通过克隆对象来创建一个新的对象叫做原型模式(prototype pattern)。原型模式属于创建设计模式的范畴,与它相对的单例模式(Singleton Pattern)相对应,这两个设计模式都很简单,也很常用。
使用场景:
1. 当有许多子类,并且仅仅是对象的类型不同而已。
2. 引用程序中,需要创建大量的类实例且这些实例的状态等差异很小。
3. 动态的绑定或者重加载方法。
4. 使用一个实例,仅仅通过改变它的状态或参数去完成一个工作。
5. 在运行时,添加和删除对象。
6. 通过修改实例的结构来指定新对象。
7. 动态地用类配置一个应用程序。
需要记住的是:当使用clone去复制时,是否需要一个浅度克隆还是深度克隆(deep clone or shallow clone). 基于具体的业务需要,选择不同的克隆方式。如果你想使用深度克隆,你能够使用内存序列化(using in memory serialization)技术来实现。当实现原型设计模式时,使用克隆去复制完全是一个设计决策。请阅读如下原型设计模式的例子。
public class Prototype {
/**
* Dynamic loading is a typical object-oriented feature and prototype example.
* For example, overriding method is a kind of prototype pattern.
*/
static Complex c1 = new Complex();
/**
* Cloning is a shallow copy of the original object.
* If the cloned object is changed, the original object
* will be changed accordingly. See the following alteration.
* @return Complex
*/
static Complex makeCopy() {
return (Complex)c1.clone();
}
public static void main(String []args){
//Dynamically load method
Shape s1 = new Line();
Shape s2 = new Square();
Shape s3 = new Circle();
paint(s1);
paint(s2);
paint(s3);
/**
* If we want to make code more readable or do more stuff,
* we can code the paint method in the following way:
static void paint(Shape s){
if ( s instanceof Line)
s.draw();
//more job here
if (s instanceof Square)
s.draw();
//more job here
if (s instanceof Circle)
s.draw();
//more job here
}
*/
Complex c1 = makeCopy();
int[] mycopy = c1.getNums();
for(int i = 0; i < mycopy.length; i++)
System.out.print(mycopy[i]);
}
static void paint(Shape s) {
s.draw();
}
}
interface Shape {
public void draw();
}
class Line implements Shape {
public void draw() {
System.out.println("line");
}
}
class Square implements Shape {
public void draw() {
System.out.println("square");
}
}
class Circle implements Shape {
public void draw() {
System.out.println("circle");
}
}
/**
*The prototype is typically used to clone an object,
* i.e. to make a copy of an object. When an object
* is complicated or time consuming to be created ,
* you may take prototype pattern to make such object
* cloneable. Assume the Complex class is a complicated,
* you need to implement Cloneable interface and override
* the clone method(protected Object clone()).
*/
class Complex implements Cloneable {
int[] nums = {1,2,3,4,5};
public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
}catch(CloneNotSupportedException cnse) {
System.out.println(cnse.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
int[] getNums() {
return nums;
}
}这个例子使用了prototype模式,减少了创建对象的花费(这个实例只是作为阐明原型设计模式,不能作为实际用途)。值得使出的是, 对于原型模式而言,克隆不是一个强制的选择。
也许你感觉上面的例子不够接近实际应用,那么就认真看看下面的实例吧,也许能够在实际的项目中应用。
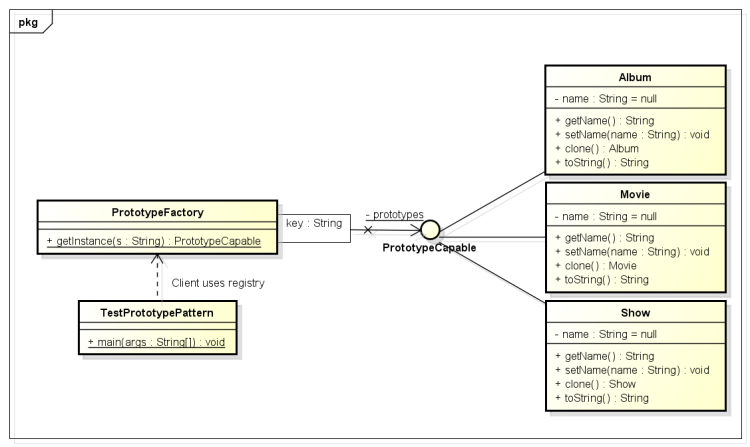
PrototypeCapable.java接口,扩展 Cloneable。
public interface PrototypeCapable extends Cloneable{
public PrototypeCapable clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
}
public class Album implements PrototypeCapable{
private String name = null;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Album clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
System.out.println("Cloning Album object..");
return (Album) super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Album";
}
}public class Movie implements PrototypeCapable{
private String name = null;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Movie clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
System.out.println("Cloning Movie object..");
return (Movie) super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Movie";
}
}
public class Show implements PrototypeCapable
{
private String name = null;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Show clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
System.out.println("Cloning Show object..");
return (Show) super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Show";
}
}
public class PrototypeFactory{
private static java.util.Map<String , PrototypeCapable> prototypes = new java.util.HashMap<String , PrototypeCapable>();
static{
prototypes.put(ModelType.MOVIE, new Movie());
prototypes.put(ModelType.ALBUM, new Album());
prototypes.put(ModelType.SHOW, new Show());
}
public static PrototypeCapable getInstance(final String s) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return ((PrototypeCapable) prototypes.get(s)).clone();
}
public static class ModelType {
public static final String MOVIE = "movie";
public static final String ALBUM = "album";
public static final String SHOW = "show";
}
}
测试这个类,测试代码如下:
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import junit.framework.Assert;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.pattern.rationaljava.creationalpattern.prototype.PrototypeFactory;
import org.pattern.rationaljava.creationalpattern.prototype.PrototypeFactory.ModelType;
public class TestPrototypeFactory {
@BeforeClass
public static void setUpBeforeClass() throws Exception {
}
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Test
public void testGetInstance() {
try {
String moviePrototype = PrototypeFactory.getInstance(ModelType.MOVIE).toString();
Assert.assertEquals("Movie", moviePrototype);
String albumPrototype = PrototypeFactory.getInstance(ModelType.ALBUM).toString();
Assert.assertEquals("Album", albumPrototype);
String showPrototype = PrototypeFactory.getInstance(ModelType.SHOW).toString();
Assert.assertEquals("Show", showPrototype);
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
UML类图



















 9381
9381











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








