学习了算法通关村的第六至十关,我们对树、递归的知识有了更深入的认识。所以本节主要是我个人本阶段的学习总结,针对我个人认为比较重要的知识点和题型进归纳整理。
1. 树的定义与存储方式
该内容是我们在刷LeetCode很容易忽视的部分,由于刷LeetCode的时候二叉树和N叉树的定义并不需要我们自己书写,这其实也导致很多同学在面试的时候定义树总是出错,因此这部分我们应该更加重视。
定义
//二叉树的定义
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNOde right;
}
//N叉树的定义
public class NTreeNode {
int val;
List<NTreeNode> nodes;
}
存储方式
-
使用数组存储二叉树
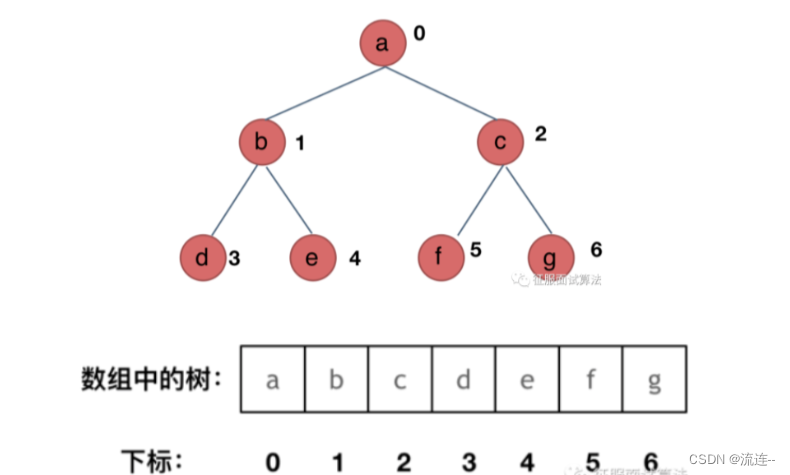
不足之处:存在大量的空间浪费,例如上图中,如果b分支没有,那么数组种1 3 4 位置都要空着,但是整个数组的大小仍然是7,因此很少使用数组来存储树。 -
使用链式存储二叉树(比较常用)
与链表相似,后面的题目都是使用链式进行存储,所以这里不做展示。
2. 树的遍历方式
深度优先遍历
即先往深处走,遇到叶子节点再往回走。
常见的深度优先遍历有三种,即前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历,由于这三个遍历方式属于重中之重,所以我们将分别使用递归和迭代的方法来实现这三种遍历方式,注意迭代法的后序遍历比较特殊,难度比较大(本文只列举最为简单的反转法)。
前序遍历
- 递归法
public static void preOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) return;
res.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left,res);
preOrder(root.right,res);
}
- 迭代法
public static List<Integer> preOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return res;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || root != null){
while (root != null){
res.add(root.val);
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
中序遍历
- 递归法
public static void preOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) return;
preOrder(root.left,res);
res.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.right,res);
}
- 迭代法
public static List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return null;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || root != null){
while (root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
后序遍历
- 递归法
public static void preOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) return;
preOrder(root.left,res);
preOrder(root.right,res);
res.add(root.val);
}
- 迭代法
这里与上面的不同,使用反转法(比较简单,易于实现),即原后续遍历为(左右中),先取(中右左),再把所得链表反转再输出。
public static List<Integer> postOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return res;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null){
while (node != null){
res.add(node.val);
stack.push(node);
node = node.right;
}
node = stack.pop();
node = node.left;
}
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
广度优先遍历(层次遍历)
层次优先遍历是面试中常见的方法,需要牢牢掌握。
这里介绍一下一些比较常见的使用层序遍历的题型。
二叉树的层序遍历
- 最简单的情况——仅仅输出全部元素(基本的层序)
public static List<Integer> simpleLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return res;
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
res.add(t.val);
if (t.left != null) {
queue.add(t.left);
}
if (t.right != null) {
queue.add(t.right);
}
}
return res;
}
- 按层序遍历得到各层的节点值。(即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
public static List<List<Integer>> level102Order(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return res;
}
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode t = queue.remove();
tmp.add(t.val);
if (t.left != null){
queue.add(t.left);
}
if (t.right != null){
queue.add(t.right);
}
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
N叉树的层序遍历
- 法一:与前面二叉树类似,先取得每层的元素个数,再进行遍历。
public static List<List<Integer>> nLevelOrder(NTreeNode root) {
ArrayList<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return res;
}
Deque<NTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.push(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
NTreeNode t = queue.remove();
tmp.add(t.val);
if (t.children != null) {
for (NTreeNode chd : t.children) {
if (chd != null) {
queue.add(chd);
}
}
}
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
- 法二:交换法实现每层的遍历(即每层构造一个新的List来获取该层的下一层全部元素,再将该List地址赋值给原list)
public static List<List<Integer>> nLevelOrder(NTreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> value = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<NTreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
