前言:这几天博客积的有点多,工作也是忙的够呛.
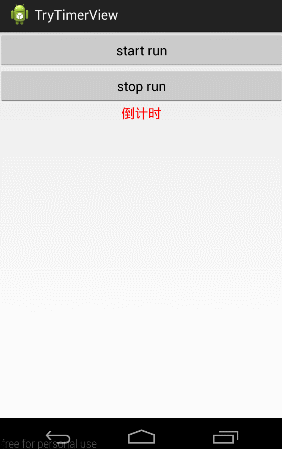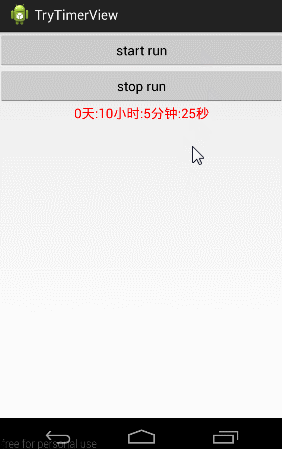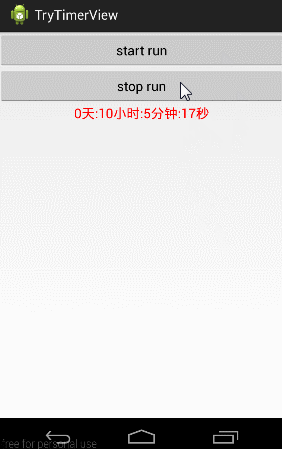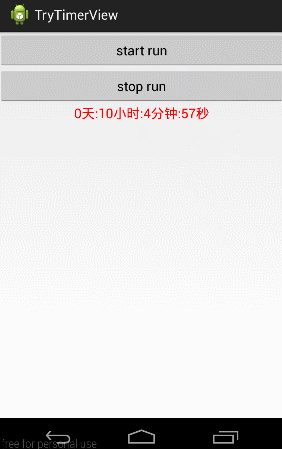
先上本篇效果图:
就是自定义一个能倒计时的TextView控件,当我们点击start run按钮时,给他传进去一个时间数字,它自己开始倒计时,不需要外部任何干预。当点击Stop run按钮时,停止倒计时。
一、自定义倒计时控件——TimerTextView
显然TimerTextView应该派生于TextView,因为他本就是显示一串Text,只是具有了自动更新的功能,这里的自动更新的实现当然只通过线程来实现了,所以要继承Runnable接口。所以它的定义应该是这样的:
- public class TimerTextView extends TextView implements Runnable{
- public TimerTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
- super(context, attrs);
- // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
- }
- @Override
- public void run() {
- //自动更新
- }
- }
public class TimerTextView extends TextView implements Runnable{
public TimerTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public void run() {
//自动更新
}
}- private long mday, mhour, mmin, msecond;//天,小时,分钟,秒
private long mday, mhour, mmin, msecond;//天,小时,分钟,秒- public void setTimes(long[] times) {
- mday = times[0];
- mhour = times[1];
- mmin = times[2];
- msecond = times[3];
- }
public void setTimes(long[] times) {
mday = times[0];
mhour = times[1];
mmin = times[2];
msecond = times[3];
}- private boolean run=false; //是否启动了
private boolean run=false; //是否启动了- public boolean isRun() {
- return run;
- }
- public void beginRun() {
- this.run = true;
- run();
- }
- public void stopRun(){
- this.run = false;
- }
public boolean isRun() {
return run;
}
public void beginRun() {
this.run = true;
run();
}
public void stopRun(){
this.run = false;
}- @Override
- public void run() {
- //标示已经启动
- if(run){
- ComputeTime();
- String strTime= mday +"天:"+ mhour+"小时:"+ mmin+"分钟:"+msecond+"秒";
- this.setText(strTime);
- postDelayed(this, 1000);
- }else {
- removeCallbacks(this);
- }
- }
@Override
public void run() {
//标示已经启动
if(run){
ComputeTime();
String strTime= mday +"天:"+ mhour+"小时:"+ mmin+"分钟:"+msecond+"秒";
this.setText(strTime);
postDelayed(this, 1000);
}else {
removeCallbacks(this);
}
}如果用户调用了StopRun()函数,将run变量置为了FALSE,即用户要停止线程运行,这里,我们调用removeCallbacks(this)来终止当前线程。
下面就是看看如何来计算当前要显示的时间的omputeTime()函数了:
- private void ComputeTime() {
- msecond--;
- if (msecond < 0) {
- mmin--;
- msecond = 59;
- if (mmin < 0) {
- mmin = 59;
- mhour--;
- if (mhour < 0) {
- // 倒计时结束
- mhour = 24;
- mday--;
- }
- }
- }
- }
private void ComputeTime() {
msecond--;
if (msecond < 0) {
mmin--;
msecond = 59;
if (mmin < 0) {
mmin = 59;
mhour--;
if (mhour < 0) {
// 倒计时结束
mhour = 24;
mday--;
}
}
}
}OK啦,重写控件的部分就讲完了,下面列出这块的完整代码,供大家参考:
- public class TimerTextView extends TextView implements Runnable{
- public TimerTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
- super(context, attrs);
- // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
- }
- private long mday, mhour, mmin, msecond;//天,小时,分钟,秒
- private boolean run=false; //是否启动了
- public void setTimes(long[] times) {
- mday = times[0];
- mhour = times[1];
- mmin = times[2];
- msecond = times[3];
- }
- /**
- * 倒计时计算
- */
- private void ComputeTime() {
- msecond--;
- if (msecond < 0) {
- mmin--;
- msecond = 59;
- if (mmin < 0) {
- mmin = 59;
- mhour--;
- if (mhour < 0) {
- // 倒计时结束,一天有24个小时
- mhour = 23;
- mday--;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- public boolean isRun() {
- return run;
- }
- public void beginRun() {
- this.run = true;
- run();
- }
- public void stopRun(){
- this.run = false;
- }
- @Override
- public void run() {
- //标示已经启动
- if(run){
- ComputeTime();
- String strTime= mday +"天:"+ mhour+"小时:"+ mmin+"分钟:"+msecond+"秒";
- this.setText(strTime);
- postDelayed(this, 1000);
- }else {
- removeCallbacks(this);
- }
- }
- }
public class TimerTextView extends TextView implements Runnable{
public TimerTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
private long mday, mhour, mmin, msecond;//天,小时,分钟,秒
private boolean run=false; //是否启动了
public void setTimes(long[] times) {
mday = times[0];
mhour = times[1];
mmin = times[2];
msecond = times[3];
}
/**
* 倒计时计算
*/
private void ComputeTime() {
msecond--;
if (msecond < 0) {
mmin--;
msecond = 59;
if (mmin < 0) {
