目录
1.2.二叉搜索树Binary Search Trees (BST)
1.2.2插入元素Inserting an Element to a Binary Search Tree
1.2.3在二叉搜索树中查找元素Searching an Element in a Binary Search Tree
1.2.4.4广度优先遍历Breadth-First Traversal
1.2.4.5深度优先遍历Depth-First Traversal
1.2.4.6使用迭代器进行遍历:Using Iterator for Traversal
1.2.5对 insert()、search() 和遍历方法的建模:
1.2.6从二叉搜索树中删除元素:Deleting Elements in a Binary Search Tree
1.2.6.1情况1:当前节点没有左子节点The current node does not have a left child
1.2.6.2情况2:当前节点有左子节点The current node has a left child
1.2.7二叉树的时间复杂度:Binary Tree Time Complexity
1.3数据压缩:哈夫曼编码Data Compression: Huffman Coding
1.二叉树
1.1二叉树Binary Trees
1.1.1介绍
- 二叉树是一种层级结构:它要么是空的,要么由一个称为根节点的元素和两个不同的二叉树组成,这两个子树分别称为左子树和右子树A binary tree is a hierarchical structure: it is either empty or consists ofan element, called the root, and two distinct binary trees, called the left subtree and right subtree
·一个节点的左(右)子树的根称为该节点的左(右)子节点 The root of left (right) subtree ofa node is called a left (right) child of the node
·没有子节点的节点被称为叶子节点A node without children is called a leaf
1.1.2表示
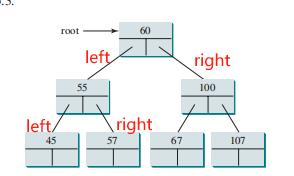
- 二叉树可以通过一组链式节点来表示:每个节点包含一个元素值,并有两个链接,分别命名为left和right,它们分别引用左子节点和右子节点。A binary tree can be represented using a set of linked nodes: each node contains an element value and two links named left and right that reference the left child and right child

1.2.二叉搜索树Binary Search Trees (BST)
1.2.1定义:
- 一种特殊类型的二叉树,称为二叉搜索树,它具有以下特点:A special type of binary trees, called binary search tree is a binary tree with
·没有重复元素(默认情况下)no duplicate elements (by deaulft)
·对于树中的每个节点,其左子树中任何节点的值都小于该节点的值,而右子树中任何节点的值都大于该节点的值he property that for every node in the tree the value of any node in its left subtree is less than the value of the node and the value of any node in its right subtree is greater than the value of the node
1.2.2插入元素Inserting an Element to a Binary Search Tree

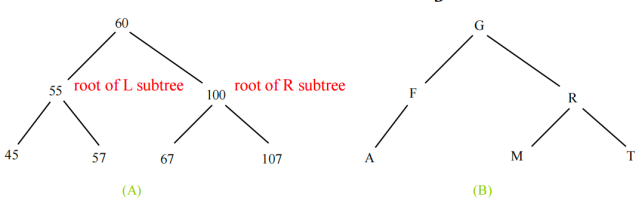
- 条件 1:如果树为空(没有根节点),使用给定的元素创建根节点。Condition 1: If the tree is empty (with no root), create the root node using the given element
- 条件 2:如果树不为空,创建两个指针 `current` 和 `parent`,并使用 `while` 循环找到我们想要插入的位置。Condition 2: If the tree is not empty, create 2 pointers ‘current’ and ‘parent’ and use the while loop to find the location we want to insert
- 找到父节点的位置后,比较元素与父节点的值,并将新创建的节点附加到父节点的左子树或右子树上。After finding the parent node location, compare the element with the value of the parent node, and attach the newly created node to either left or right of the parent
- 示例:追踪将 101 插入到以下树中:Trace Inserting 101 into the following tree
1.2.3在二叉搜索树中查找元素Searching an Element in a Binary Search Tree

