学了这么久的android开发,总算到了这一天。网络框架。
工欲善其事,必先利其器。
写一个框架,之前先看volley究竟是怎么写的。
看volley之前,先学会如何使用。ok,来看看如何使用。
一、Volley使用:
1)网络请求代码如下:
RequestQueue mQueue = Volley.newRequestQueue(this);
StringRequest stringRequest = new StringRequest("http://182.61.37.49:8080/spring-mvc-study/hello/login",
new Response.Listener<String>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(String response) {
Log.d("TAG", response);
}
}, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
Log.e("TAG", error.getMessage(), error);
}
});
mQueue.add(stringRequest);2)看看我写的demo的效果:
二.阅读源码
读前辈读烂的源码最简单的方法:先把代码书写逻辑弄懂。打个比方,就好像读书的时候写作文,先知道个中心思想大纲,再做平铺扩充。(参考自郭神博客)
《一》中心思想
写写关于我自己的理解:
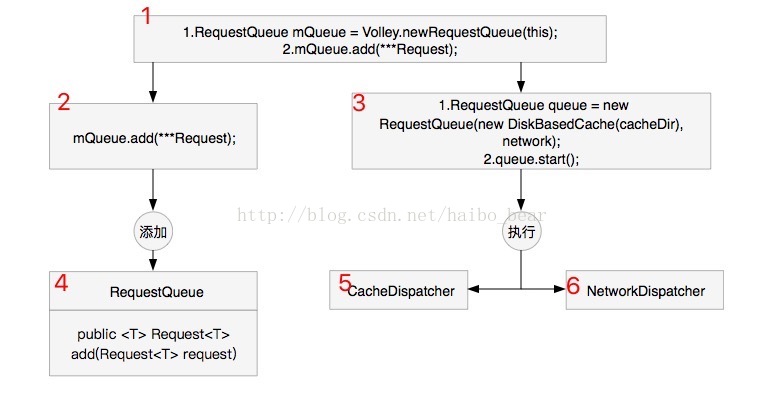
- 先画一个思路总体图。
- 按标注说明:
1.维护一个“请求队列”;
2.向队列中添加请求(4.队列添加请求的具体方法);
3.队列执行请求(5.缓存分发线程;6.网络分发线程);
- 总结各个对象间关系说明:
Volley初始化维护了一个请求队列(包含缓存队列,网络请求队列两种)。该队列包含两种线程,一是缓存分发线程,二是网络请求分发线程。见名知意,缓存分发线程用来从缓存队列取出缓存(请求)分发到网络请求队列,网络请求分发线程用来将网络请求队列的数据(请求)取出并通过网络请求得到返回结果。
- 流程:
当网络请求进来,添加进队列,队列按顺序执行请求,获得返回结果。
- 核心:
该队列包含两种线程,一是缓存分发线程,二是网络请求分发线程。缓存分发线程用来从缓存队列取出缓存(请求)分发到网络请求队列,网络请求分发线程用来将网络请求队列的数据(请求)取出并通过网络请求得到返回结果。
《二》核心代码对应:
1)初始化4个对象
先初始化缓存队列、网络请求队列,然后初始化缓存分发器并start,网络请求分发器并start,按照如下先后顺序执行。
- 缓存队列
/** The cache triage queue. */
private final PriorityBlockingQueue<Request<?>> mCacheQueue =
new PriorityBlockingQueue<Request<?>>();- 网络请求队列
/** The queue of requests that are actually going out to the network. */
private final PriorityBlockingQueue<Request<?>> mNetworkQueue =
new PriorityBlockingQueue<Request<?>>();- 缓存分发器(Thread)
mCacheDispatcher = new CacheDispatcher(mCacheQueue, mNetworkQueue, mCache, mDelivery);- 网络请求分发器(Thread)
NetworkDispatcher networkDispatcher = new NetworkDispatcher(mNetworkQueue, mNetwork,
mCache, mDelivery);2)当添加请求,分几种情况。
public <T> Request<T> add(Request<T> request) {
...
// If the request is uncacheable, skip the cache queue and go straight to the network.
if (!request.shouldCache()) {
mNetworkQueue.add(request);
return request;
}
...
}先判断 是否需要缓存 ,如果不需要直接加入网络请求队列,over。
如果有,则获取到请求缓存链表,添加该请求到缓存链表。并更新等待请求Map。如果需要缓存,则判断是否等待请求Map中是否有该请求的缓存。
如果没有,则在等待请求Map中添加该请求缓存key(即URL),缓存队列添加该请求。
if (mWaitingRequests.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
// There is already a request in flight. Queue up.
