输入设备一般包括键盘,鼠标,触摸屏等,在内核中都是以输入设备出现的。
下面分析input输入子系统的结构,以及功能实现。
一. Input子系统结构与功能实现
(1)其中硬件驱动层负责操作具体的硬件设备,这层的代码是针对具体的驱动程序的,需要驱动程序的作者来编写。
(2)子系统核心层是链接其他两个层之间的纽带与桥梁,向下提供驱动层的接口,向上提供事件处理层的接口。
(3)事件处理层负责与用户程序打交道,将硬件驱动层传来的事件报告给用户程序。
事件有三种属性:类型(type),编码(code),值(value).
Input子系统支持的所有事件都定义在input.h中,包括所有支持的类型,所属类型支持的编码等。
事件传送的方向是 硬件驱动层-->子系统核心-->事件处理层-->用户空间
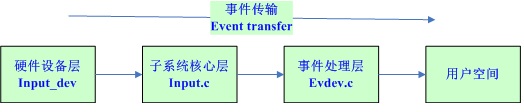
注:mini2440的触摸屏驱动所用驱动层对应的模块文件为:s3c2410_ts.c,事件处理层对应的模块文件为 evdev.c
(1)s3c2410_ts模块初始化函数中将触摸屏注册到了输入子系统中,于此同时,注册函数在事件处理层链表中寻找事件处理器,这里找到的是evdev,并且将驱动与事件处理 器挂载。
并且在/dev/input中生成设备文件event0,以后我们访问这个文件就会找的我们的触摸屏驱动程序。
(2)应用程序打开设备文件/dev/input/event0,读取设备文件,调用evdev模块中read,如果没有事件进程就会睡眠。
(3)当触摸屏按下,驱动层通过子系统核心将事件(就是X,Y坐标),传给事件处理层也就是evdev,evdev唤醒睡眠的进程,将事件传给进程处理。
二.主要input通用数据结构
1.input_dev
这是input设备基本的设备结构,每个input驱动程序中都必须分配初始化这样一个结构,成员比较多
(1)有以下几个数组:
/**
* struct input_dev - represents an input device
* @name: name of the device
* @phys: physical path to the device in the system hierarchy
* @uniq: unique identification code for the device (if device has it)
* @id: id of the device (struct input_id)
* @evbit: bitmap of types of events supported by the device (EV_KEY,
* EV_REL, etc.)
* @keybit: bitmap of keys/buttons this device has
* @relbit: bitmap of relative axes for the device
* @absbit: bitmap of absolute axes for the device
* @mscbit: bitmap of miscellaneous events supported by the device
* @ledbit: bitmap of leds present on the device
* @sndbit: bitmap of sound effects supported by the device
* @ffbit: bitmap of force feedback effects supported by the device
* @swbit: bitmap of switches present on the device
* @keycodemax: size of keycode table
* @keycodesize: size of elements in keycode table
* @keycode: map of scancodes to keycodes for this device
* @setkeycode: optional method to alter current keymap, used to implement
* sparse keymaps. If not supplied default mechanism will be used.
* The method is being called while holding event_lock and thus must
* not sleep
* @getkeycode: optional method to retrieve current keymap. If not supplied
* default mechanism will be used. The method is being called while
* holding event_lock and thus must not sleep
* @ff: force feedback structure associated with the device if device
* supports force feedback effects
* @repeat_key: stores key code of the last key pressed; used to implement
* software autorepeat
* @timer: timer for software autorepeat
* @sync: set to 1 when there were no new events since last EV_SYNC
* @abs: current values for reports from absolute axes
* @rep: current values for autorepeat parameters (delay, rate)
* @key: reflects current state of device's keys/buttons
* @led: reflects current state of device's LEDs
* @snd: reflects current state of sound effects
* @sw: reflects current state of device's switches
* @absmax: maximum values for events coming from absolute axes
* @absmin: minimum values for events coming from absolute axes
* @absfuzz: describes noisiness for axes
* @absflat: size of the center flat position (used by joydev)
* @absres: resolution used for events coming form absolute axes
* @open: this method is called when the very first user calls
* input_open_device(). The driver must prepare the device
* to start generating events (start polling thread,
* request an IRQ, submit URB, etc.)
* @close: this method is called when the very last user calls
* input_close_device().