1.2.4树的遍历Tree Traversal
- 树的遍历是逐一访问树中每一个节点的过程,每个节点只访问一次。树的遍历方式有多种:前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历等。Tree traversal is the process of visiting each node in the tree exactly once. There are several ways to traverse a tree: preorder, inorder, postorder, depth-first, breadth-first traversals
1.2.4.1前序遍历
- 在前序遍历中,访问顺序是:With preorder traversal
·首先访问当前节点,the current node is visited first
·然后递归地访问当前节点的左子树,then recursively left subtree of the current node
·最后递归地访问当前节点的右子树finally the right subtree of current node recursively
·递归地:表示在每一个子树的访问中,仍然遵循节点 → 左子树 → 右子树的顺序。Recursively : follow the same Node-Left-Right order in every subtree we will visit
1.2.4.2中序遍历
- 在中序遍历中,访问顺序是:
·首先递归地访问当前节点的左子树visit the left subtree of current node first recursively
·然后访问当前节点本身,then the current node itself
·最后递归地访问当前节点的右子树finally the right subtree of current node recursively
·即遵循左子树 → 节点 → 右子树(Left-Node-Right)的顺序。

1.2.4.3后序遍历:
- 在后序遍历中,访问顺序是:
·首先访问当前节点的左子树,visit the left subtree of the current node first
·然后访问当前节点的右子树,then the right subtree of the current node
·最后访问当前节点本身。finally the current node itself
·即遵循左子树 → 右子树 → 节点(Left-Right-Node)的顺序。

1.2.4.4广度优先遍历Breadth-First Traversal
- 在广度优先遍历中,访问顺序是:
·首先访问根节点,first visit the root
·然后从左到右访问根节点的所有子节点,then all children of the root from left to right
·接着从左到右访问根节点的孙子节点,then grandchildren of the root from left to right
·以此类推,逐层向下访问整棵树。
1.2.4.5深度优先遍历Depth-First Traversal
- 按照一条分支一条分支地从左到右访问节点的方式进行的。visit the nodes branch by branch from left to right
1.2.4.6使用迭代器进行遍历:Using Iterator for Traversal
- 方法 inorder()、preorder() 和 postorder()仅限于显示树中的元素。The methods inorder(), preorder(), and postorder() are limited to displaying the elements in a tree.
·如果你希望对二叉树中的元素进行处理而不仅仅是显示,这些方法就不够用了。If you wish to process the elements in a binary tree rather than just display them, these methods cannot be used
- 因此需要使用 Iterator,因为它允许对树中的元素进行更灵活和可自定义的处理,而不仅仅是输出。Iterator is needed because it allows flexible and customizable processing of tree elements, beyond just displaying them
·例如:

- Tree 接口扩展自 java.util.Collection,而 Collection又扩展了 java.lang.Iterable,因此 BST` 也是 Iterable 的子类。The Tree interface extends java.util.Collection. Since Collection extends java.lang.Iterable, BST is also a subclass of Iterable.
·因此我们可以直接在 `BST` 中定义一个迭代器类,**实现 `java.util.Iterator` 接口**。这样就可以使用增强的 `for` 循环对树元素进行遍历与处理。So we directly define an iterator class in BST to implement the java.util.Iterator interface.

