欢迎前往个人博客 驽马点滴 和视频空间 哔哩哔哩-《挨踢日志》
问题重述:
捕食者-被捕食者模型非线性微分方程的一个例子是捕食者-被捕食者模型。设x(t)和y(t)分别表示兔子和狐狸在时刻t的数量,捕食者-被捕食者模型表明,x(t)和y(t)满足:
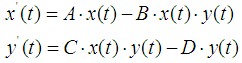
一个典型的计算机模拟可作用系数:
A=2, B=0.02, C=0.0002, D=0.8
且满足:
x(0)=3000只兔子,y(0)=120只狐狸。
在区间[0,5]内:
(1) 用Euler法、Heun法和经典4阶Runge-kutta法取多种步长求解。
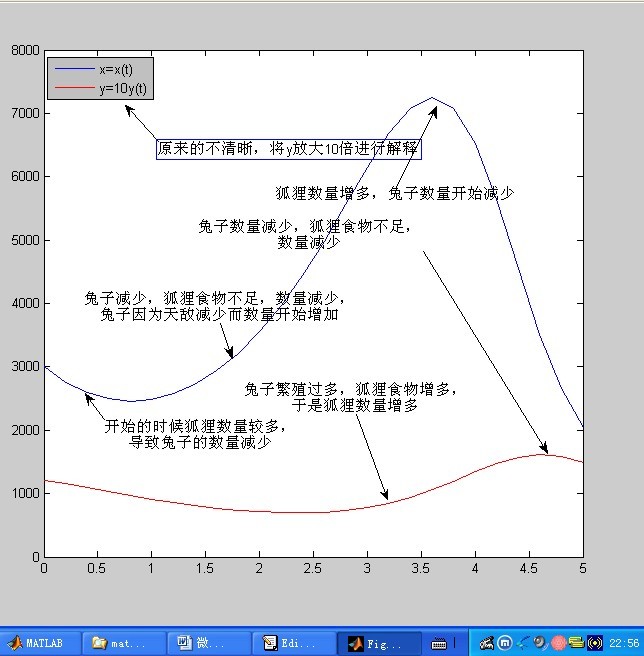
把x=x(t) 和y=y(t)画在同一张图上并给以解释。
(2) 为考察变量x和y之间的关系,将计算结果画在以x、y为坐标的图上,对所得结果加以解释。
原理介绍:
Euler Method
对于
dx=f(t,x,y)dt和dy=g(t,x,y)dt
将 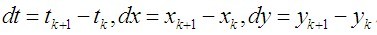 代入上式得到:
代入上式得到:
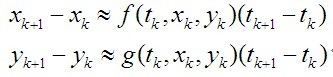
将区间分为M个子区间,宽度h=(b-a)/M,网格点为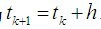
于是得到Euler Method:
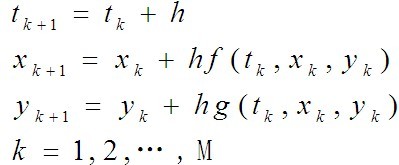
Heun Method
在区间[ , ]上对微分方程积分:
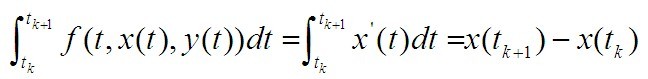
再利用trapezoidal rule可以得到:
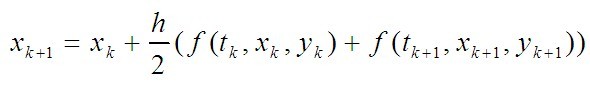
但右边含有 ,利用Euler Method 得到Heun Method:
,利用Euler Method 得到Heun Method:
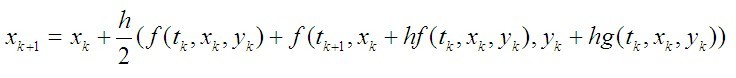
在每一步中,用Euler Method 作为预报,trapezoidal rule 进行校正,得到最终值。Heun Method的一般步骤如下:
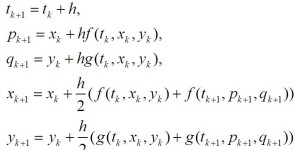
Runge-Kutta Method of Order 4
基于Heum Method 的推导过程,我们得到
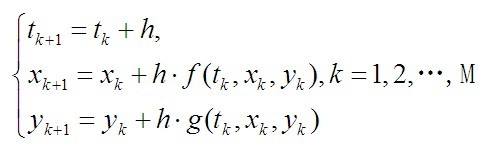
提高精度,得到4价Runge-Kutta Method:
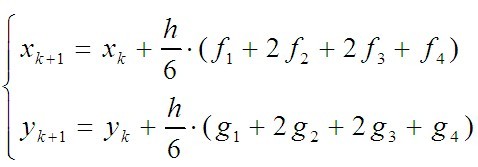
其中:
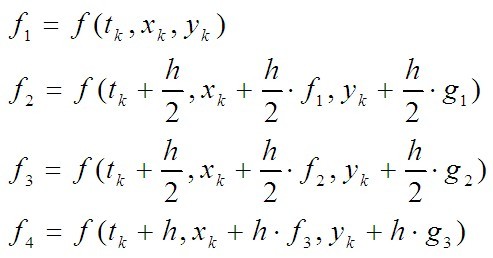
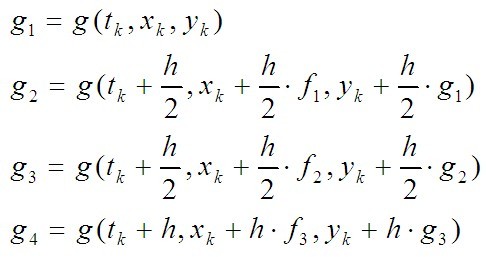
下面是程序:
function E=euler(f,g,a,b,xa,ya,M)
%Input - f is the function entered as a string 'f'
% - g is the function entered as a string 'g'
% - a and b are the left and right endpoints
% - xa is the initial condition x(a)
% - ya is the initial condition y(a)
% - M is the number of steps