* @flush: purges the device. Most commonly used to get rid of force
* feedback effects loaded into the device when disconnecting
* from it
* @event: event handler for events sent _to_ the device, like EV_LED
* or EV_SND. The device is expected to carry out the requested
* action (turn on a LED, play sound, etc.) The call is protected
* by @event_lock and must not sleep
* @grab: input handle that currently has the device grabbed (via
* EVIOCGRAB ioctl). When a handle grabs a device it becomes sole
* recipient for all input events coming from the device
* @event_lock: this spinlock is is taken when input core receives
* and processes a new event for the device (in input_event()).
* Code that accesses and/or modifies parameters of a device
* (such as keymap or absmin, absmax, absfuzz, etc.) after device
* has been registered with input core must take this lock.
* @mutex: serializes calls to open(), close() and flush() methods
* @users: stores number of users (input handlers) that opened this
* device. It is used by input_open_device() and input_close_device()
* to make sure that dev->open() is only called when the first
* user opens device and dev->close() is called when the very
* last user closes the device
* @going_away: marks devices that are in a middle of unregistering and
* causes input_open_device*() fail with -ENODEV.
* @dev: driver model's view of this device
* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the device. When
* accessing the list dev->mutex must be held
* @node: used to place the device onto input_dev_list
*/
struct input_dev {
const char *name;
const char *phys;
const char *uniq;
struct input_id id;
unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)];
unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)];
unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)];
unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)];
unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)];
unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
unsigned int keycodemax;
unsigned int keycodesize;
void *keycode;
int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int scancode, unsigned int keycode);
int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int scancode, unsigned int *keycode);
struct ff_device *ff;
unsigned int repeat_key;
struct timer_list timer;
int sync;
int abs[ABS_CNT];
int rep[REP_MAX + 1];
unsigned long key[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long led[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long snd[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long sw[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
int absmax[ABS_CNT];
int absmin[ABS_CNT];
int absfuzz[ABS_CNT];
int absflat[ABS_CNT];
int absres[ABS_CNT];
int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev);
void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev);
int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file);
int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
struct input_handle *grab;
spinlock_t event_lock;
struct mutex mutex;
unsigned int users;
bool going_away;
struct device dev;
struct list_head h_list;
struct list_head node;
};
#define to_input_dev(d) container_of(d, struct input_dev, dev) evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)]; 这个数组以位掩码的形式,代表了这个设备支持的事件的类型。设置方式如:
dev->evbit[0] = BIT(EV_SYN) | BIT(EV_KEY) | BIT(EV_ABS)
absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)]; 这个数组也是以位掩码的形式,代表这个类型的事件支持的编码
触摸屏驱动支持EV_ABS,所以要设置这个数组, 有一个专门设置这个数组的函数input_set_abs_params,代码如下:
static inline void input_set_abs_params(struct input_dev *dev, int axis, int min, int max, int fuzz, int flat)
{
dev->absmin[axis] = min;
dev->absmax[axis] = max;
dev->absfuzz[axis] = fuzz;
dev->absflat[axis] = flat;
dev->absbit[BIT_WORD(axis)] |= BIT_MASK(axis); //填充了absbit这个数组
}触摸屏驱动中是这样调用的
input_set_abs_params(dev, ABS_X, 0, 0x3FF, 0, 0); //这个是设置ad转换的x坐标
input_set_abs_params(dev, ABS_Y, 0, 0x3FF, 0, 0); //这个是设置ad转换的y坐标
input_set_abs_params(dev, ABS_PRESSURE, 0, 1, 0, 0); //这个是设置触摸屏是否按下的标志
设置ABS_X编码值范围为0-0x3ff,因为mini2440的AD转换出的数据最大为10位,所以不会超过0x3ff。
(2) struct input_id id 成员
这个是标识设备驱动特征的
/*
* IOCTLs (0x00 - 0x7f)
*/
struct input_id {
__u16 bustype;
__u16 vendor;
__u16 product;
__u16 version;
};也无关紧要。
(3) 还有其他一些成员,也比较重要,但是驱动程序可以不用管,都是由子系统核心来处理的。
(4) 可以看出input_dev 结构所属层为硬件驱动层,以后就用input_dev来表示输入设备。
2. input_handler
这是事件处理器的数据结构,代表一个事件处理器:
/**
* struct input_handler - implements one of interfaces for input devices
* @private: driver-specific data
* @event: event handler. This method is being called by input core with
* interrupts disabled and dev->event_lock spinlock held and so
* it may not sleep
* @filter: similar to @event; separates normal event handlers from
* "filters".