- 测试


1.2.5对 insert()、search() 和遍历方法的建模:
Modelling for the insert(), search() and the traversal methods
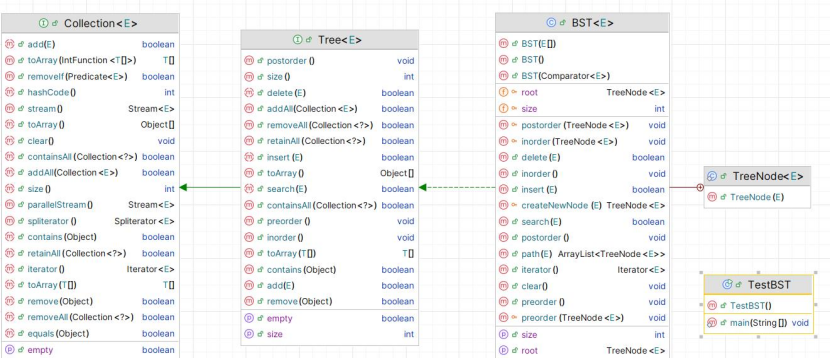
- Tree 接口扩展了 Collection 接口(用于代码重用)Tree Interface extends Collection Interface (for code reuse)
- BST 类实现了 Tree 接口,用于具体实现与二叉搜索树相关的操作BST implements Tree Interface for concrete implementation of BST-specific operations
- TreeNode 是一个内部类,用于表示二叉搜索树中的节点,并支持与 BST 相关的操作TreeNode is an inner class to represent nodes in the BST and support BST-specific operations
- TestBST 类包含主方法,程序从这里开始执行,并在其中对所有操作进行测试TestBST includes the main method where the program execution begins and all operations are tested.
1.2.6从二叉搜索树中删除元素:Deleting Elements in a Binary Search Tree
- 要从二叉树中删除一个元素,首先需要找到包含该元素的节点(记作 `current`)以及它的父节点(记作 `parent`)。To delete an element from a binary tree, you need to first locate the node that contains the element and also its parent node
·current 指向要删除的节点,parent指向其父节点。Let current point to the node that contains the element to be deleted in the binary tree and parent point to the parent of the current node
·current 节点可能是parent的左子节点,也可能是右子节点。The current node may be a left child or a right child of the parent node
·删除操作分为以下两种情况进行处理:There are two cases to consider:
>情况1:current 节点没有左子节点The current node does not have a left child
>情况2:current 节点有左子节点The current node has a left child
1.2.6.1情况1:当前节点没有左子节点The current node does not have a left child
- 只需将父节点与当前节点的右子节点连接即可。Simply connect the parent with the right child ofthe current node.
- 例如:要删除节点 10,只需将节点 10 的父节点与节点 10 的右子节点相连。to delete node 10 connect the parent of node 10 with the right child of node 10
- 操作逻辑如下:
·设 `current` 为我们要删除的元素Let current = the element we want to delete
·设 `parent` 为 `current` 的父节点Let parent = the parent of current
·如果 `current` 没有左子节点:IF current has no left child
·直接将 `current` 的右子节点连接到 `parent`。Directly connect the current’s right child to current’s parent
- 这样,current(即需要被删除的节点)就被移除 —— 因为它不再被任何其他节点引用。The current (the element need to be deleted) is then eliminated (because it is no longer referenced by any other node)
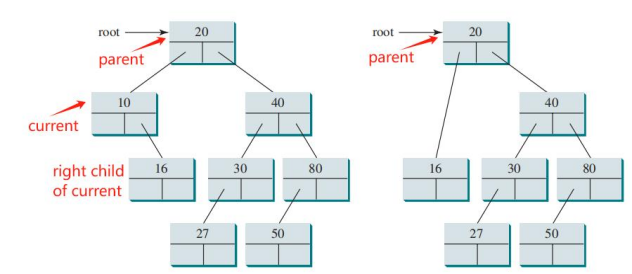
1.2.6.2情况2:当前节点有左子节点The current node has a left child
- 具体操作如下
·设current为我们要删除的元素。Let current = the element we want to delete
·在 current 的左子树中找到最右边的节点(即最大值节点,记作 `rightMost`)。
Find the rightMost node in current’s left subtree
·找到 rightMost的父节点(记作 rightMostParent)。Find the rightMost’s parent
·将rightMost的值复制到current(此时我们要删除的值已经被覆盖,相当于删除current)
Copy rightMost to current (the element we want to delete has been deleted now)
·然后通过将 rightMost的左子节点连接到 rightMost的父节点,删除原来的 rightMost节点。Remove the orginal rightMost by linking rightMost’s left child to rightMost’s parent
1.2.6.3代码实现:


- 测试:

1.2.7二叉树的时间复杂度:Binary Tree Time Complexity
- 中序遍历、先序遍历、后序遍历的时间复杂度为 O(n),因为每个节点只会被遍历一次。The time complexity for the inorder, preorder, and postorder traversals is O(n), since each node is traversed only once
- 查找、插入和删除的时间复杂度取决于树的高度。The time complexity for search, insertion and deletion is the height ofthe tree
·在最坏情况下(例如树退化成链表),树的高度为 O(n)。In the worst case, the height of the tree is O(n)
1.2.8实践一个程序:
使用二叉搜索树创建一棵二叉树,将字符串添加到该二叉树中,并以中序、后序和前序的方式遍历这棵树。A program that creates a binary tree using BST and adds strings into the binary tree and traverse the tree in inorder, postorder, and preorder:

