数据源自动配置剖析
数据源配置方式
首先我们需要选择数据库驱动的库文件
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>
配置数据库连接
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/springboot
username: root
password: 123456
配置spring-boot-start-jdbc
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
编写测试类
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void contextLoads()throws SQLException{
Connection connection =dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
连接池配置方式
SpringBoot提供了三种连接池:
- HikariCP
- Commons DBCP2
- Tomcat JDBC Connection Pool
其中SpringBoot默认使用HikariCP
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
要使用其他两个要改为
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.zaxxer</groupId>
<artifactId>HikariCP</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.zaxxer</groupId>
<artifactId>HikariCP</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
数据库自动配置
为什么前面我们说SpringBoot默认使用HikariCP?这是在哪里指定的?
首先我们需要找到DataSourceAutoConfiguration这个类
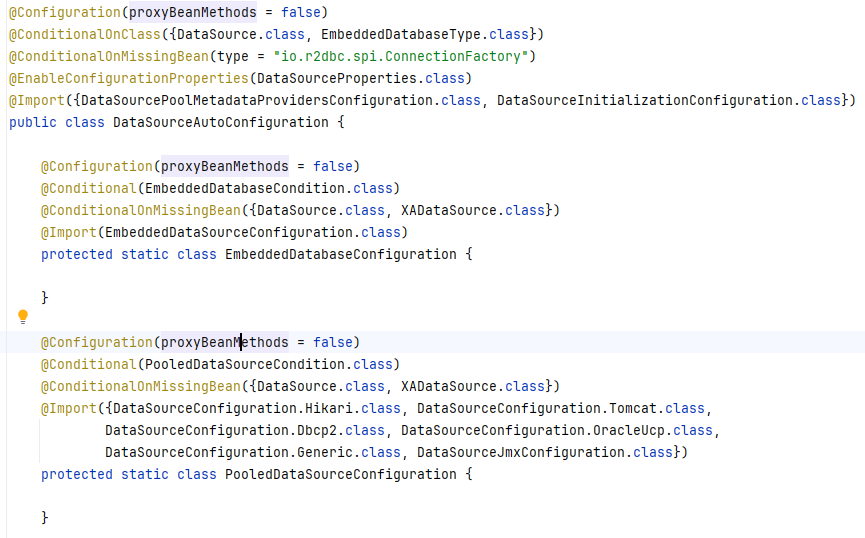
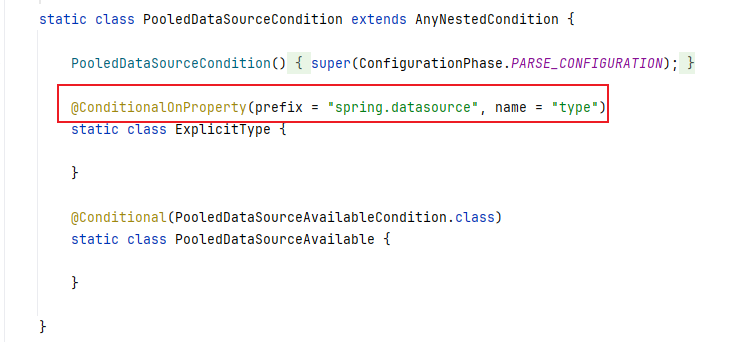
@Conditional(PooledDataSourceCondition.class)这个告诉我们指定的配置文件中,必须要有type属性。
现在我们进入DataSourceConfiguration这个里面

里面配置类SpringBoot启动的连接池。
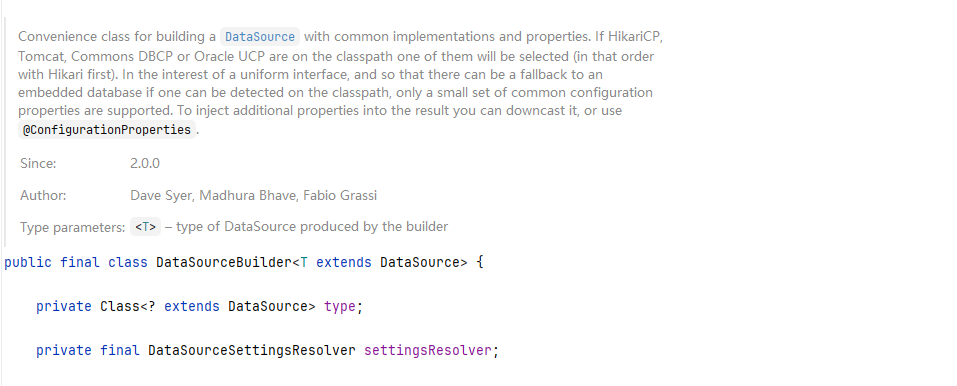
private static final String[] DATA_SOURCE_TYPE_NAMES = new String[]
{"com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource",
"org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource",
"org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource"};
所以我们可以看出来在没有指定Type时,默认就是HikariDataSource。
Druid连接池的配置
首先么要整合druid数据源
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
在application.yml中引入druid的相关配置
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/springboot
username: root
password: 123456
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
整合的配置类
public class DruidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}
SpringBoot整合Mybatis
首先我们要添加maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