Queue<Request<?>> stagedRequests = mWaitingRequests.get(cacheKey);
if (stagedRequests == null) {
stagedRequests = new LinkedList<Request<?>>();
}
stagedRequests.add(request);
mWaitingRequests.put(cacheKey, stagedRequests);
if (VolleyLog.DEBUG) {
VolleyLog.v("Request for cacheKey=%s is in flight, putting on hold.", cacheKey);
}
} else {
// Insert 'null' queue for this cacheKey, indicating there is now a request in
// flight.
mWaitingRequests.put(cacheKey, null);
mCacheQueue.add(request);
}3)执行请求逻辑(核心)
缓存分发线程CacheDispatcher执行请求:
整体代码附上:(不用看,后紧跟着具体分析)
@Override
public void run() {
if (DEBUG) VolleyLog.v("start new dispatcher");
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
// Make a blocking call to initialize the cache.
mCache.initialize();
while (true) {
try {
// Get a request from the cache triage queue, blocking until
// at least one is available.
final Request<?> request = mCacheQueue.take();
request.addMarker("cache-queue-take");
// If the request has been canceled, don't bother dispatching it.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("cache-discard-canceled");
continue;
}
// Attempt to retrieve this item from cache.
Cache.Entry entry = mCache.get(request.getCacheKey());
if (entry == null) {
request.addMarker("cache-miss");
// Cache miss; send off to the network dispatcher.
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}
// If it is completely expired, just send it to the network.
if (entry.isExpired()) {
request.addMarker("cache-hit-expired");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}
// We have a cache hit; parse its data for delivery back to the request.
request.addMarker("cache-hit");
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(
new NetworkResponse(entry.data, entry.responseHeaders));
request.addMarker("cache-hit-parsed");
if (!entry.refreshNeeded()) {
// Completely unexpired cache hit. Just deliver the response.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} else {
// Soft-expired cache hit. We can deliver the cached response,
// but we need to also send the request to the network for
// refreshing.
request.addMarker("cache-hit-refresh-needed");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
// Mark the response as intermediate.
response.intermediate = true;
// Post the intermediate response back to the user and have
// the delivery then forward the request along to the network.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Not much we can do about this.
}
}
});
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.
if (mQuit) {
return;
}
continue;
}
}
}<1>取本地缓存结果,如果本地缓存结果为空,则将请求添加到网络请求队列。
// Attempt to retrieve this item from cache.
Cache.Entry entry = mCache.get(request.getCacheKey());
if (entry == null) {
request.addMarker("cache-miss");
// Cache miss; send off to the network dispatcher.
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}<2>如果结果已经过期,则将请求添加到网络请求队列。
// If it is completely expired, just send it to the network.
if (entry.isExpired()) {
request.addMarker("cache-hit-expired");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}<3>如果结果存在,并且不过期,则通过请求解析结果
// We have a cache hit; parse its data for delivery back to the request.
request.addMarker("cache-hit");
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(
new NetworkResponse(entry.data, entry.responseHeaders));
request.addMarker("cache-hit-parsed");<4>如果结果不需要刷新,将结果发送给response,否则添加到网络请求队列。(网络请求具体见后续分析)(response返回见后续分析)
if (!entry.refreshNeeded()) {
// Completely unexpired cache hit. Just deliver the response.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} else {
// Soft-expired cache hit. We can deliver the cached response,
// but we need to also send the request to the network for
// refreshing.
request.addMarker("cache-hit-refresh-needed");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
// Mark the response as intermediate.
response.intermediate = true;
// Post the intermediate response back to the user and have
// the delivery then forward the request along to the network.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Not much we can do about this.
}
}
});
}
整体代码如下:(不用细看,后紧跟着具体分析)
@Override
public void run() {
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
while (true) {
long startTimeMs = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
Request<?> request;
try {
// Take a request from the queue.
request = mQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.
if (mQuit) {
return;
}
continue;
}
try {
request.addMarker("network-queue-take");
// If the request was cancelled already, do not perform the
// network request.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("network-discard-cancelled");
continue;
}
addTrafficStatsTag(request);
// Perform the network request.
NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);
request.addMarker("network-http-complete");
// If the server returned 304 AND we delivered a response already,
// we're done -- don't deliver a second identical response.
if (networkResponse.notModified && request.hasHadResponseDelivered()) {
request.finish("not-modified");
continue;
}
// Parse the response here on the worker thread.
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(networkResponse);
request.addMarker("network-parse-complete");
// Write to cache if applicable.
// TODO: Only update cache metadata instead of entire record for 304s.
if (request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) {
mCache.put(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry);
request.addMarker("network-cache-written");
}
// Post the response back.
request.markDelivered();
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} catch (VolleyError volleyError) {
volleyError.setNetworkTimeMs(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTimeMs);
parseAndDeliverNetworkError(request, volleyError);
} catch (Exception e) {
VolleyLog.e(e, "Unhandled exception %s", e.toString());
VolleyError volleyError = new VolleyError(e);
volleyError.setNetworkTimeMs(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTimeMs);
mDelivery.postError(request, volleyError);
}
}
}1)从网络请求队列取请求
request = mQueue.take();2)执行网络请求并解析网络请求数据。(网络请求具体见后续分析)
// Perform the network request.
NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);其中:解析response代码:
// Parse the response here on the worker thread.
