单链表经典题目+解答,从简到易
单链表面试题 + 画图分析 + 源代码
1.移除链表元素
移除链表元素。 OJ链接
画图分析
本题提供两种思路
第一种思路:
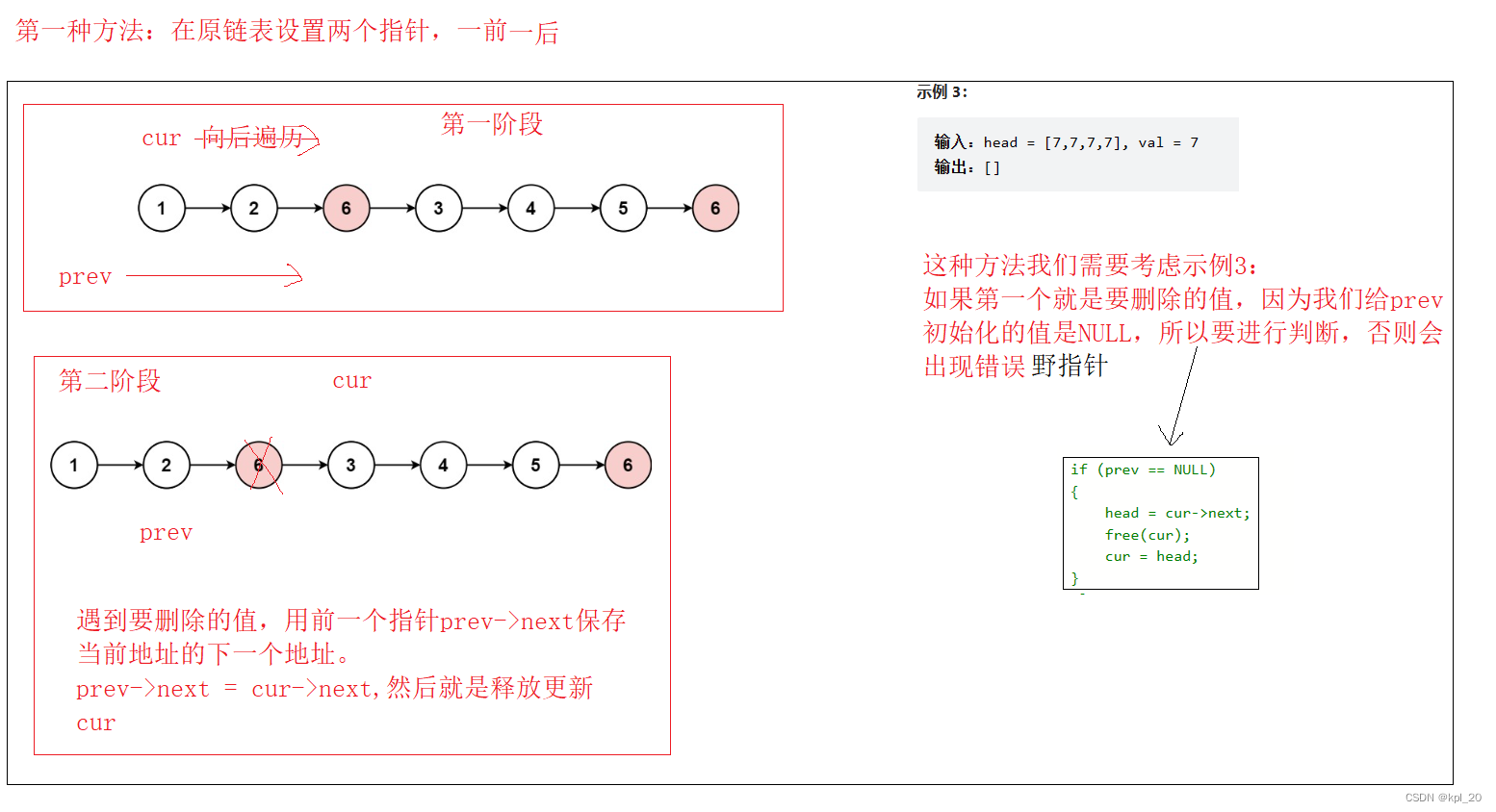
第二种思路:
源代码
第一种思路
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val != val)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
//解决prev为空的情况
if (prev == NULL)
{
head = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = head;
}
else
{
//常规移除链表元素操作
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
cur = prev->next;
}
}
}
return head;
}
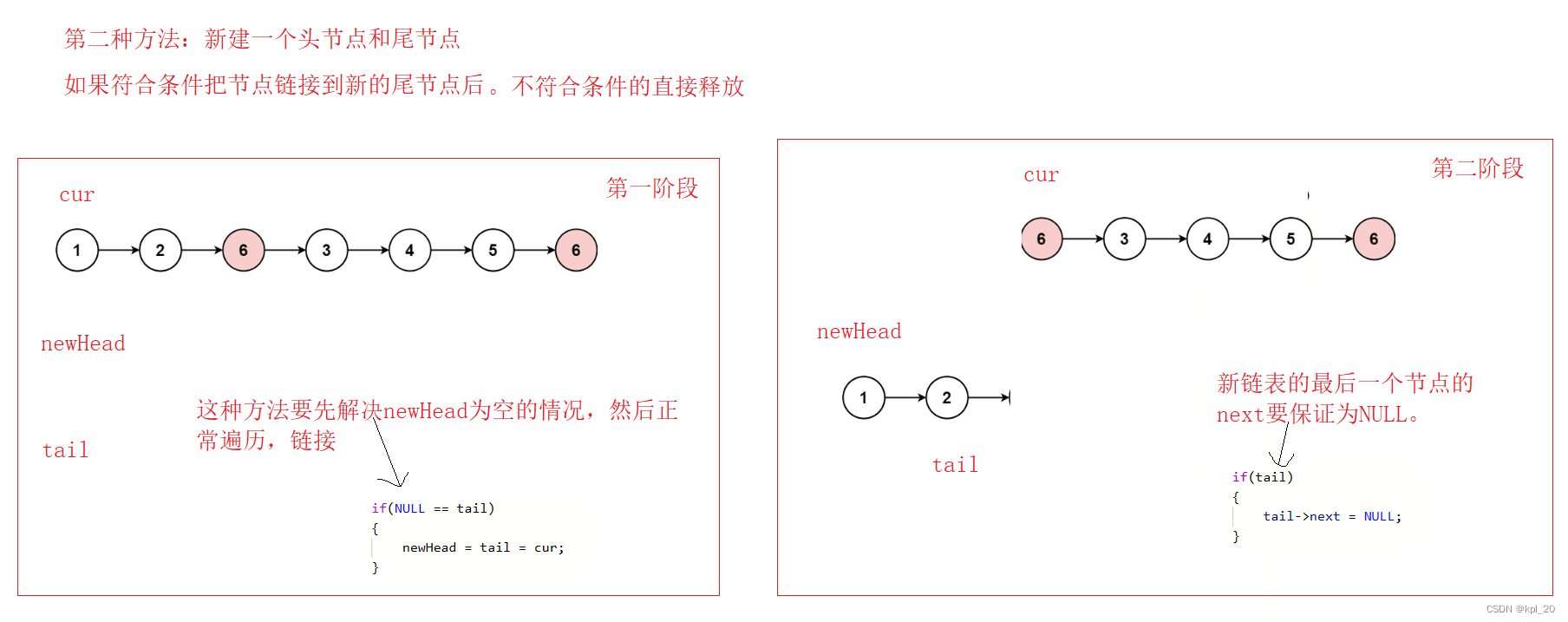
第二种思路:
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
//建立新链表的头节点和尾节点
struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
//用cur循环,以防后期用到head
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
if(cur->val != val)
{
//解决新节点为空的情况
if(NULL == tail)
{
newHead = tail = cur;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur;
