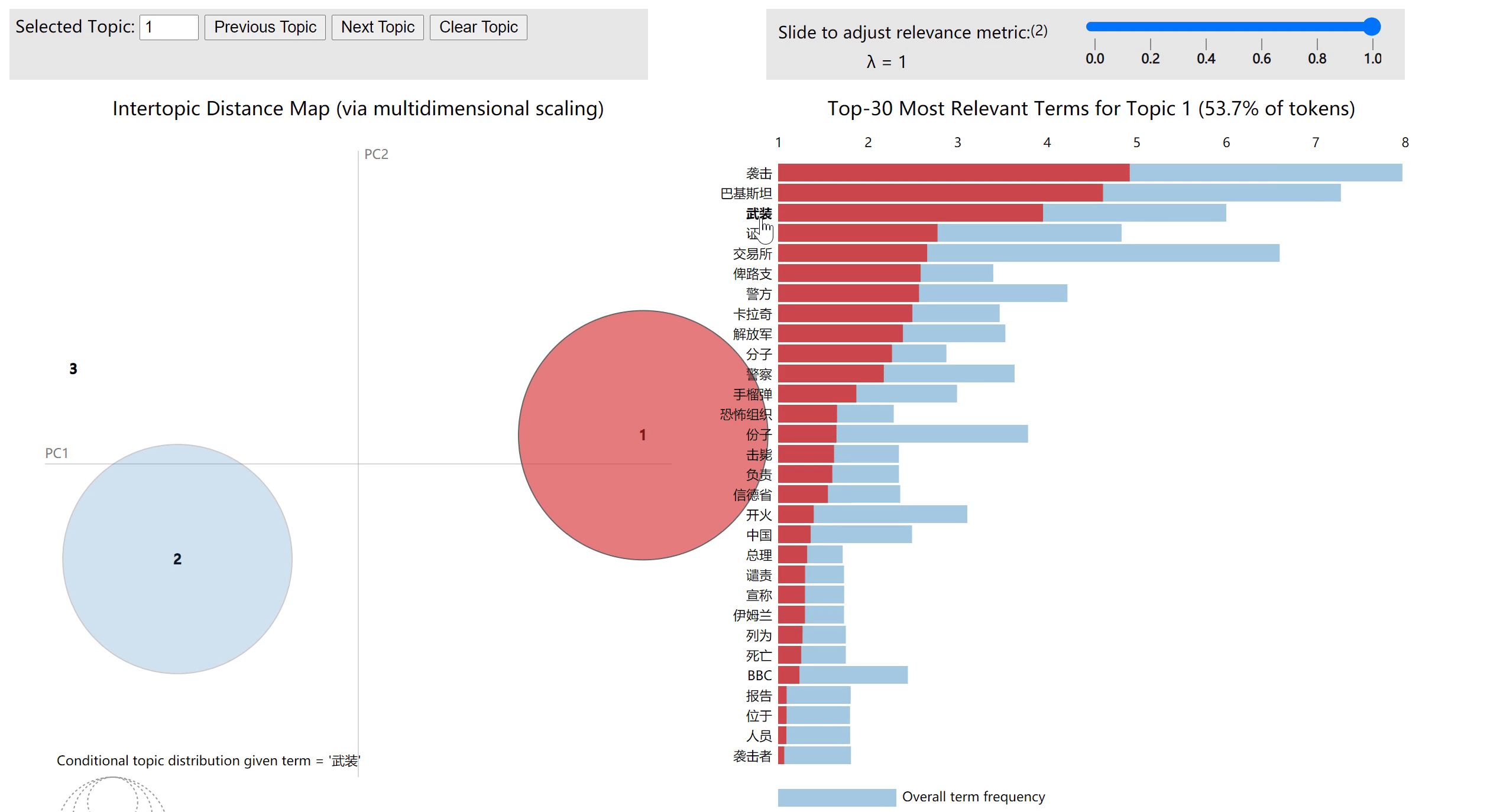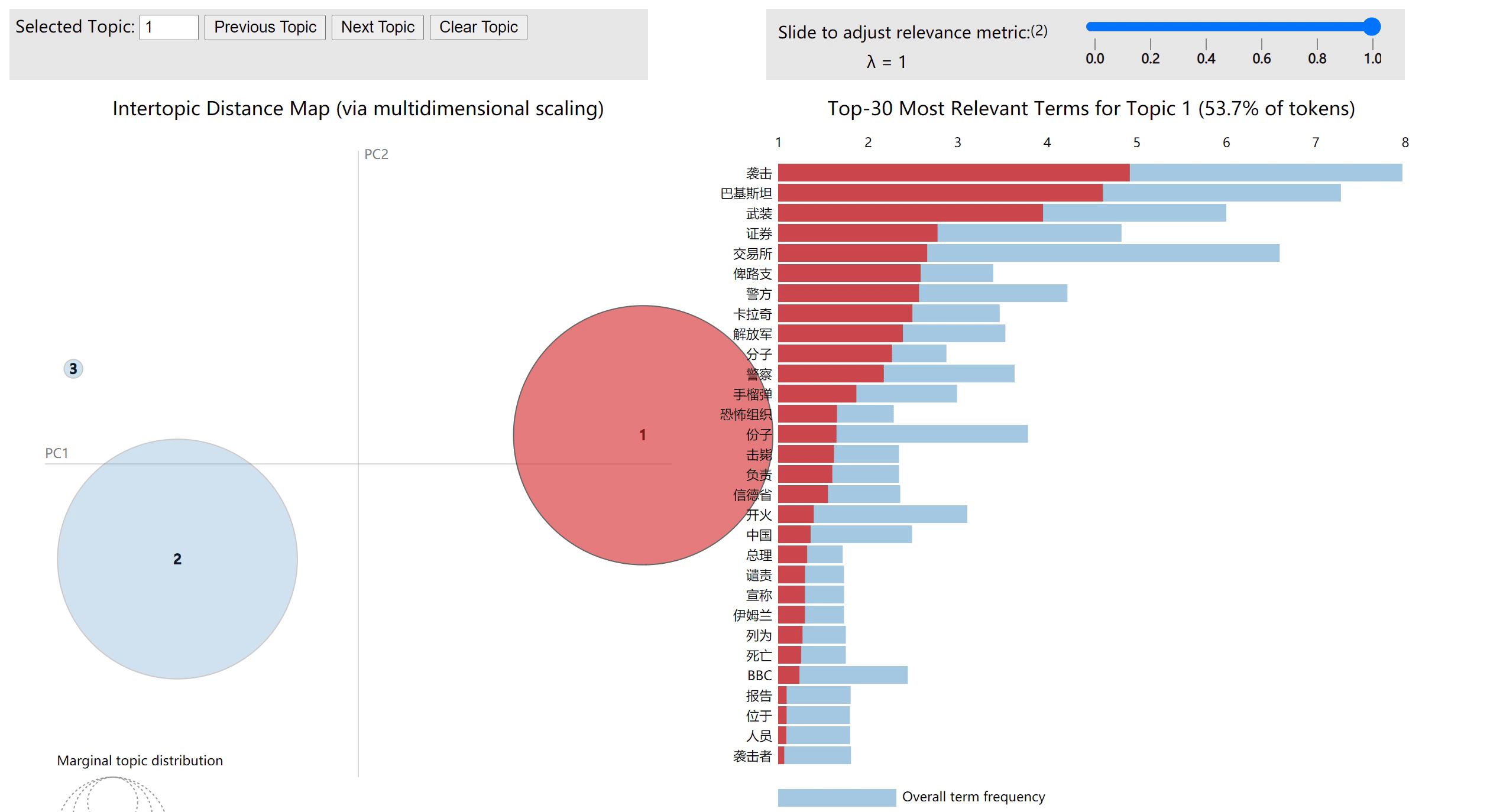
LDA模型可视化
# 用pyLDAvis将LDA模式可视化
plot =pyLDAvis.gensim_models.prepare(lda,corpus,dictionary)
# 保存到本地html
pyLDAvis.save_html(plot, './result/pyLDAvis.html')
完整代码
# encoding=utf-8
import pyLDAvis.gensim_models
import jieba.posseg as jp,jieba
from gensim.models.coherencemodel import CoherenceModel
from gensim.models.ldamodel import LdaModel
from gensim.corpora.dictionary import Dictionary
# 读取需要处理的文本
doc1=open('./data/text1.txt','rb').read()
doc2=open('./data/text2.txt','rb').read()
# 构建文本集
texts = [doc1,doc2]
# 词性标注条件
flags = ('n', 'nr', 'ns', 'nt', 'eng', 'v', 'd','vn','vd')
# 停用词表
stopwords = open("./stop_words.txt","r",encoding='utf-8').read()
# 分词
words_ls = []
for text in texts:
# 采用jieba进行分词
words = [word.word for word in jp.cut(text) if word.flag in flags and word.word not in stopwords]
words_ls.append(words)
# 构造词典
dictionary = Dictionary(words_ls)
# 基于词典,使【词】→【稀疏向量】,并将向量放入列表,形成【稀疏向量集】
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(words) for words in words_ls]
# lda模型,num_topics设置主题的个数
lda = LdaModel(corpus=corpus, id2word=dictionary, num_topics=3, random_state=100, iterations=50)
# U_Mass Coherence
ldaCM = CoherenceModel(model=lda, corpus=corpus, dictionary=dictionary, coherence='u_mass')
# 打印所有主题,每个主题显示10个词
for topic in lda.print_topics(num_words=10):
print(topic)
# 用pyLDAvis将LDA模式可视化
plot =pyLDAvis.gensim_models.prepare(lda,corpus,dictionary)
# 保存到本地html
pyLDAvis.save_html(plot, './result/pyLDAvis.html')
运行
python main.py
运行完成后,本地打开对应路径下的pyLDAvis.html,可以得到可视化结果
代码地址:详见





















 1520
1520











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








