TITLE: Wider or Deeper: Revisiting the ResNet Model for Visual Recognition
AUTHOR: Zifeng Wu, Chunhua Shen, Anton van den Hengel
ASSOCIATION: The University of Adelaide
FROM: arXiv:1611.10080
CONTRIBUTIONS
- A further developed intuitive view of ResNets is introduced, which helps to understand their behaviours and find possible directions to further improvements.
- A group of relatively shallow convolutional networks is proposed based on our new understanding. Some of them achieve the state-of-the-art results on the ImageNet classification datase.
- The impact of using different networks is evaluated on the performance of semantic image segmentation, and these networks, as pre-trained features, can boost existing algorithms a lot.
SUMMARY
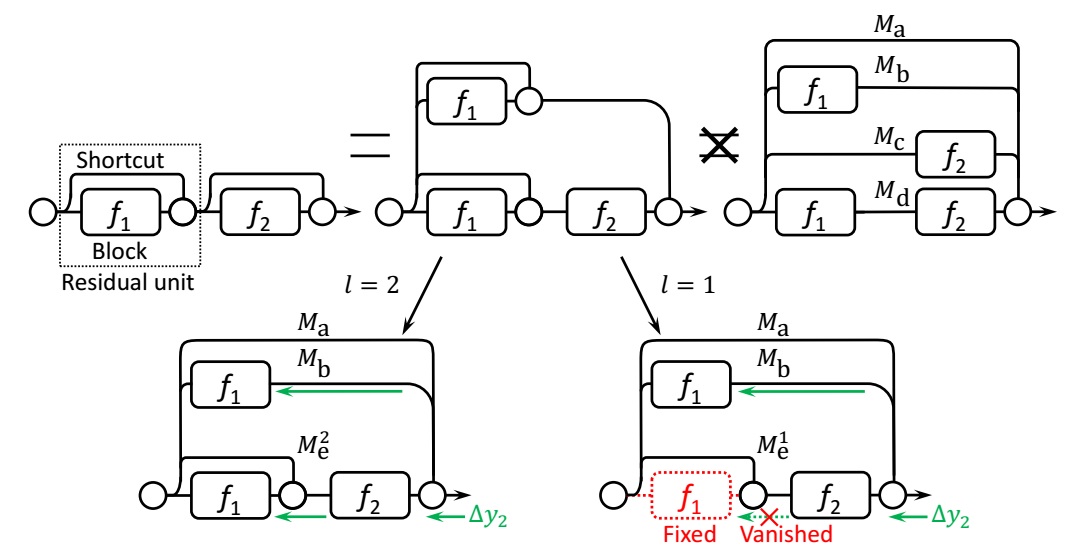
For the residual unit i , let yi−1 be the input, and let fi(⋅) be its trainable non-linear mappings, also named Blok i . The output of unit i is recursively defined as
where ωi denotes the trainalbe parameters, and fi(⋅) is often two or three stacked convolution stages in a ResNet building block. Then top left network can be formulated as
Thus, in SGD iteration, the backward gradients are:
Ideally, when effective depth l≥2 , both terms of Δω1 are non-zeros as the bottom-left case illustrated. However, when effective depth l=1 , the second term goes to zeros, which is illustrated by the bottom-right case. If this case happens, we say that the ResNet is over-deepened, and that it cannot be trained in a fully end-to-end manner, even with those shortcut connections.
To summarize, shortcut connections enable us to train wider and deeper networks. As they growing to some point, we will face the dilemma between width and depth. From that point, going deep, we will actually get a wider network, with extra features which are not completely end-to-end trained; going wider, we will literally get a wider network, without changing its end-to-end characteristic.
The author designed three kinds of network structure as illustrated in the following figure
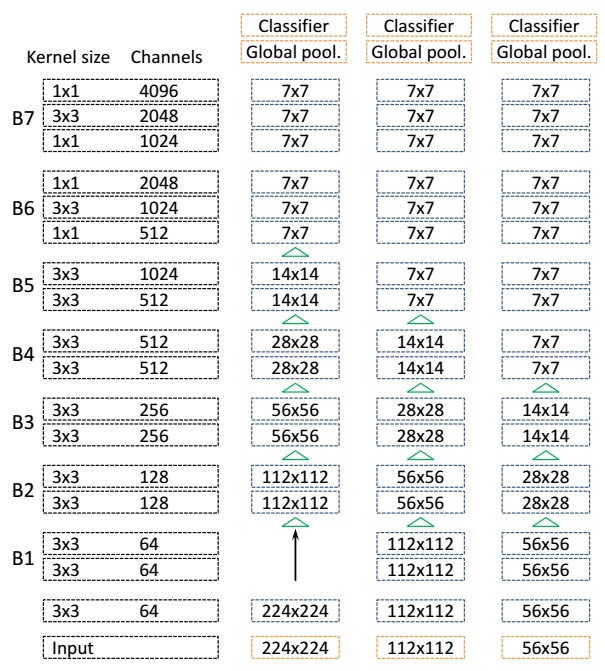
and the classification performance on ImageNet validation set is shown as below

























 616
616

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








