init.rc的构成
在系统启动时,内核启动完成后会去启动init程序,在init中会去解析init.rc文件。
/* ---system/core/init/init.c--- */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//将init.rc中的东西都解析出来
init_parse_config_file("/init.rc");
}而init.rc文件主要包括三种类型的东东,代码中取名叫section:
import
顾名思义,就是去import其他的init.rc文件。
import /init.usb.rcservice
init.rc文件中占半壁江山的东东,都是些native的service,因为这时候还未到android启动的时候,首先能启动的是一些核心的native service。但是单纯的service自己并不会启动,这里的service只是描述了service的构成。
#service后面跟着service名字 native应用程序bin文件 有些service还有一些启动参数
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
class core
user system
group system
critical
onrestart restart healthd
onrestart restart zygote
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart surfaceflinger
onrestart restart drm在service下面,我们能看到很多类似service的属性的东东,下面是service的结构体定义,解析init.rc其实很多时候就是在填充这个service结构体。
struct service {
/* list of all services */
struct listnode slist;
//service名字
const char *name;
//service属于哪个类,例如class core,属于core这个class,后续init后去启动所有class为core的service
const char *classname;
unsigned flags;
pid_t pid;
//service启动的时间,崩的时间,次数,有些service是critial,如果崩的次数多余4次android就会
//重启进入recovery
time_t time_started; /* time of last start */
time_t time_crashed; /* first crash within inspection window */
int nr_crashed; /* number of times crashed within window */
uid_t uid;
gid_t gid;
gid_t supp_gids[NR_SVC_SUPP_GIDS];
size_t nr_supp_gids;
char *seclabel;
//service下面的socket
struct socketinfo *sockets;
struct svcenvinfo *envvars;
//如果service崩了,下次重启的时候,还要干啥?启动其他的相关service什么的
struct action onrestart; /* Actions to execute on restart. */
/* keycodes for triggering this service via /dev/keychord */
int *keycodes;
int nkeycodes;
int keychord_id;
int ioprio_class;
int ioprio_pri;
//service启动的时候,有可能有启动参数
int nargs;
/* "MUST BE AT THE END OF THE STRUCT" */
char *args[1];
}; /* ^-------'args' MUST be at the end of this struct! */on
on在代码中取名为action,上面的service只是描述了一个service的构成,并不会自己启动service,即执行这些native的应用程序。那么这些程序由谁触发去执行呢?就是on。
init.rc中的另半壁江山就是on这个section,每一个on下面又包含了很多类似linux命令的东东,init中将其称为command。
on early-init
# Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
write /proc/1/oom_score_adj -1000
# Apply strict SELinux checking of PROT_EXEC on mmap/mprotect calls.
write /sys/fs/selinux/checkreqprot 0
# Set the security context for the init process.
# This should occur before anything else (e.g. ueventd) is started.
setcon u:r:init:s0
# Set the security context of /adb_keys if present.
restorecon /adb_keys
#启动ueventd这个service
start ueventd
# Configuration for namespaces support
mkdir /var 0770 root system
mount tmpfs none /var mode=0770,uid=0,gid=1000
mkdir /var/run 0750 root system
mkdir /var/run/netns 0700 root root
# create mountpoints
mkdir /mnt 0775 root system首先,我们看上面这个on,其名字为early-init。on在init中用结构体action表示,读取init.rc中的on时就是对该结构体的填充。
