本文摘抄至 : skywang12345
摘要 : OutputStreamWriter、InputStreamReader分别为InputStream、OutputStream的低级输入输出流提供将字节转换成字符的桥梁。在java——io中只有将字节转换成字符的类、没有将字符转换成字节的类、原因很简单——字符流的存在本来就像对字节流进行了装饰、加工处理以便更方便的去使用、在使用这两个流的时候要注意:由于这两个流要频繁的对读取或者写入的字节或者字符进行转码、解码和与底层流的源和目的地进行交互、所以使用的时候要使用BufferedWriter、BufferedReader进行包装、以达到最高效率、和保护存储介质。
InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter 是 字节流通向字符流的桥梁:它使用指定的 charset 读写字节并将其解码为字符。
InputStreamReader 的所用是将“字节输入流”转换成“字符输入流”。它继承与 Reader。
OutputStreamWrit 的作用是将“字节输出流”转换成“字符输出流”。它继承于 Writer。
InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter源码分析
1. InputStreamReader 源码(基于jdk1.7.40)
package java.io;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
import sun.nio.cs.StreamDecoder;
// 将“字节输入流”转换成“字符输入流”
public class InputStreamReader extends Reader {
//使用默认或者指定的编码将字节转换成字符、
private final StreamDecoder sd;
// 根据in创建InputStreamReader,使用默认的编码
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in) {
super(in);
try {
sd = StreamDecoder.forInputStreamReader(in, this, (String)null); // ## check lock object
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// The default encoding should always be available
throw new Error(e);
}
}
// 根据in创建InputStreamReader,使用编码charsetName(编码名)
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException
{
super(in);
if (charsetName == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charsetName");
sd = StreamDecoder.forInputStreamReader(in, this, charsetName);
}
// 根据in创建InputStreamReader,使用编码cs
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs) {
super(in);
if (cs == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charset");
sd = StreamDecoder.forInputStreamReader(in, this, cs);
}
// 根据in创建InputStreamReader,使用解码器dec
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecoder dec) {
super(in);
if (dec == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charset decoder");
sd = StreamDecoder.forInputStreamReader(in, this, dec);
}
// 获取解码器
public String getEncoding() {
return sd.getEncoding();
}
// 读取并返回一个字符
public int read() throws IOException {
return sd.read();
}
// 将InputStreamReader中的数据写入cbuf中,从cbuf的offset位置开始写入,写入长度是length
public int read(char cbuf[], int offset, int length) throws IOException {
return sd.read(cbuf, offset, length);
}
// 能否从InputStreamReader中读取数据
public boolean ready() throws IOException {
return sd.ready();
}
// 关闭InputStreamReader
public void close() throws IOException {
sd.close();
}
}2. OutputStreamWriter 源码(基于jdk1.7.40)
package java.io;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder;
import sun.nio.cs.StreamEncoder;
// 将“字节输出流”转换成“字符输出流”
public class OutputStreamWriter extends Writer {
private final StreamEncoder se;
// 根据out创建OutputStreamWriter,使用编码charsetName(编码名)
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException
{
super(out);
if (charsetName == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charsetName");
se = StreamEncoder.forOutputStreamWriter(out, this, charsetName);
}
// 根据out创建OutputStreamWriter,使用默认的编码
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) {
super(out);
try {
se = StreamEncoder.forOutputStreamWriter(out, this, (String)null);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
// 根据out创建OutputStreamWriter,使用编码cs
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs) {
super(out);
if (cs == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charset");
se = StreamEncoder.forOutputStreamWriter(out, this, cs);
}
// 根据out创建OutputStreamWriter,使用编码器enc
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc) {
super(out);
if (enc == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charset encoder");
se = StreamEncoder.forOutputStreamWriter(out, this, enc);
}
// 获取编码器enc
public String getEncoding() {
return se.getEncoding();
}
// 刷新缓冲区
void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
se.flushBuffer();
}
// 将单个字符写入到OutputStreamWriter中
public void write(int c) throws IOException {
se.write(c);
}
// 将字符数组cbuf从off开始的数据写入到OutputStreamWriter中,写入长度是len
public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
se.write(cbuf, off, len);
}
// 将字符串str从off开始的数据写入到OutputStreamWriter中,写入长度是len
public void write(String str, int off, int len) throws IOException {
se.write(str, off, len);
}
// 刷新“输出流”
// 它与flushBuffer()的区别是:flushBuffer()只会刷新缓冲,而flush()是刷新流,flush()包括了flushBuffer。
public void flush() throws IOException {
se.flush();
}
// 关闭“输出流”
public void close() throws IOException {
se.close();
}
}说明:
OutputStreamWriter 作用和原理都比较简单。
作用就是将“字节输出流”转换成“字符输出流”。它的原理是,我们创建“字符输出流”对象时,会指定“字节输出流”以及“字符编码”。
示例程序
InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter的使用示例,参考源码(StreamConverter.java):
public class StreamConverter {
private static final String FileName = "file.txt";
private static final String CharsetName = "utf-8";
public static void main(String[] args) {
testWrite();
testRead();
}
private static void testWrite() {
try {
// 创建文件“file.txt”对应File对象
File file = new File(FileName) ;
// 创建FileOutputStream对应OutputStreamWriter:将字节流转换为字符流,
//即写入out1的数据会自动由字节转换为字符。
OutputStreamWriter out1 = new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream(file),CharsetName) ;
// 写入10个汉字
out1.write("字节流转为字符流示例");
// 向“文件中”写入"0123456789"+换行符
out1.write("0123456789\n");
out1.close() ;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace() ;
}
}
private static void testRead() {
try {
// 方法1:新建FileInputStream对象
// 新建文件“file.txt”对应File对象
File file = new File(FileName) ;
InputStreamReader in1 = new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream(file),CharsetName) ;
// 测试read(),从中读取一个字符
char c1 = (char) in1.read();
System.out.println("c1 = "+c1);
// 测试skip(long byteCount),跳过6个字符
in1.skip(6) ;
// 测试read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
char[] buf = new char[10] ;
in1.read(buf,0,buf.length) ;
System.out.println("buf = "+new String(buf));
in1.close() ;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
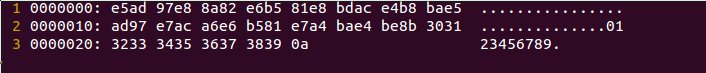
}- testWrite()的作用是将“内容写入到输出流”。写入的时候,会将写入的内容转换成 UTF-8编码并导入。
- testReader()的作用是将“内容读取到输入流”。读取的时候,会将UTF-8的内容转换成字节并去出来。






















 766
766

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








