搭建TCP服务端、客户端
TCP基础介绍
TCP协议(Transmission Control Protocol)是一个安全、可靠、稳定、有序的数据报传输协议。如果说网络层(通过ip地址)解决了主机识别的问题,那么TCP协议则是(通过端口号)解决了如何识别主机上唯一一个进程的问题。
TCP还定义数据报的请求序号和确认序号,以确保消息的准确有序。
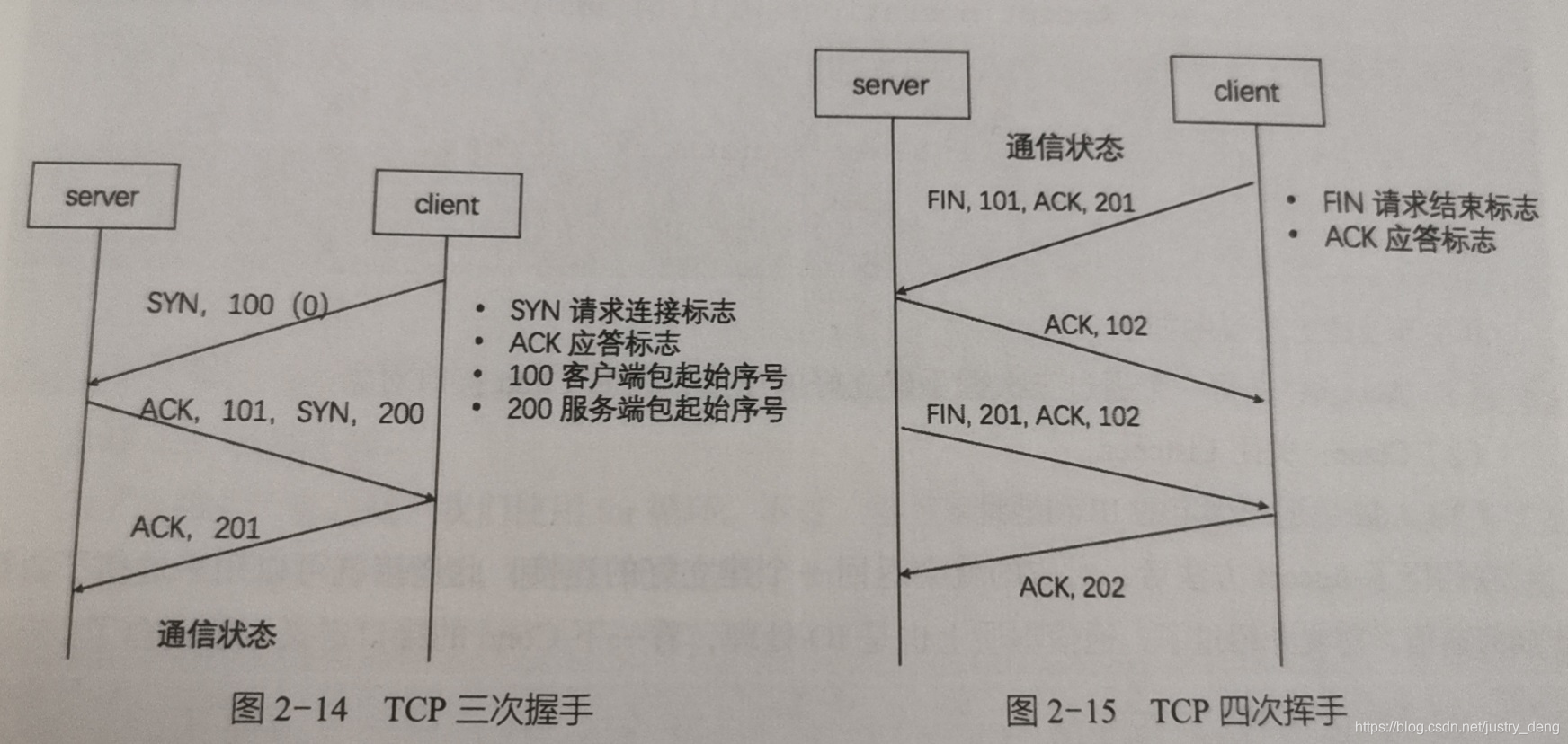
TCP通过三次握手、四次挥手,保障传输的安全性。
服务端Listen函数
Listen函数:
func Listen(network, address string) (Listener, error)
network:网络类型,可以填写tcp或udp。
address:设定服务器地址,格式为[ip]:端口,ip可以省略,缺省默认值为0.0.0.0
error:返回nil代表无错误,否者存在错误
Listener:监听者对象,用于后续的步骤处理
Listener:// A Listener is a generic network listener for stream-oriented protocols. // // Multiple goroutines may invoke methods on a Listener simultaneously. type Listener interface { // Accept waits for and returns the next connection to the listener. Accept() (Conn, error) // Close closes the listener. // Any blocked Accept operations will be unblocked and return errors. Close() error // Addr returns the listener's network address. Addr() Addr }
Listener#Accept返回的Conn:// Conn is a generic stream-oriented network connection. // // Multiple goroutines may invoke methods on a Conn simultaneously. type Conn interface { // Read reads data from the connection. // Read can be made to time out and return an error after a fixed // time limit; see SetDeadline and SetReadDeadline. Read(b []byte) (n int, err error) // Write writes data to the connection. // Write can be made to time out and return an error after a fixed // time limit; see SetDeadline and SetWriteDeadline. Write(b []byte) (n int, err error) // Close closes the connection. // Any blocked Read or Write operations will be unblocked and return errors. Close() error // LocalAddr returns the local network address. LocalAddr() Addr // RemoteAddr returns the remote network address. RemoteAddr() Addr // SetDeadline sets the read and write deadlines associated // with the connection. It is equivalent to calling both // SetReadDeadline and SetWriteDeadline. // // A deadline is an absolute time after which I/O operations // fail instead of blocking. The deadline applies to all future // and pending I/O, not just the immediately following call to // Read or Write. After a deadline has been exceeded, the // connection can be refreshed by setting a deadline in the future. // // If the deadline is exceeded a call to Read or Write or to other // I/O methods will return an error that wraps os.ErrDeadlineExceeded. // This can be tested using errors.Is(err, os.ErrDeadlineExceeded). // The error's Timeout method will return true, but note that there // are other possible errors for which the Timeout method will // return true even if the deadline has not been exceeded. // // An idle timeout can be implemented by repeatedly extending // the deadline after successful Read or Write calls. // // A zero value for t means I/O operations will not time