tail = tail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
//释放需要移除的节点,防止内存泄漏
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
}
//把最后一个节点的next置空
if(tail)
{
tail->next = NULL;
}
return newHead;
}
2.反转链表
反转链表。OJ链接
画图分析
本题也有两个思路解答,数据结构的特性使其很灵活,所以解题思路也很灵活。本题我会把两种解题思路都介绍一下,选一种详细介绍,另一种介绍一下思路。
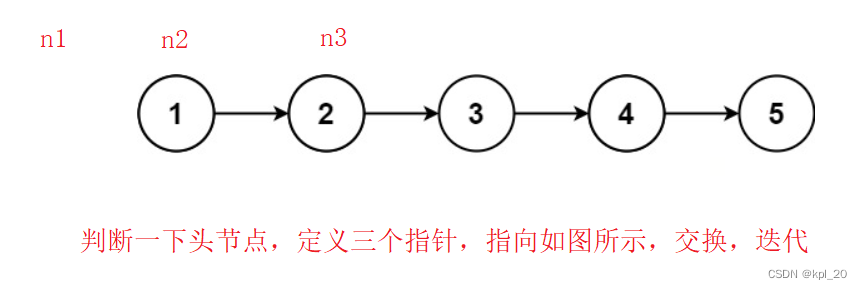
第一种思路:
就是在原链表上反转。再判断一下为空的情况
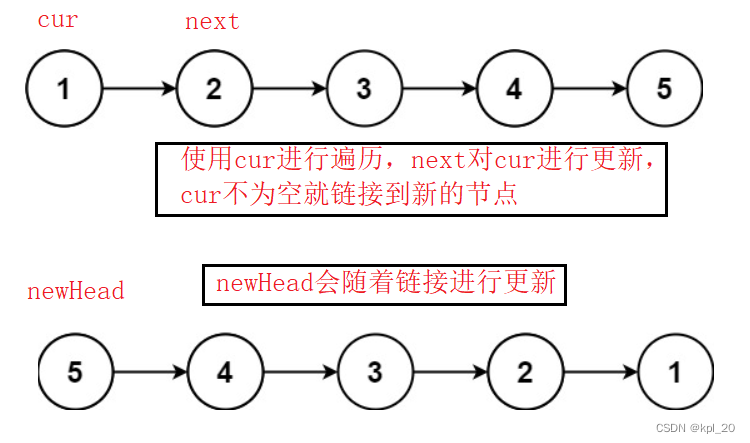
第二种思路:
建立一个新的节点newHead进行链接
源代码
第一种思路
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* n1 = NULL;
struct ListNode* n2 = head;
struct ListNode* n3 = head->next;
while (n2)
{
//reverse
n2->next = n1;
//迭代
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if (n3)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
第二种思路
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
//建立新的头节点
struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;
