1.什么是反射
反射是框架设计的灵魂,框架:它是一个半成品,可以拿来使用,添加上自己的业务代码。提高开发效率。
反射就是把类中成员抽取成其他类的过程。这就是反射。
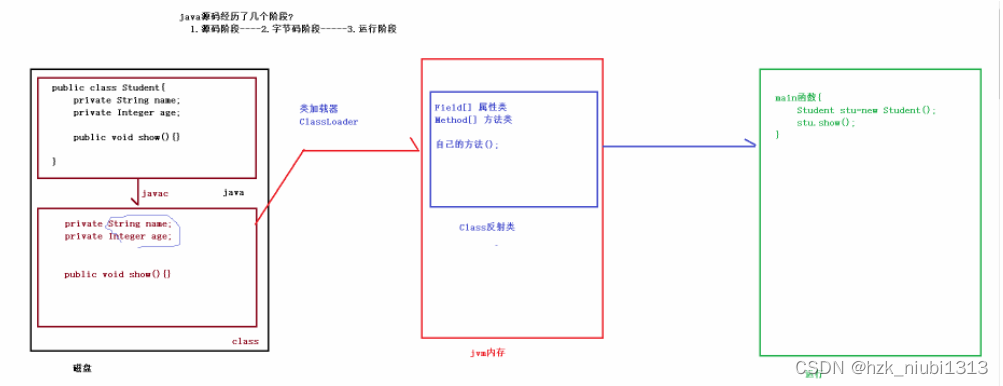
2.如何获取反射类对象
有三种:
(1) 通过Class.forName获取反射对象.
Class.forName("全路径")
–spring它就是使用的该模式
(2)通过类名.class获取
类名.class;
—代理类—>SqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class)
(3) 通过对象.getClass()方法获取
对象.getClass();
—当知道对象时可以通过这种方式获取反射对象
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1.通过Class.forName来获取反射类对象。
Class aClass = Class.forName("demo.People");
//2.通过类名调用.class获取反射类对象
Class aClass1 = People.class;
//3.通过对象获取反射类对象
People p=new People();
Class aClass2 = p.getClass();
//思考:上面三个反射对象的引用地址是否一致! 是一致的。 一个类只会被加在到内存中一次。
System.out.println(aClass==aClass1);
System.out.println(aClass2==aClass1);
}
}
3.通过反射类获取类对象
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
//1.获取反射类对象
Class<People> aClass = People.class;
//2.由反射类创建类对象---调用为无参构造函数
People people = aClass.newInstance();
People people2 = aClass.newInstance();
//3.他们的地址是否相同
System.out.println(people==people2);
}
}
4.通过反射获取对应的Field属性对象
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("demo.People");
//获取本类中指定的属性对象
Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name);
//获取本类以及父类中指定的属性---必须为public修饰的。
Field name1 = aClass.getField("sex");
System.out.println(name1);
//获取本类中所有的属性对象
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field:declaredFields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
//获取本类以及父类中所有public修饰的属性对象
Field[] fields = aClass.getFields();
for (Field field:
fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
}
5.Field属性对象中常见的方法
getName():获取属性名
setAccessible(true):设置属性可访问。
set(o,v):为对象o的属性赋值v
get(o):获取对象o的属性值
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<People> peopleClass = People.class;
Field nameField = peopleClass.getDeclaredField("name");
//1.获取属性的名称
String name = nameField.getName();
System.out.println("属性名称:"+name);
//2.为属性赋值.
//Object obj,对象
// Object value
People people = peopleClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(people);
nameField.setAccessible(true);//为nameField设置可访问权限,打破了封装性
nameField.set(people,"张三");
System.out.println(people);
//3.获取属性值
Object o = nameField.get(people);
System.out.println(o);
//nameField.getAnnotation();//获取nameField属性上的注解对象
}
6.通过反射获取对应的Method方法对象
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<People> aClass = People.class;
//获取本类中所有的方法。
Method[] declaredMethods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method:declaredMethods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("======================================================");
//获取本类和父类中所有public修饰的方法
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("**************************************************************");
//本类中指定的 方法对象
Method fun = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("fun");
System.out.println(fun);
Method setName = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("setName",String.class);
System.out.println(setName);
//获取本类以及父类中指定名称的方法对象
Method equals = aClass.getMethod("equals", Object.class);
System.out.println(equals);
}
}
6.1 Method类中常见的方法
//method.invoke(对象,方法参数值);
invoke(people,“15”);//回调。动态代理
7.获取相应注解对象
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class<Student> aClass = Student.class;
//获取类对象的指定注解
MyAnnotation annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(annotation.value());
Field idField = aClass.getDeclaredField("id");
MyAnnotation annotation1 = idField.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(annotation1.value());
System.out.println(annotation1.sex());
}
}





















 155
155











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