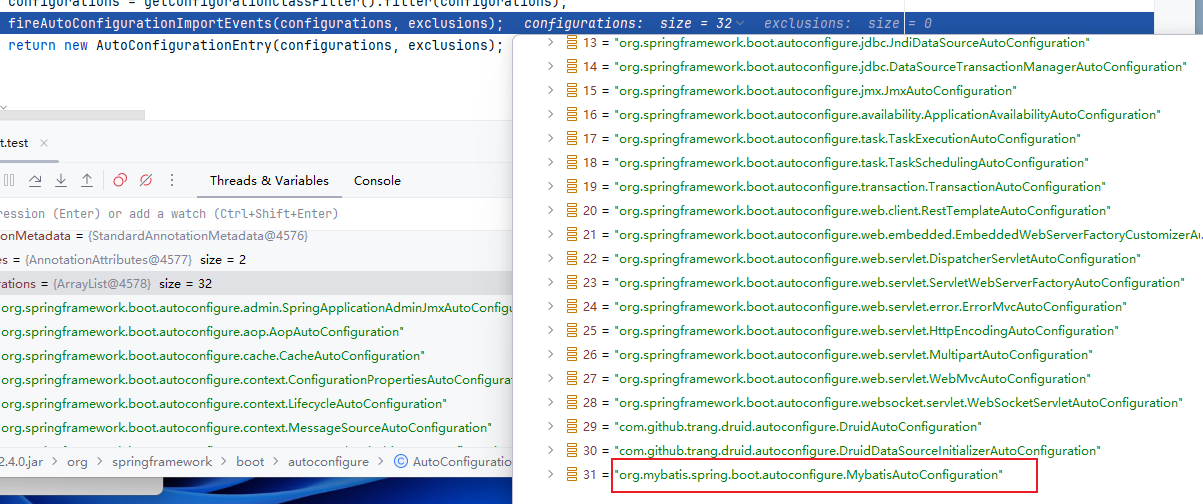
所以我们需要打开MybatisAutoConfiguration这个类
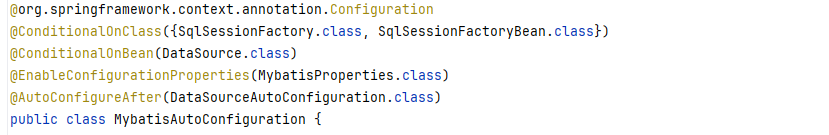
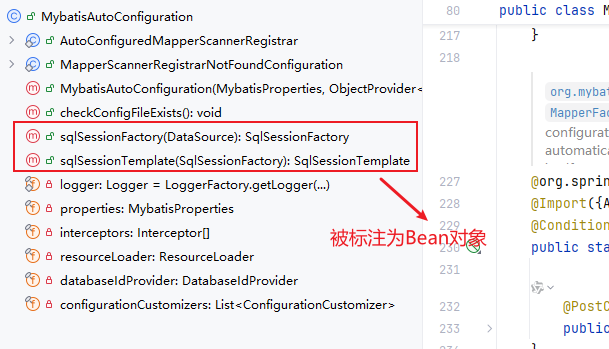
Mybatis自动配置源码剖析
- springBoot项目最核心的就是自动加载配置,该功能依赖的是一个注解
@SpringBootApplication中的@EnableAutoConfiguration; @EnableAutoConfiguration主要是通过@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)类来加载的;- MybatisAutoConfiguration
-
- 其中有个MybatisProperties,该类是对应mybatis的配置文件
- 有个SqlSessionFactory方法,作用是创建SqlSession类,Configuration类(mybatis最主要的类,保存着与mybatis相关的东西)
- SqlSessionTemplate,作用是mapperProoxy代理类有关
然后我们要看MapperScan注解
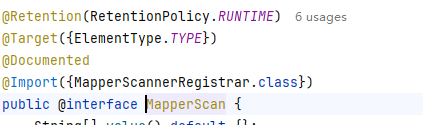
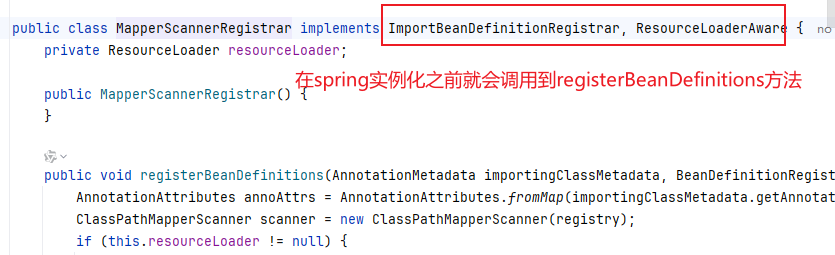
通过进一步分析源码我们可以得出以下结论
@MapperScan这个定义,是扫描指定包下面的mapper接口,然后设置每个mapper接口的beanClass属性为MapperFactoryBean类型并加入到spring的bean容器中。
MapperFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean接口,所以当spring从待实例化的bean容器中变量到这个bean并开始执行实例化使返回的对象实际上就是getObject方法中返回的对象。
最后我们看一下MapperFactoryBean的getObject方法,实际上返回的就是mybatis中通过getMapper拿到的对象,熟悉mybatis源码的就应该清楚,这个就是mybatis通过动态代理生成的mapper接口实现类。
到此,mapper接口现在也通过动态代理生成了实现类,并且注入到spring的bean容器中了,之后使用者就可以通过@Autowired或者getBean等方法,从spring容器中获取到了。
Spring+Mybatis实现动态数据源切换
动态数据源介绍
现在我们的项目中订单模块氛围正向和逆向两个部分;
- 正向模块中记录了订单的基本信息,包括订单基本信息,订单商品信息,优惠卷信息,发票信息,账期信息,结算信息,订单备注信息,收货人信息等;
- 逆向模块主要包含了商品退货信息和维修信息;
- 当我们数据量超过500万时就需要考虑分库分表和读写分类,需要动态切换到对应的数据库中。
解决思路
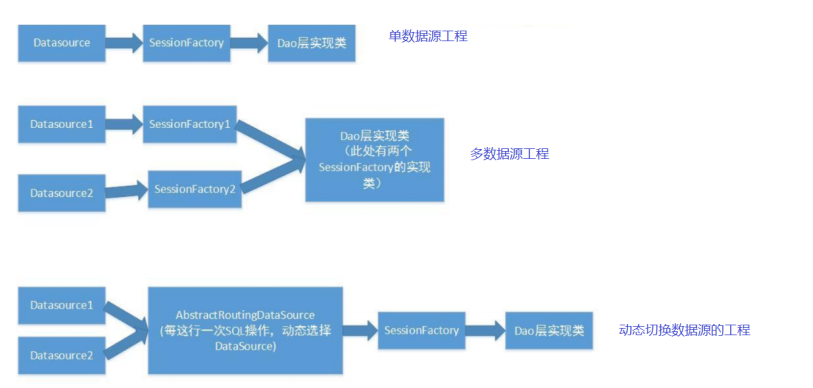
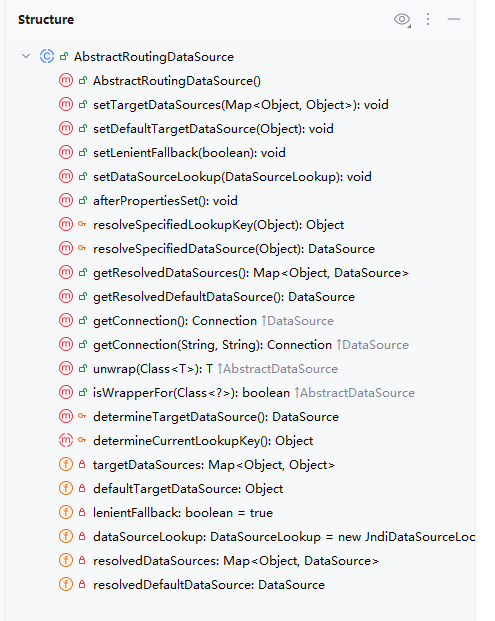
Spring内置了一个AbstractRoutingDataSource,它可以把多个数据源配置为一个Map,然后根据不同的key返回不同的数据源。
编码实战
首先我们需要准备基础的环境
@Data
public class Product {
private Integer id ;
private String name;
private Double price;
}
@Mapper
public interface ProductMapper {
//查询主数据库
@Select("select * from product")
public List<Product> getAllProductsM();
//查询从数据库
@Select("select * from product")
public List<Product> getAllProductsS();
}
@Service
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductMapper productMapper;
@Override
public void getAllProductsM() {