//建立新的节点,进行循环
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
//保存当前节点的下一个节点,用来更新
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
//返回新的头节点
return newHead;
}
3.链表的中间结点
链表的中间结点。OJ链接
画图分析
快慢指针:
本题的解题思路是建立两个指针(快慢指针),最开始都指向头节点,然后两个指针向后移动,一个指针一次移动一个位置,一个指针一次移动两个位置。当然我们还要考虑链表元素个数的奇偶性。
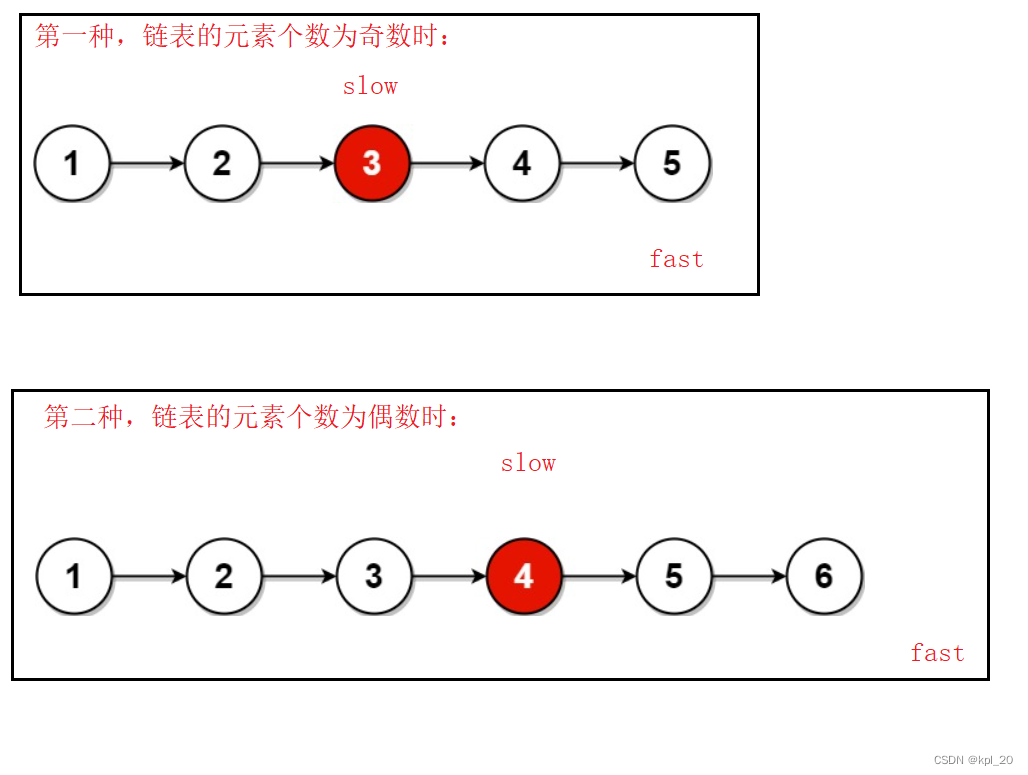
源代码
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
//慢指针
struct ListNode* slow = head;
//快指针
struct ListNode* fast = head;
//由上图分析,两种遍历结束情况,并在一起。
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//返回慢指针,慢指针就是指向链表的中间节点
return slow;
}
4.链表中倒数第k个结点
链表中倒数第k个结点。 OJ链接
画图分析
本题也是快慢指针只不过有稍微一些的变化。快指针先走k步,然后快指针和慢指针一起走。快指针结束的时候,慢指针就是我们所找的节点。
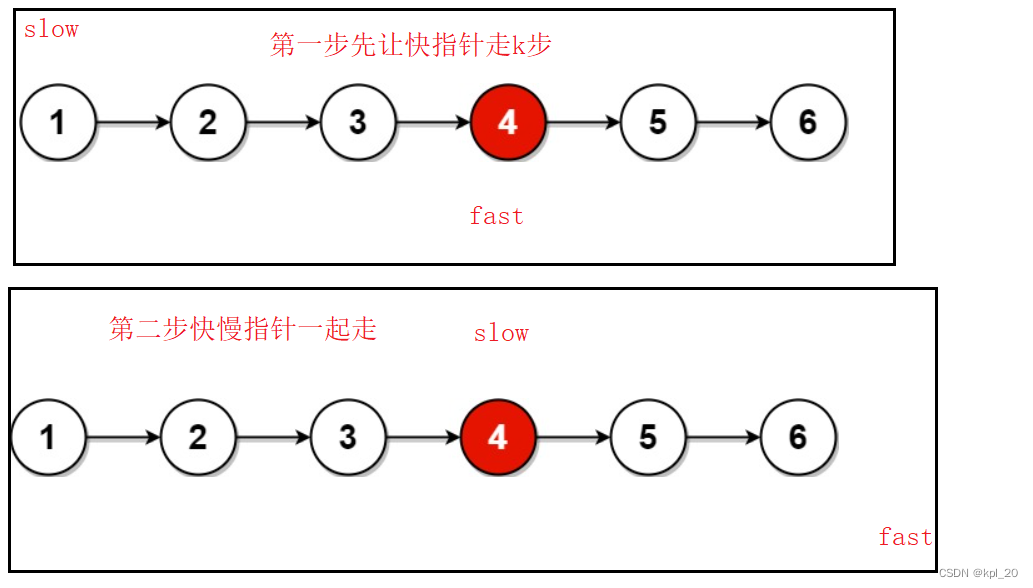
源代码
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{
// 建立快慢指针
struct ListNode* slow = pListHead;
struct ListNode* fast = pListHead;
//快指针先走k步