%Output - E=[T' X' Y'] where T is the vector of abscissas
% and X and Y are the vectors of ordinates
h=(b-a)/M;
T=zeros(1,M+1);
X=zeros(1,M+1);
Y=zeros(1,M+1);
T=a:h:b;
X(1)=xa;
Y(1)=ya;
for j=1:M
X(j+1)=X(j)+h*feval(f,T(j),X(j),Y(j));
Y(j+1)=Y(j)+h*feval(g,T(j),X(j),Y(j));
end
E=[T' X' Y'];
function H=heun(f,g,a,b,xa,ya,M)
%Input - f is the function entered as a string 'f'
% - g is the function entered as a string 'g'
% - a and b are the left and right endpoints
% - xa is the initial condition x(a)
% - ya is the initial condition y(a)
% - M is the number of steps
%Output - H=[T' X' Y'] where T is the vector of abscissas
% and X and Y are the vectors of ordinates
h=(b-a)/M;
T=zeros(1,M+1);
X=zeros(1,M+1);
Y=zeros(1,M+1);
T=a:h:b;
X(1)=xa;
Y(1)=ya;
for j=1:M
k1=feval(f,T(j),X(j),Y(j));
k2=feval(g,T(j),X(j),Y(j));
k3=feval(f,T(j+1),X(j)+h*k1,Y(j)+h*k2);
k4=feval(g,T(j+1),X(j)+h*k1,Y(j)+h*k2);
X(j+1)=X(j)+(h/2)*(k1+k3);
Y(j+1)=Y(j)+(h/2)*(k2+k4);
end
H=[T' X' Y'];
function R=rk4(f,g,a,b,xa,ya,M)
%Input - f is the function entered as a string 'f'
% - g is the function entered as a string 'g'
% - a and b are the left and right endpoints
% - xa is the initial condition x(a)
% - ya is the initial condition y(a)
% - M is the number of steps
%Output -R=[T' X' Y'] where T is the vector of abscissas
% and X and Y are the vectors of ordinates
h=(b-a)/M;
T=zeros(1,M+1);
X=zeros(1,M+1);
Y=zeros(1,M+1);
T=a:h:b;
X(1)=xa;
Y(1)=ya;
for j=1:M
k1=h*feval(f,T(j),X(j),Y(j));
k2=h*feval(g,T(j),X(j),Y(j));
k3=h*feval(f,T(j)+h/2,X(j)+k1/2,Y(j)+k2/2);