struct action {
/* node in list of all actions */
struct listnode alist;
/* node in the queue of pending actions */
struct listnode qlist;
/* node in list of actions for a trigger */
struct listnode tlist;
unsigned hash;
//action的名字
const char *name;
//action下面有很多的命令,其实都是类似linux的命令,必须去执行,mkdir start什么的
struct listnode commands;
struct command *current;
};on下面的每条命令用command结构体表示,
struct command
{
/* list of commands in an action */
struct listnode clist;
//命令函数
int (*func)(int nargs, char **args);
// 函数参数
int nargs;
char *args[1];
};继续看early-init这个action,init将mkdir这些command都保存在action的commands双向链表中,而这些命令中有类似start ueventd这样的启动上面service的命令。
就像early-init名字写的那样,android在启动的过程中,是个顺序的过程,有些命令需要先启动执行,有些需要后启动,例如early-init,init,late-init。
在init.rc中还有另外一类action,它属于属性触发的,例如,
on property:vold.decrypt=trigger_restart_framework
class_start main
class_start late_start当vold.decrypt这个属性值,变为trigger_restart_framework时,去执行on下面的command,这里的command是class_start,前面在介绍service的时候,service有class这个属性值,这句话的意思执行所有的class为main的service。当然也可以不用去启动一类class,也可以用start去启动某个service。
init.rc的读取
利用init_parse_config_file函数完成对init.rc相关文件的读取,
/* ---system/core/init/init.c--- */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//将init.rc中的东西都解析出来
init_parse_config_file("/init.rc");
}读取时,init将init.rc按照下面的方式组织:
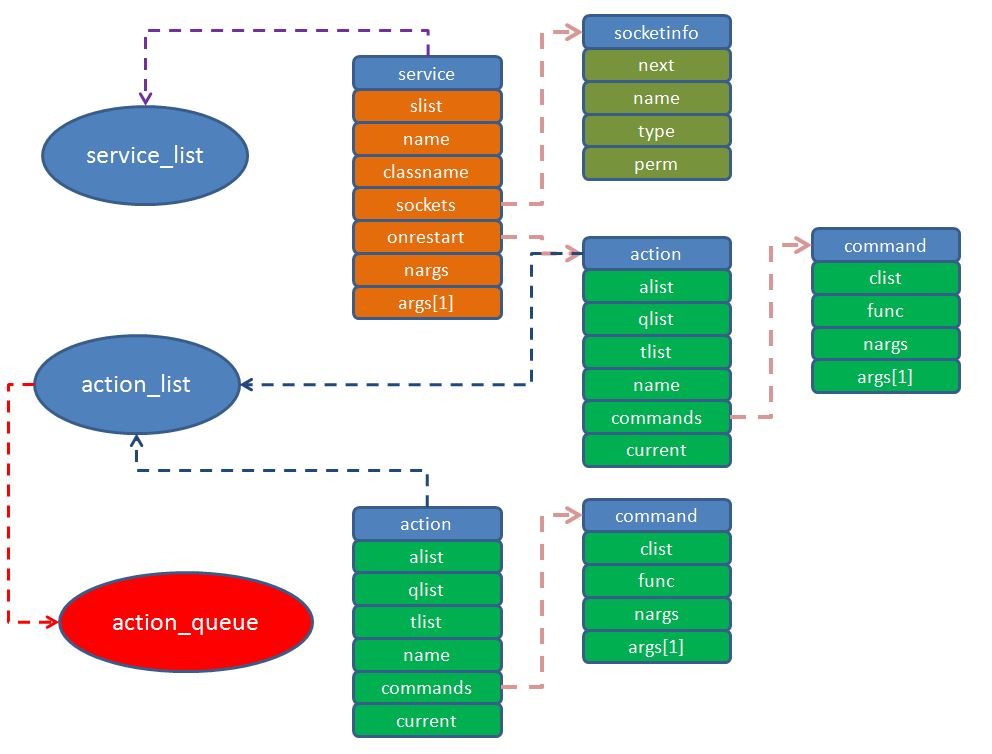
1.所有的service都保存到service_list这个双项链表中,service属性的socket保存在参数sockets中,用单向链表socketinfo去组织,onrestart保存了这个service重启时需要做的事情(action),例如启动其他相关service;
2.所有的on相关的都保存到action_list这个双项链表中。
init.rc中service和action下命令的执行
上面只是将init.rc中的东东都保存到结构体中,并利用service_list和action_list去组织,但是到此为止,这些command和service并没有执行,从哪开始执行的呢?
init中还有个全局的双项链表,名字为action_queue,放到这个链表中的action,其下面的命令都会去执行,后续代码有说明,首先看action_queue这个链表是如何被填充的,一种方式是init中执行类似action_for_each_trigger的函数,
action_for_each_trigger("early-init", action_add_queue_tail);//取出action_list中的early-init这个on,执行func,也就是action_add_queue_tail
void action_for_each_trigger(const char *trigger,
void (*func)(struct action *act))
{
struct listnode *node;
struct action *act;
list_for_each(node, &action_list) {
act = node_to_item(node, struct action, alist);
if (!strcmp(act->name, trigger)) {
func(act);
}
}
}//将该action添加到全局的queue list
void action_add_queue_tail(struct action *act)
{
if (list_empty(&act->qlist)) {
list_add_tail(&action_queue, &act->qlist);
}
}前面讲过,还有一种on property这种属性触发的action,因为某个属性的值设置的时间可能不确定,例如有些是系统启动后才去设置属性,这类action是如何添加到action_queue中的?
//init执行时首先会去初始化property service
queue_builtin_action(property_service_init_action, "property_service_init");static int property_service_init_action(int nargs, char **args)
{
/* read any property files on system or data and
* fire up the property service. This must happen
* after the ro.foo properties are set above so
* that /data/local.prop cannot interfere with them.