while (k--)
{
//判断一下,如果快指针还没走k步就为空,就代表链表找不到第k个节点,属于野指针
if(fast == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
fast = fast->next;
}
//快慢指针一起走
while (fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
5. 合并两个有序链表
合并两个有序链表。OJ链接
画图分析
本题可以定义一个哨兵位的头节点,这样可以不用再分析链表是否为空。
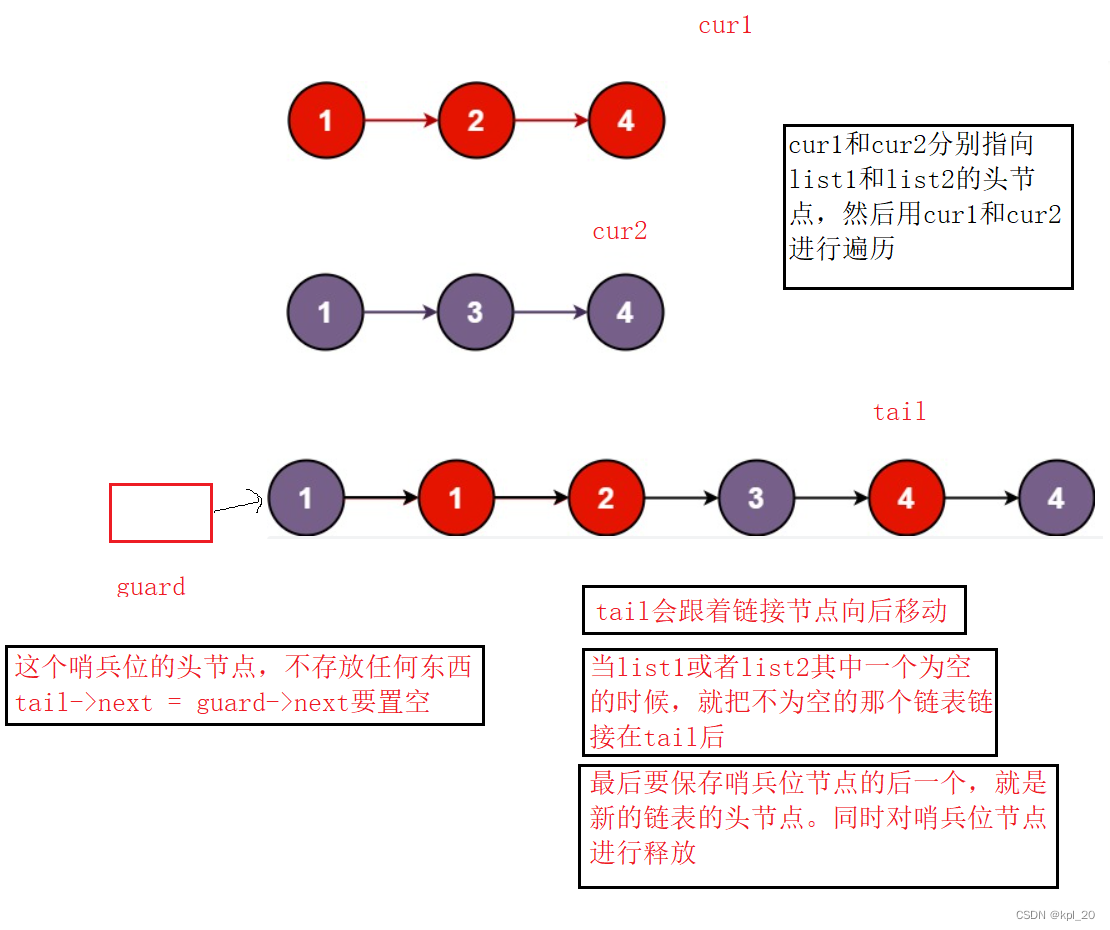
源代码
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
//定义合并后链表的哨兵位
struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* tail = guard;
//这里要对头节点置空
guard->next = NULL;
//定义两个链表的头节点,进行遍历
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2;
while (cur1 && cur2)
{
//符合条件就移动到新的链表tail后
if (cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
tail->next = cur1;
tail = tail->next;
cur1 =cur1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur2;
tail = tail->next;
cur2 =cur2->next;
}
}
//当cur1或者cur2某一链表为空的时候,把不为空的直接链接到tail后