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(networkResponse);3)将请求结果networkResponse存入缓存
if (request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) {
mCache.put(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry);
request.addMarker("network-cache-written");
}4)将结果返回(response返回见后续分析)
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
4.网络请求
思路总体图中的内容分析差不多了。然后把网络请求部分具体说下。请求网络的时候,我们使用了如下代码:
mNetwork.performRequest(request)Network network = new BasicNetwork(stack);@Override
public NetworkResponse performRequest(Request<?> request) throws VolleyError {
long requestStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
while (true) {
HttpResponse httpResponse = null;
byte[] responseContents = null;
Map<String, String> responseHeaders = Collections.emptyMap();
try {
// Gather headers.
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<String, String>();
addCacheHeaders(headers, request.getCacheEntry());
httpResponse = mHttpStack.performRequest(request, headers);
StatusLine statusLine = httpResponse.getStatusLine();
int statusCode = statusLine.getStatusCode();
responseHeaders = convertHeaders(httpResponse.getAllHeaders());
// Handle cache validation.
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED) {
Entry entry = request.getCacheEntry();
if (entry == null) {
return new NetworkResponse(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED, null,
responseHeaders, true,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
}
// A HTTP 304 response does not have all header fields. We
// have to use the header fields from the cache entry plus
// the new ones from the response.
// http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec10.html#sec10.3.5
entry.responseHeaders.putAll(responseHeaders);
return new NetworkResponse(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED, entry.data,
entry.responseHeaders, true,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
}
// Some responses such as 204s do not have content. We must check.
if (httpResponse.getEntity() != null) {
responseContents = entityToBytes(httpResponse.getEntity());
} else {
// Add 0 byte response as a way of honestly representing a
// no-content request.
responseContents = new byte[0];
}
// if the request is slow, log it.
long requestLifetime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart;
logSlowRequests(requestLifetime, request, responseContents, statusLine);
if (statusCode < 200 || statusCode > 299) {
throw new IOException();
}
return new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents, responseHeaders, false,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {
attemptRetryOnException("socket", request, new TimeoutError());
} catch (ConnectTimeoutException e) {
attemptRetryOnException("connection", request, new TimeoutError());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Bad URL " + request.getUrl(), e);
} catch (IOException e) {
int statusCode = 0;
NetworkResponse networkResponse = null;
if (httpResponse != null) {
statusCode = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
} else {
throw new NoConnectionError(e);
}
VolleyLog.e("Unexpected response code %d for %s", statusCode, request.getUrl());
if (responseContents != null) {
networkResponse = new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents,
responseHeaders, false, SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_UNAUTHORIZED ||
statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_FORBIDDEN) {
attemptRetryOnException("auth",
request, new AuthFailureError(networkResponse));
} else {
// TODO: Only throw ServerError for 5xx status codes.
throw new ServerError(networkResponse);
}
} else {
throw new NetworkError(networkResponse);
}
}
}
}httpResponse = mHttpStack.performRequest(request, headers);if (stack == null) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 9) {
stack = new HurlStack();
} else {
// Prior to Gingerbread, HttpUrlConnection was unreliable.
// See: http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2011/09/androids-http-clients.html
stack = new HttpClientStack(AndroidHttpClient.newInstance(userAgent));
}
}5.结果返回(response返回)
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);mDelivery即默认的new ExecutorDelivery(new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()))
public ExecutorDelivery(final Handler handler) {
// Make an Executor that just wraps the handler.
mResponsePoster = new Executor() {
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
handler.post(command);
}
};
}@Override
public void postResponse(Request<?> request, Response<?> response, Runnable runnable) {
request.markDelivered();
request.addMarker("post-response");
mResponsePoster.execute(new ResponseDeliveryRunnable(request, response, runnable));
}/**
* A Runnable used for delivering network responses to a listener on the
* main thread.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private class ResponseDeliveryRunnable implements Runnable {
private final Request mRequest;
private final Response mResponse;
private final Runnable mRunnable;
public ResponseDeliveryRunnable(Request request, Response response, Runnable runnable) {
mRequest = request;
mResponse = response;
mRunnable = runnable;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public void run() {
// If this request has canceled, finish it and don't deliver.
if (mRequest.isCanceled()) {
mRequest.finish("canceled-at-delivery");
return;
}
// Deliver a normal response or error, depending.
if (mResponse.isSuccess()) {
mRequest.deliverResponse(mResponse.result);
} else {
mRequest.deliverError(mResponse.error);
}
// If this is an intermediate response, add a marker, otherwise we're done
// and the request can be finished.
if (mResponse.intermediate) {
mRequest.addMarker("intermediate-response");
} else {
mRequest.finish("done");
}
// If we have been provided a post-delivery runnable, run it.
if (mRunnable != null) {
mRunnable.run();
}
}
}mRequest.deliverResponse(mResponse.result);以StringRequest为例:其中mListener接口为外部传入接口,见文章最开始使用。至于这个parseNetworkResponse则是用来解析网络请求的返回数据response的。
@Override
protected void deliverResponse(String response) {
mListener.onResponse(response);
}
@Override
protected Response<String> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
String parsed;
try {
parsed = new String(response.data, HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
parsed = new String(response.data);
}
return Response.success(parsed, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
}

























 110
110











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