List<Product> products = productMapper.getAllProductsM();
System.out.println("MyBatis查询结果:"+products);
}
@Override
public void getAllProductsS() {
List<Product> products = productMapper.getAllProductsS();
System.out.println("MyBatis查询结果:"+products);
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("/getAllProductsM")
public String getAllProductsM() {
productService.getAllProductsM();
return "master";
}
@GetMapping("/getAllProductsS")
public String getAllProductsS() {
productService.getAllProductsS();
return "slave";
}
}
配置类
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class MyDataSourceConfiguration {
@Bean(name = "dataSourceM")
DataSource dataSourceM(){
log.info("主数据库");
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "dataSourceS")
DataSource dataSourceS(){
log.info("从数据库");
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
}
配置文件
spring:
druid:
datasource:
master:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/product_m
username: root
password: 123456
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
slave:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/product_s
username: root
password: 123456
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
其次需要编写RoutingDataSource,把两个真实的数据源代理为一个动态数据源:
@Slf4j
public class RoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return "master数据库";
}
@Bean
@Primary
DataSource primaryDataSource(@Autowired @Qualifier("dataSourceM")DataSource dataSourceM,
@Autowired @Qualifier("dataSourceS")DataSource dataSourceS){
log.info("正在动态创建数据库");
Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("master数据库", dataSourceM);
map.put("slave数据库", dataSourceS);
RoutingDataSource routingDataSource = new RoutingDataSource();
routingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(map);
routingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(dataSourceM);
return routingDataSource;
}
}
现在RoutingDataSource配置好了,但是路由的选择是写死的,永远返回master数据库。
现在问题来了,我们该如何存储动态选择的key已经在哪里设置key?