if (cur1)
{
tail->next = cur1;
}
if(cur2)
{
tail->next = cur2;
}
//释放哨兵位节点
struct ListNode* next = guard->next;
free(guard);
guard =NULL;
//返回新链表的头节点
return next;
}
6. 链表分割
链表分割 。OJ链接
画图分析
本题的思路,需要建立两个链表,一个链表存放小于x的,另一个链表存放大于等于x的,完成以上操作,把存放小值的链表链接到存放大值链表的前面,同时要注意要对存放大值链表最后一个节点的next置空。
这里也使用哨兵位的头节点,建立两个哨兵位的头节点,分别指向两个链表。
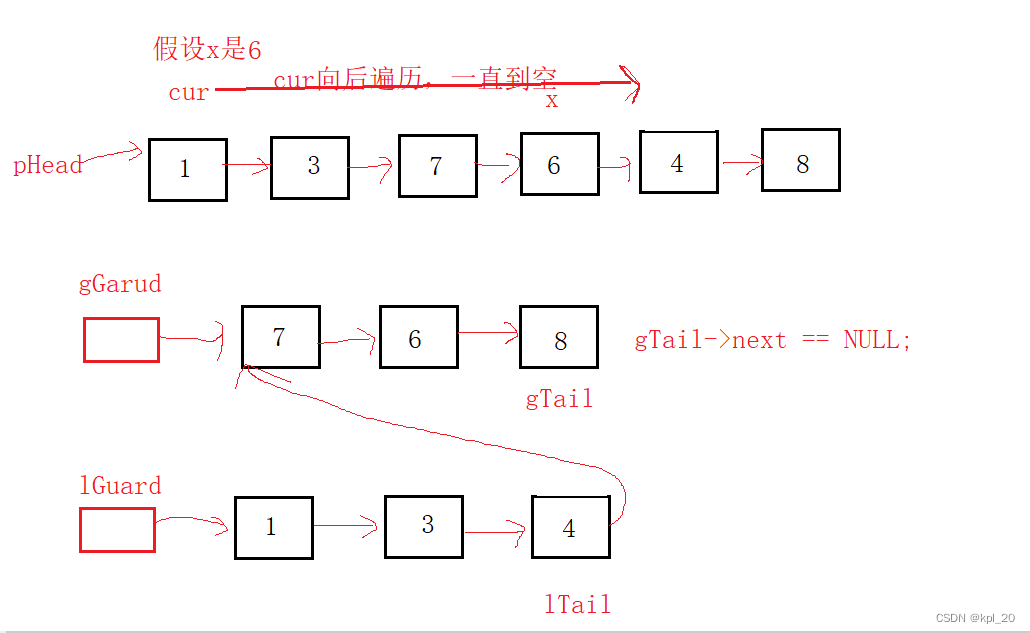
源代码
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
//建立存放大值链表的哨兵位节点
struct ListNode* gGarud;
//建立存放大值链表的哨兵位节点
struct ListNode* lGarud;
//与上面的哨兵位对应的链表尾节点
struct ListNode* gTail;
struct ListNode* lTail;
gGarud = gTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
lGarud = lTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
//对头节点置空
gTail->next = NULL;
lTail->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = pHead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val >= x)
{