mmin = 59;
mhour--;
if (mhour < 0) {
// 倒计时结束,一天有24个小时
mhour = 23;
mday--;
}
}
}
}
public boolean isRun() {
return run;
}
public void beginRun() {
this.run = true;
run();
}
public void stopRun(){
this.run = false;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//标示已经启动
if(run){
ComputeTime();
String strTime= mday +"天:"+ mhour+"小时:"+ mmin+"分钟:"+msecond+"秒";
this.setText(strTime);
postDelayed(this, 1000);
}else {
removeCallbacks(this);
}
}
}二、控件使用
下面我们就在MainActivity中使用一下,先看看MainActivity的布局(activity_main.xml)从最开头的演示中也可以看出,使用的是垂直布局,两个BTN,一个倒计时TextView
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- tools:context="com.example.trytimerview.MainActivity" >
- <Button android:id="@+id/main_start_btn"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="start run"/>
- <Button android:id="@+id/main_stop_btn"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="stop run"/>
- <com.example.trytimerview.TimerTextView
- android:id="@+id/timer_text_view"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:textSize="18sp"
- android:textColor="#ff0000"
- android:gravity="center_horizontal"
- android:text="倒计时"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.trytimerview.MainActivity" >
<Button android:id="@+id/main_start_btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="start run"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/main_stop_btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="stop run"/>
<com.example.trytimerview.TimerTextView
android:id="@+id/timer_text_view"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:textColor="#ff0000"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="倒计时"
/>
</LinearLayout>- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- //初始化倒计时控件
- final TimerTextView timerTextView = (TimerTextView)findViewById(R.id.timer_text_view);
- long[] times = {0,10,5,30};
- timerTextView.setTimes(times);
- Button startBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.main_start_btn);
- Button stopBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.main_stop_btn);
- //开始倒计时
- startBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- if(!timerTextView.isRun()){
- timerTextView.beginRun();
- }
- }
- });
- //停止倒计时
- stopBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- if(timerTextView.isRun()){
- timerTextView.stopRun();
- }
- }
- });
- }
- }
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化倒计时控件
final TimerTextView timerTextView = (TimerTextView)findViewById(R.id.timer_text_view);
long[] times = {0,10,5,30};
timerTextView.setTimes(times);
Button startBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.main_start_btn);
Button stopBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.main_stop_btn);
//开始倒计时
startBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(!timerTextView.isRun()){
timerTextView.beginRun();
}
}
});
//停止倒计时
stopBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(timerTextView.isRun()){
timerTextView.stopRun();
}
}
});
}
}初始化为从10个小时,5分钟,30秒开始倒计时
- final TimerTextView timerTextView = (TimerTextView)findViewById(R.id.timer_text_view);
- long[] times = {0,10,5,30};
- timerTextView.setTimes(times);
final TimerTextView timerTextView = (TimerTextView)findViewById(R.id.timer_text_view);
long[] times = {0,10,5,30};
timerTextView.setTimes(times);- startBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- if(!timerTextView.isRun()){
- timerTextView.beginRun();
- }
- }
- });
startBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(!timerTextView.isRun()){
timerTextView.beginRun();
}
}
});- stopBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- if(timerTextView.isRun()){
- timerTextView.stopRun();
- }
- }
- });
stopBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(timerTextView.isRun()){
timerTextView.stopRun();
}
}
});
如果这篇文章有帮到你,记得关注哦
源码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/harvic880925/8271087
请大家尊重原创者版权,转载请标时出处:http://blog.csdn.net/harvic880925/article/details/41977569 谢谢。






















 86
86

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