使用ThreadLocal存储key最合适。
public class RoutingDataSourceContext {
static final ThreadLocal<String> threadLocalDataSourceKey = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static String getDataSourceKey() {
String key = threadLocalDataSourceKey.get();
return key == null ? "master数据库" : key;
}
public RoutingDataSourceContext(String key) {
threadLocalDataSourceKey.set(key);
}
public void close() {
threadLocalDataSourceKey.remove();
}
}
现在我们修改RoutingDataSource,获取key的代码
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return RoutingDataSourceContext.getDataSourceKey() ;
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("/getAllProductsM")
public String getAllProductsM() {
RoutingDataSourceContext routingDataSourceContext = new RoutingDataSourceContext("master数据库");
productService.getAllProductsM();
return "master";
}
@GetMapping("/getAllProductsS")
public String getAllProductsS() {
RoutingDataSourceContext routingDataSourceContext = new RoutingDataSourceContext("salve数据库");
productService.getAllProductsS();
return "slave";
}
}
测试结果
2025-12-12 14:07:48.541 [http-nio-8080-exec-3] DEBUG com.guslegend.mapper.ProductMapper.getAllProductsS - ==> Preparing: select * from product
2025-12-12 14:07:48.541 [http-nio-8080-exec-3] DEBUG com.guslegend.mapper.ProductMapper.getAllProductsS - ==> Parameters:
2025-12-12 14:07:48.543 [http-nio-8080-exec-3] DEBUG com.guslegend.mapper.ProductMapper.getAllProductsS - <== Total: 1
MyBatis查询结果:[Product(id=1, name=桌子, price=100.0)]
2025-12-12 14:07:50.442 [http-nio-8080-exec-4] DEBUG com.guslegend.mapper.ProductMapper.getAllProductsM - ==> Preparing: select * from product
2025-12-12 14:07:50.442 [http-nio-8080-exec-4] DEBUG com.guslegend.mapper.ProductMapper.getAllProductsM - ==> Parameters:
2025-12-12 14:07:50.443 [http-nio-8080-exec-4] DEBUG com.guslegend.mapper.ProductMapper.getAllProductsM - <== Total: 1
MyBatis查询结果:[Product(id=1, name=桌子, price=100.0)]
优化
上面需要读取数据库的地方就要加上这样的一段话,是否太过于复杂了?
RoutingDataSourceContext routingDataSourceContext = new RoutingDataSourceContext();
我们可以使用声明式事务管理,或者自定义注解来解决
首先我们要添加aop的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
自定义注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RoutingWith {
String value() default "master";
}
切面类
@Aspect
@Component
public class RoutingAspect {
@Around("@annotation(routingWith)")
public Object routingWithDataSource(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint,RoutingWith routingWith)throws Throwable{
String key =routingWith.value();
RoutingDataSourceContext routingDataSourceContext = new RoutingDataSourceContext(key);
return proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
}
}
改造controller方法
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@RoutingWith("master")
@GetMapping("/getAllProductsM")
public String getAllProductsM() {
// RoutingDataSourceContext routingDataSourceContext = new RoutingDataSourceContext("master数据库");
productService.getAllProductsM();
return "master";
}
@RoutingWith("slave")
@GetMapping("/getAllProductsS")
public String getAllProductsS() {
// RoutingDataSourceContext routingDataSourceContext = new RoutingDataSourceContext("salve数据库");
productService.getAllProductsS();
return "slave";
}
}
至此,我们实现了注解动态选择数据源功能。





















 912
912

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