gTail->next = cur;
gTail = gTail->next;
}
else
{
lTail->next = cur;
lTail = lTail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
//把存放小值的链表链接到存放大值链表的前面
lTail->next = gGarud->next;
//对大值链表的尾节点的next置空
gTail->next = NULL;
//把新的链表的头节点交给指针pHead维护
pHead = lGarud->next;
//释放
free(gGarud);
free(lGarud);
//返回分割后链表的头节点
return pHead;
}
7. 链表的回文结构
链表的回文结构。OJ链接
画图分析
本题的解题思路,借用了上面两个题目。寻找链表的中间节点。然后把链表的后一半逆置,这时对两个链表进行遍历比较。
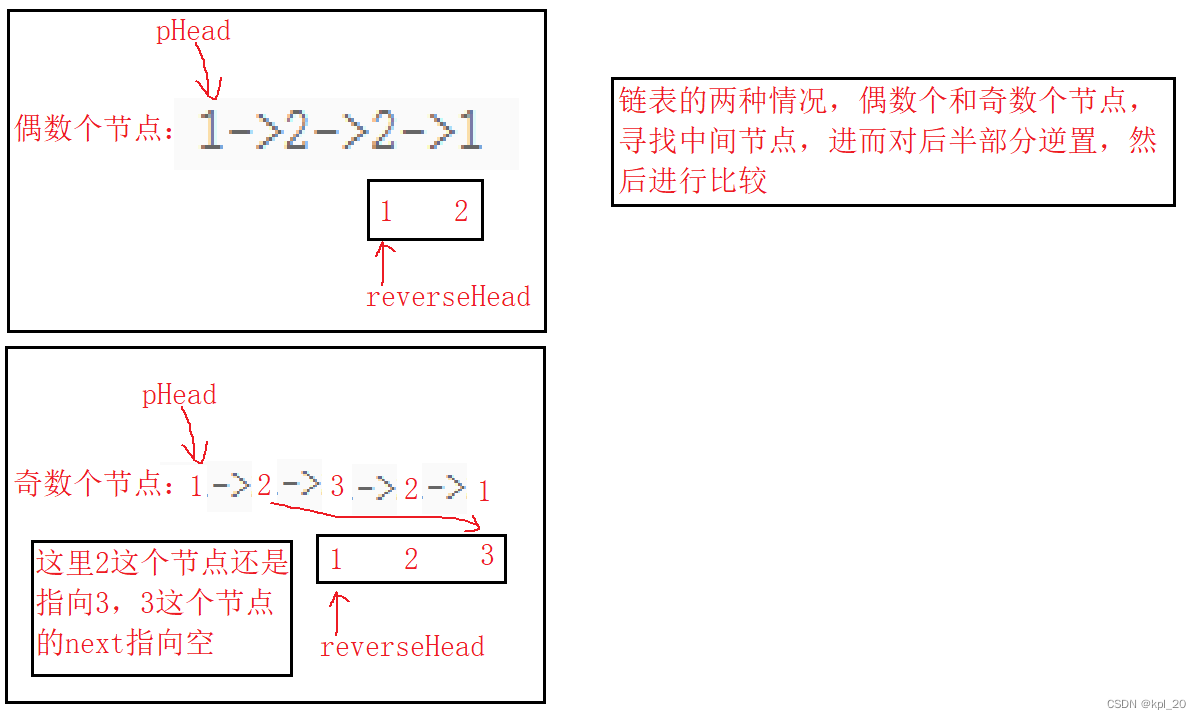
源代码
//寻找中间节点
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
//慢指针
struct ListNode* slow = head;
//快指针
struct ListNode* fast = head;
//由上图分析,两种遍历结束情况,并在一起。
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//返回慢指针,慢指针就是指向链表的中间节点
return slow;
}
//链表倒置
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
//建立新的头节点
struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;
//建立新的节点,进行循环