* @match: called after comparing device's id with handler's id_table
* to perform fine-grained matching between device and handler
* @connect: called when attaching a handler to an input device
* @disconnect: disconnects a handler from input device
* @start: starts handler for given handle. This function is called by
* input core right after connect() method and also when a process
* that "grabbed" a device releases it
* @fops: file operations this driver implements
* @minor: beginning of range of 32 minors for devices this driver
* can provide
* @name: name of the handler, to be shown in /proc/bus/input/handlers
* @id_table: pointer to a table of input_device_ids this driver can
* handle
* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the handler
* @node: for placing the driver onto input_handler_list
*
* Input handlers attach to input devices and create input handles. There
* are likely several handlers attached to any given input device at the
* same time. All of them will get their copy of input event generated by
* the device.
*
* The very same structure is used to implement input filters. Input core
* allows filters to run first and will not pass event to regular handlers
* if any of the filters indicate that the event should be filtered (by
* returning %true from their filter() method).
*
* Note that input core serializes calls to connect() and disconnect()
* methods.
*/
struct input_handler {
void *private;
void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev);
int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);
void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);
void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);
const struct file_operations *fops;
int minor;
const char *name;
const struct input_device_id *id_table;
struct list_head h_list;
struct list_head node;
};(1)几个操作函数
void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);
void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);
void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);connect 函数是当一个input设备模块注册到内核的时候调用的,将事件处理器与输入设备联系起来的函数,也就是将input_dev和input_handler配对的函数。
disconnect 函数实现connect相反的功能。
start 暂时没有发现有什么作用。
(2) 两个id
const struct input_device_id *id_table; //这个是事件处理器所支持的input设备
const struct input_device_id *blacklist; //这个是事件处理器应该忽略的input设备(3) 两个链表
struct list_headh_list; //这个链表用来链接他所支持的input_handle结构,input_dev与input_handler配对之后就会生成一个input_handle结构
struct list_headnode; //链接到input_handler_list,这个链表链接了所有注册到内核的事件处理器3. input_handle : 代表一个成功配对的input_dev和input_handler.
/**
* struct input_handle - links input device with an input handler
* @private: handler-specific data
* @open: counter showing whether the handle is 'open', i.e. should deliver
* events from its device
* @name: name given to the handle by handler that created it
* @dev: input device the handle is attached to
* @handler: handler that works with the device through this handle
* @d_node: used to put the handle on device's list of attached handles
* @h_node: used to put the handle on handler's list of handles from which
* it gets events
*/
struct input_handle {
void *private; //每个配对的事件处理器都会分配一个对应的设备结构,如evdev事件处理器的evdev结构,注意这个结构与设备驱动层的input_dev不同,初始化handle时,保存到这里。
int open; //打开标志,每个input_handle 打开后才能操作,这个一般通过事件处理器的open方法间接设置
const char *name;
struct input_dev *dev; //关联的input_dev结构
struct input_handler *handler; //关联的input_handler结构
struct list_head d_node; //input_handle通过d_node连接到了input_dev上的h_list链表上
struct list_head h_node; //input_handle通过h_node连接到了input_handler的h_list链表上
};input_dev 是硬件驱动层,代表一个input设备
input_handler 是事件处理层,代表一个事件处理器
input_handle 个人认为属于核心层,代表一个配对的input设备与input事件处理器
input_dev 通过全局的input_dev_list链接在一起。设备注册的时候实现这个操作。
input_handler 通过全局的input_handler_list链接在一起。事件处理器注册的时候实现这个操作(事件处理器一般内核自带,一般不需要我们来写)
input_handle 没有一个全局的链表,它注册的时候将自己分别挂在了input_dev 和 input_handler 的h_list上了。通过input_dev 和input_handler就可以找到input_handle 在设备注册和事件处理器, 注册的时候都要进行配对工作,配对后就会实现链接。通过input_handle也可以找到input_dev和input_handler。






















 570
570











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