out. SetDeadline(t time.Time) error // SetReadDeadline sets the deadline for future Read calls // and any currently-blocked Read call. // A zero value for t means Read will not time out. SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error // SetWriteDeadline sets the deadline for future Write calls // and any currently-blocked Write call. // Even if write times out, it may return n > 0, indicating that // some of the data was successfully written. // A zero value for t means Write will not time out. SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error }
客户端Dial函数
Dial函数:
func Dial(network, address string) (Conn, error)
network:网络类型,可以填写tcp或udp。
address:设定服务器地址,格式为[ip]:端口,ip可以省略,缺省默认值为0.0.0.0
error:返回nil代表无错误,否者存在错误
Conn:和服务端通信的连接对象。注:
Conn对象的具体信息上文已经给出,这里不再赘述。
搭建TCP服务端、客户端示例
- TCP服务端
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
)
func main() {
// 1. 绑定ip和端口,设置监听
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:8888")
if err != nil {
log.Panic("Failed to Listen", err)
}
// 延迟关闭,释放资源
defer listener.Close()
// 2. 循环等待新连接
for {
// 从连接列表获取新连接
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Failed to Accept", err)
}
// 3. 与新连接通信(为了不同步阻塞,这里开启异步协程进行函数调用)
go handle_conn(conn)
}
}
/**
* 处理连接
*/
func handle_conn(conn net.Conn) {
defer conn.Close()
fmt.Println("New connection ", conn.RemoteAddr())
// 通信
buf := make([]byte, 256)
for {
// 从网络中读
readBytesCount, err := conn.Read(buf)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Failed to read", err)
break
}
// 提示:buf[:n]的效果为:读取buf[总长度-n]至buf[n]处的字节
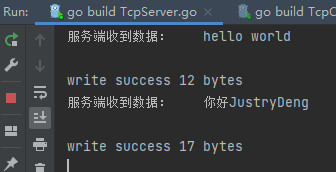
fmt.Println("服务端收到数据:\t", string(buf[:readBytesCount]))
// 写回网络 -- 收到什么就写回什么,即:回射服务器
writeByteCount, err := conn.Write(buf[:readBytesCount])
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Failed to write", err)
break
}
fmt.Printf("write success %d bytes\n", writeByteCount)
}
}
- TCP客户端
import (
"fmt"
"net"
"os"
)
func main() {
// 1. 建立连接
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", "localhost:8888")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Failed to Dial")
return
}
// 延迟关闭,释放资源
defer conn.Close()
// 2. 与服务端通信
buf := make([]byte, 256)
for {
// 2.1 从控制台读取输入
readBytesCount, _ := os.Stdin.Read(buf)
// 2.2 写到网络(即:发送请求)
conn.Write(buf[:readBytesCount])
// 2.3 读网络(即:获取响应)
readBytesCount, _ = conn.Read(buf)
// 2.4 输出到控制台
// 提示:buf[:n]的效果为:读取buf[总长度-n]至buf[n]处的字节
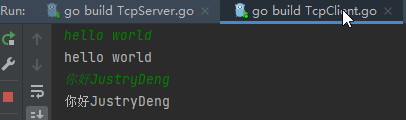
os.Stdout.Write(buf[:readBytesCount])
}
}
- 通信测试
先启动server端,再启动client端,然后在client端的控制台进行任意输入触发进行TCP请求,
- 在server端控制台,可看到来自client的请求信息
- 在client端控制台,可看到来自server端的响应信息
^_^ 整理自《Go语言区块链应用开发从入门到精通》高野 编著
^_^ 本文已经被收录进《程序员成长笔记》 ,笔者JustryDeng




















 452
452











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