if (root != null)
q.addLast(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Deque<NTreeNode> next = new ArrayDeque<>();
List<Integer> nd = new ArrayList<>();
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
NTreeNode cur = q.pollFirst();
nd.add(cur.val);
for (NTreeNode chd : cur.children) {
if (chd != null)
next.add(chd);
}
}
q = next;
value.add(nd);
}
return value;
}
3. 二叉树的经典问题(多使用递归)
双指针的使用(例:合并二叉树)
本部分我们以LeetCode617题为例,给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
public static TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null){
return t2;
}
if (t2 == null){
return t1;
}
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
node.left = mergeTrees(t1.left,t2.left);
node.right = mergeTrees(t1.right,t2.right);
return node;
}
路径问题(例:路径总和II)
LeetCode113.给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
本题有一定难度,使用了回溯、递归的思想。
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root,targetSum);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null)
return;
targetSum -= root.val;
queue.offerLast(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == 0){
res.add(new LinkedList<>(queue));
}
dfs(root.left,targetSum);
dfs(root.right,targetSum);
queue.pollLast();
}
高度问题(例:判断平衡树)
LeetCode110 判断平衡二叉树:给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
本题运用了递归的思想,我们来简要分析一下:
对于该题目,我们不难想到在找到左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值超过 1之前,我们必须在每次递归的时候都获取对应节点的高度,才能方便后序的比较。
因此,我们定义了一个新方法,recur, 其形参为当前节点,作用是在左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值超过 1之前返回当前节点的高度,若绝对值超过 1则返回-1,标记该树不为平衡树。记住,对于递归方法,我们只需明确其形参含义和返回值(即作用是什么),无需考虑其内部实现。
public static boolean isBalanced_1(TreeNode root) {
return recur(root) != -1;
}
public static int recur(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
int left = recur(root.left);
int right = recur(root.right);
if (left == -1) return -1;
if (right == -1) return -1;
return Math.abs(left - right) < 2 ? Math.max(left,right) + 1 : -1;
}
4. 二分查找与分治
最基本的二分查找
public static int binarySearch1(int[] array, int low, int high, int target) {
// 循环
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
//1.右移提高性能
if (array[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (array[mid] > target) {
// 由于array[mid]不是目标值,因此再次递归搜索时,可以将其排除
high = mid - 1;
} else {
// 由于array[mid]不是目标值,因此再次递归搜索时,可以将其排除
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
含有重复元素的二分查找(返回最左元素的下标)
该部分建议不懂的就根据代码画图进行理解
public static int search(int[] arr, int val) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0)
return -1;
return binarySearch(arr, val);
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int val) {
int left = 0, right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (arr[mid] < val) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return left;
}
中序与搜索树(例:验证二叉搜索树)
//递归法
static long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE;
public static boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return true;
if (!isValidBST(root.left)){
return false;
}
if (root.val <= pre){
return false;
}
pre = root.val;
return isValidBST(root.right);
}
//迭代法
public static boolean isValidBST2(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
double pre1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || root != null){
while (root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (root.val <= pre1){
return false;
}
pre1 = root.val;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
}






















 137
137











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