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
//保存当前节点的下一个节点,用来更新
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
//返回新的头节点
return newHead;
}
//判断是不是回文结构
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* pHead)
{
struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(pHead);
struct ListNode* reverseHead = reverseList(mid);
while (pHead)
{
if(pHead->val != reverseHead->val)
{
return false;
}
//更新递进
pHead = pHead->next;
reverseHead = reverseHead->next;
}
return true;
}
8. 相交链表
相交链表。OJ链接
画图分析
本题的思路,遍历两个链表,分别计算出两个链表的长度,让长的链表先走连个链表长度之差步。然后再一起向后遍历,当指针相同时,就是最初的相交点。如果遍历完都没有相同的,就是没有相交的节点。
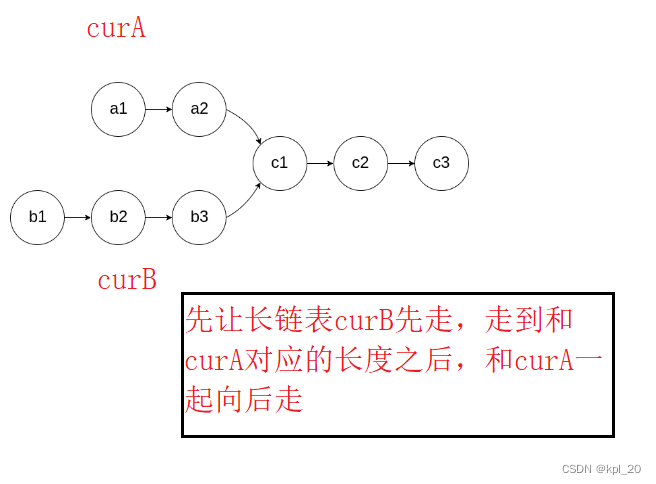
源代码
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
//分别重新定义两个头节点,因为后面还需要使用头节点,所以不能直接使用所给的头节点,以防找不到链表的头节点
struct ListNode* curA = headA;
struct ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
//分别进行循环,计算两个链表的长度
while (curA)
{
curA = curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while (curB)
{
curB = curB->next;
lenB++;
}
//判断,如果两个链表的尾指针不相等,也就意味着没有相交的地方,所以没必要向下执行,直接返回NULL
if (curA != curB)
{
return NULL;
}
//abs是表示绝对值的函数,在平常使用abs时,需要使用库函数<stdlib.h>
int absVal = abs(lenA - lenB);
//我们假设headA是短链表,headB是长链表
struct ListNode* shortList = headA;
struct ListNode* longList = headB;
//如果假设不成立,在这里面改一下
if (lenA > lenB)
{
longList = headA;
shortList = headB;
}
//让长链表先走absVal步
while (absVal--)
{
longList = longList->next;
}
//寻找两个链表相等的时候,那个指针就是所找的相交节点
while(longList != shortList)
{
longList = longList->next;
shortList = shortList->next;
}
//这里返回长短链表都行
return shortList;
}
总结
多做多思考,多进行调试,帮助自己努力提高,不能对照着写,建议看看思路,然后自己写,出错进行调试,写出来之后可以对照一下,有没有需要改进的地方。






















 1549
1549











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










