目录
1.system( ) 函数原型:
NAME
system - execute a shell command
SYNOPSIS
#include <stdlib.h>
int system(const char *command);
2.system( ) 函数返回值
成功,则返回进程的状态值;
当sh不能执行时,返回127;
失败返回-1;
3.system( ) 函数源码
int system(const char * cmdstring)
{
pid_t pid;
int status;
if(cmdstring == NULL)
{
return (1); //如果cmdstring为空,返回非零值,一般为1
}
if((pid = fork())<0)
{
status = -1; //fork失败,返回-1
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", cmdstring, (char *)0);
_exit(127); /* exec执行失败返回127,注意exec只在失败时才返回现在的进程,成功的话现在的
进程就不存在啦8*/
}
else //父进程
{
while(waitpid(pid, &status, 0) < 0)
{
if(errno != EINTR)
{
status = -1; //如果waitpid被信号中断,则返回-1
break;
}
}
}
return status; //如果waitpid成功,则返回子进程的返回状态
}3. system( ) 函数小应用代码demo
3.1实现小功能,执行 vim 中的 ps - l 命令
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//函数原型:int system(const char *command);
int main(void)
{
printf("this pro get system date:\n");
if(system("ps -l") == -1)
{
printf("system failed!\n");
perror("why");
}
printf("after system!!!\n");
return 0;
}
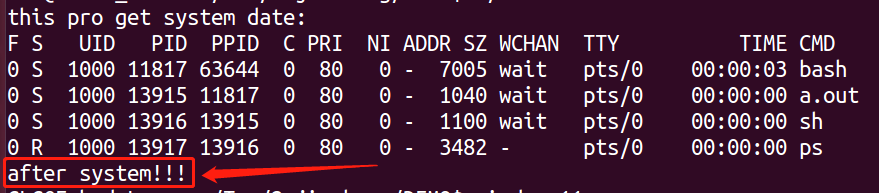
通过运行结果可以看出:system( ) 函数调用完之后,代码还会往下走。 而exec族函数则不会往下走。
system( ) 函数的参数书写的规律是,可执行文件怎么执行,就怎么写:比如 system("./a.out aa bb");























 5571
5571











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










