迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法是典型最短路径算法,用于计算一个节点到其他节点的最短路径。
它的主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展(广度优先搜索思想),直到扩展到终点为止。
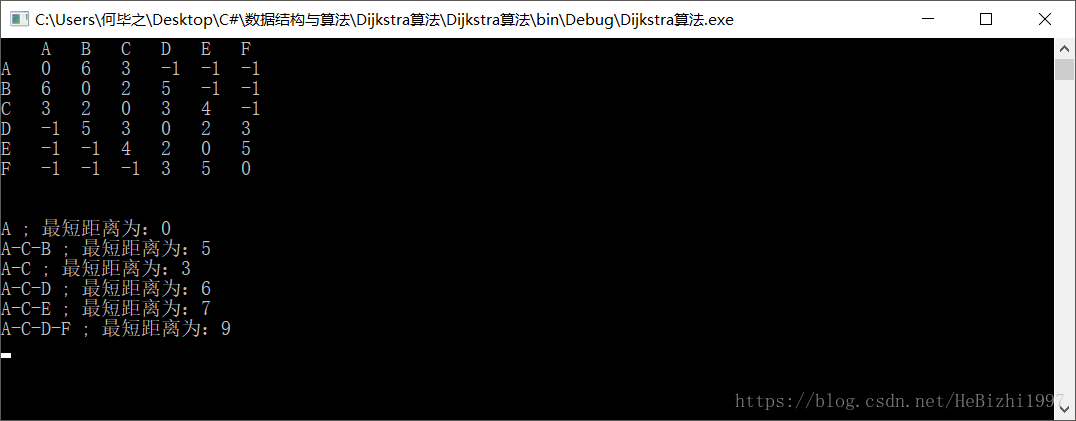
图解步骤:

C# 代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace Dijkstra
{
internal class Program
{
static readonly int M = -1;
static int[,] map = new int[,] {
{ 0, 6, 3, M,M,M },
{ 6, 0, 2, 5,M,M },
{ 3, 2, 0, 3, 4, M },
{ M, 5, 3, 0, 2, 3 },
{ M,M, 4, 2, 0, 5 },
{ M,M,M, 3, 5, 0 }
};//路径图
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var pointCount = (int)Math.Sqrt(map.Length);
//存放从0到其他节点的最短路径
var shortest = new List<Node> { new Node { Key = 0, Value = 0, Path = "0" } };
//存放未计算结点的索引
var unVisited = Enumerable.Range(1, pointCount - 1).ToList();
while (unVisited.Count > 0)
{
//缓存 0到未计算点的最短路径
var temp = new List<Node>();
for (int i = 0; i < shortest.Count; i++)
{
var flag = shortest[i].Key;
var val = shortest[i].Value;
var path = shortest[i].Path;
for (int j = 0; j < pointCount; j++)
{
//跳过 已经计算好的点
if (shortest.Select(p => p.Key).Contains(j)) continue;
// 跳过不相邻的点
if (map[flag, j] == M) continue;
//获取前面计算点到当前未计算点的距离
var node = temp.FirstOrDefault(p => p.Key == j);
//若无 生成一个计算点 并加入缓存
if (node == null)
{
node = new Node { Key = j, Value = val + map[flag, j], Path = path + j };
temp.Add(node);
}
//若有 则比较距离 更新数据
else if (val + map[flag, j] < node.Value)
{
node.Value = val + map[flag, j];
node.Path = path + j;
}
}
}
//将队列按距离排序 将最短路径的点 更新为已计算完成
temp = temp.OrderBy(p => p.Value).ToList();
var par = temp.Min(c => c.Value);
if (temp?.Count > 0)
{
shortest.Add(temp.First());
unVisited.Remove(temp.First().Key);
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("path:{0} ; distence:{1}", temp.First().Path, temp.First().Key));
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
public class Node
{
public int Key { get; set; }
public int Value { get; set; }
public string Path { get; set; }
}
}




















 6万+
6万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