1.3数据压缩:哈夫曼编码Data Compression: Huffman Coding
1.3.1介绍
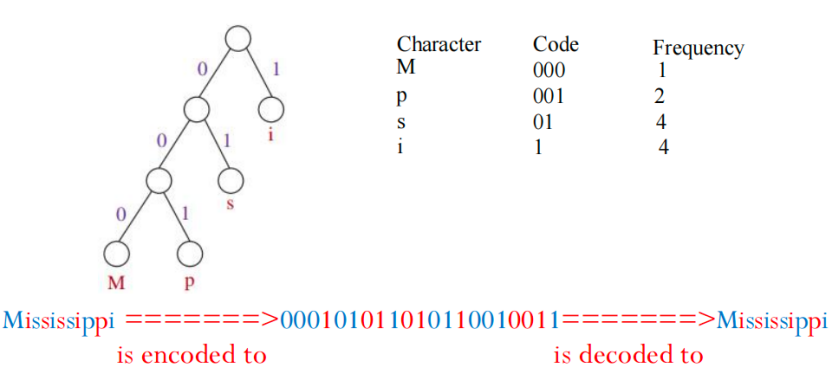
- 在 ASCII(美国信息交换标准代码)中,每个字符都用 8 位二进制表示(例如:M → `01001101`)。 In ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange), every character is encoded in 8 bits (e.g., M -> 01001101)
·哈夫曼编码通过对出现频率较高的字符使用更少的比特进行编码,从而实现数据压缩。Huffman coding compresses data by using fewer bits to encode more frequently occurring characters is encoded to is decoded to
Mississippi =======> 000101011010110010011 =======> Mississippi
>在这个例子中,哈夫曼编码只用了 22 位(二进制)≈ 3 字节,而使用 ASCII 编码则需要 11 字节。this example uses 22 bits (~3 bytes) instead of 11 bytes (for ASCII encoding)
>各字符的编码是根据它们在文本中出现的频率构建的,并使用一种二叉树结构哈夫曼编码树来完成。The codes for characters are constructed based on the occurrence of characters in the text using a binary tree, called the Huffman coding tree
1.3.2演示
- 二叉树中每个节点的左边和右边的边分别被赋值为 0或1。The left and right edges of any node are assigned a value 0 or 1
- 每个字符对应于树中的一个叶子节点。Each character is a leaf in the tree
- 某个字符的编码由从根节点到该叶子节点路径上的边的值组成。The code for a character consists of the edge values in the path from the root to the leaf
1.3.3实现
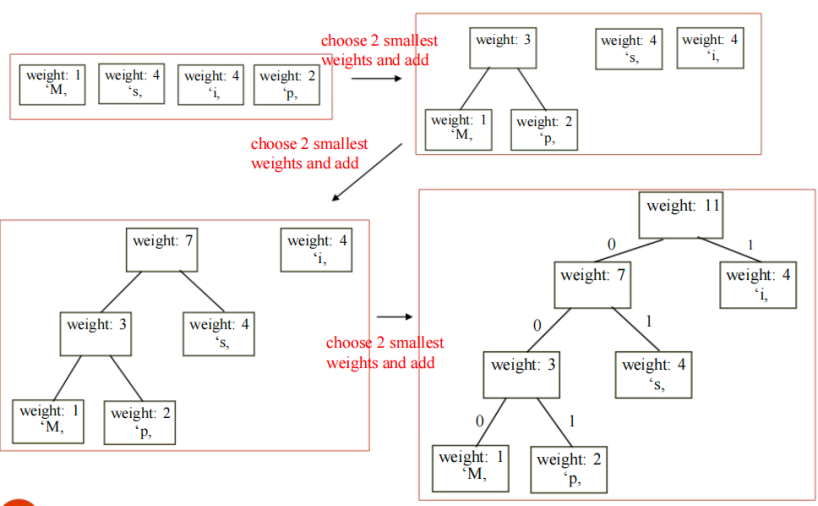
- 构建哈夫曼编码树时,使用的贪心算法,具体过程如下:To construct a Huffman coding tree, use a greedy algorithm as follows:
·从一个森林开始**,其中:Begin with a forest of trees where:
>每棵树都只包含一个节点,该节点表示一个字符;Each tree contains a single node for a character, and
>节点的权重等于该字符在文本中出现的频率。The weight of the node is the frequency of the character in the text
·重复以下步骤,直到只剩下一棵树为止:Repeat this step until there is only one tree:
>从森林中选择权重最小的两棵树(可以使用**堆实现的优先队列**来加速选择);Choose two trees with the smallest weight (using a priority queue implemented with a Heap) and create a new node as their parent
>创建一个新节点作为这两棵树的父节点。The weight of the new tree is the sum of the weight of the subtrees
·新树的权重为其两个子树的权重之和。
























 2250
2250

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