k4=h*feval(g,T(j)+h/2,X(j)+k1/2,Y(j)+k2/2);
k5=h*feval(f,T(j)+h/2,X(j)+k3/2,Y(j)+k4/2);
k6=h*feval(g,T(j)+h/2,X(j)+k3/2,Y(j)+k4/2);
k7=h*feval(f,T(j)+h,X(j)+k5,Y(j)+k6);
k8=h*feval(g,T(j)+h,X(j)+k5,Y(j)+k6);
X(j+1)=X(j)+(k1+2*k3+2*k5+k7)/6;
Y(j+1)=Y(j)+(k2+2*k4+2*k6+k8)/6;
end
R=[T' X' Y'];
由于前面的原理介绍已经比较清楚了,所以程序中的计算就不赘述了
下面是M文件的截图:
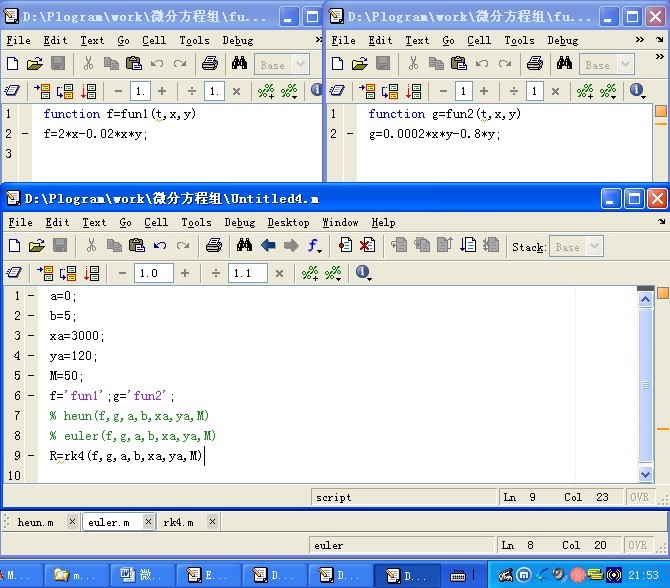
部分解释:
下面在同一个图中作出Euler,Heun,Runge-Kutta Method 对应的y-x图象:
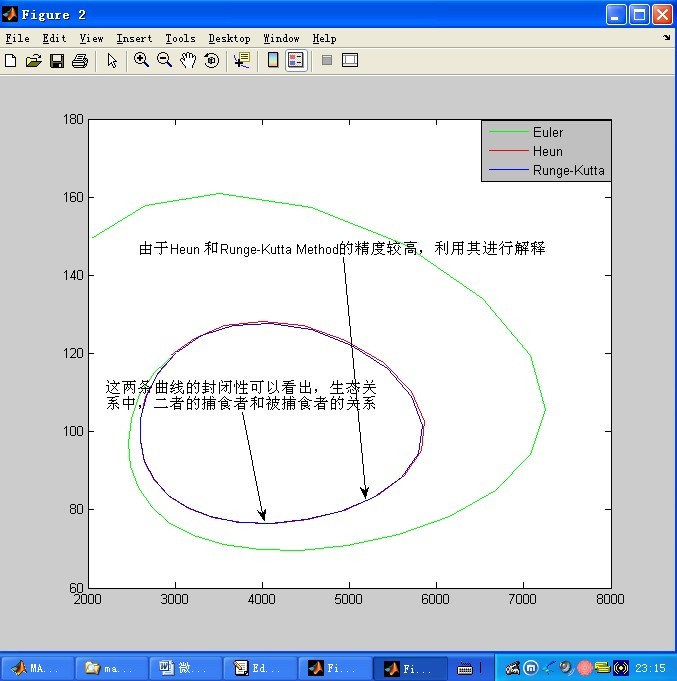
既然看出二者在同一个图中表示的是一条封闭曲线,说明了生态系统的自我调节过程,揭示了捕食者和被捕食者的在数量上的动态关系,图象的闭合性也说明了模型的正确性:具有周期性、在周期内的数量呈现振荡关系,一段时间内此消彼长,一段时间内,共同增加,但是增长率随着一方数量的增加而减小。具体的说,在捕食者和被捕食者模型中临界点为(D/C,A/B)=(4000,100),并且知道这个临界点是中心。可以参考上图。初值条件X0越靠近(4000,100),周期解就越像相应线性方程组的椭圆解。g’((4000,100))的特征值为λ=±√(AD)*i=±2/5*√10i,所以周期为(√10)π/2,或者约等于4.97
总结:
可以看到,这个模型中,Heun Method 和Runge-Kutta Method对模型的拟合程度较高,精度也比Euler Method 高,从纵向比较,我们可以看出,随着步长的减小,Euler Method,Heun Method 和Runge-Kutta Method的精度提高。
这里,仍然有必要对x=x(t)和y=y(t)图象进行总的说明:
兔子和狐狸的数量在一开始的时候,由于狐狸的数量超过生态系统中的数量(换句话说,就是兔子的数量满足不了狐狸的需求),狐狸在一段时间内,由于食物缺乏而死亡,兔子由于过多狐狸的捕食而减少数量,当狐狸的数量减少到一定程度时,兔子由于天敌的减少而不断繁殖,于是数量增加,狐狸自身减少的同时,由于食物的增加,于是渐渐的食物充足而开始不断繁殖;狐狸不断繁殖,导致兔子的增长率减小,达到一定的程度时,兔子的数量满足不了狐狸的需求,狐狸开始减少,于是这样的周而复始……
对于y-x图象,前面已经说过,这是一条封闭的曲线,封闭性同说明了生态系统的自我调节过程,揭示了捕食者和被捕食者的在数量上的动态关系,图象的闭合性也说明了模型的正确性:具有周期性、在周期内的数量呈现的振荡关系:一段时间内此消彼长,一段时间内,共同增加――恰恰从另一个方面说明了x(t)-t,y(t)-t,的关系。
必须再次强调的是
在捕食者和被捕食者模型中临界点为(D/C,A/B)=(4000,100),并且知道这个临界点是中心。初值条件X0越靠近(4000,100),周期解就越像相应线性方程组的椭圆解。g’((4000,100))的特征值为λ=±√(AD)*i=±2/5*√10i,所以周期为(√10)π/2,或者约等于4.97。
欢迎前往个人博客 驽马点滴 和视频空间 哔哩哔哩-《挨踢日志》



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