*/
start_property_service();
return 0;
}init中其实就是创建了property相关的一个unix域套接字,我们能够想象在通过adb 调用命令setprop时,setprop的函数实现肯定会和这个域套接字打交道,关于这个后续分析。
void start_property_service(void)
{
int fd;
load_properties_from_file(PROP_PATH_SYSTEM_BUILD);
load_properties_from_file(PROP_PATH_SYSTEM_DEFAULT);
load_override_properties();
/* Read persistent properties after all default values have been loaded. */
load_persistent_properties();
//PROP_SERVICE_NAME为 "property_service"
fd = create_socket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM, 0666, 0, 0);
if(fd < 0) return;
fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
listen(fd, 8);
property_set_fd = fd;
}在init的for循环中会对上面的property fd进行poll,
nr = poll(ufds, fd_count, timeout);在该描述符有数据时,会去执行,
handle_property_set_fd();接着会去执行init下的property_set,
int property_set(const char *name, const char *value)
{
prop_info *pi;
int ret;
size_t namelen = strlen(name);
size_t valuelen = strlen(value);
if (!is_legal_property_name(name, namelen)) return -1;
if (valuelen >= PROP_VALUE_MAX) return -1;
pi = (prop_info*) __system_property_find(name);
//read only的是不能修改的
if(pi != 0) {
/* ro.* properties may NEVER be modified once set */
if(!strncmp(name, "ro.", 3)) return -1;
__system_property_update(pi, value, valuelen);
} else {
ret = __system_property_add(name, namelen, value, valuelen);
if (ret < 0) {
ERROR("Failed to set '%s'='%s'\n", name, value);
return ret;
}
}
//如果是设置net.开头的属性,
//如果是net.change,不做任何东西
//net.change是为了记录当前哪个net.开头的属性被设置了
//[net.change]: [net.qtaguid_enabled]
/* If name starts with "net." treat as a DNS property. */
if (strncmp("net.", name, strlen("net.")) == 0) {
if (strcmp("net.change", name) == 0) {
return 0;
}
/*
* The 'net.change' property is a special property used track when any
* 'net.*' property name is updated. It is _ONLY_ updated here. Its value
* contains the last updated 'net.*' property.
*/
property_set("net.change", name);
} else if (persistent_properties_loaded &&
strncmp("persist.", name, strlen("persist.")) == 0) {
/*
* Don't write properties to disk until after we have read all default properties
* to prevent them from being overwritten by default values.
*/
write_persistent_property(name, value);
} else if (strcmp("selinux.reload_policy", name) == 0 &&
strcmp("1", value) == 0) {
selinux_reload_policy();
}
property_changed(name, value);
return 0;
}
void property_changed(const char *name, const char *value)
{
if (property_triggers_enabled)
queue_property_triggers(name, value);
}
void queue_property_triggers(const char *name, const char *value)
{
struct listnode *node;
struct action *act;
list_for_each(node, &action_list) {
act = node_to_item(node, struct action, alist);
if (!strncmp(act->name, "property:", strlen("property:"))) {
const char *test = act->name + strlen("property:");
int name_length = strlen(name);
//如果属性值相同,则将act加入到action_queue
if (!strncmp(name, test, name_length) &&
test[name_length] == '=' &&
(!strcmp(test + name_length + 1, value) ||
!strcmp(test + name_length + 1, "*"))) {
action_add_queue_tail(act);
}
}
}
}通过上面的步骤,我们已经将on property这种属性触发的action添加到全局链表action_queue中了,那么action_queue中的command是如何被执行的呢?
在init的for循环中,execute_one_command()函数会去从action_queue中取下action,然后执行该action下面的一个个command,这些command中有start service,也有一些类似mkdir的命令。init.rc中的service有些是执行一次结束后就退出的,有些是意外退出需要init把他们重启起来的,是用信号处理函数和socketpair实现的,后续再详细分析下该实现。
for(;;) {
int nr, i, timeout = -1;
execute_one_command();
//重启service,有些执行完不用重启,有些需要重启
restart_processes();
if (!signal_fd_init && get_signal_fd() > 0) {
//信号处理函数在子进程挂掉后会给signal_fd写东西
//这时候socketpair的对端,signal_recv_fd会受到,这里监听了该signal_recv_fd
ufds[fd_count].fd = get_signal_fd();
ufds[fd_count].events = POLLIN;
ufds[fd_count].revents = 0;
fd_count++;
signal_fd_init = 1;
}
}
void execute_one_command(void)
{
int ret;
// 从全局的action_queue中取
//如果当前command是action中的最后一个,取下一个action
if (!cur_action || !cur_command || is_last_command(cur_action, cur_command)) {
//从全局的action_queue中取出一个action
cur_action = action_remove_queue_head();
cur_command = NULL;
if (!cur_action)
return;
INFO("processing action %p (%s)\n", cur_action, cur_action->name);
//从action中的commands中取第一个command
cur_command = get_first_command(cur_action);
} else {
//继续取当前action中的command
cur_command = get_next_command(cur_action, cur_command);
}
if (!cur_command)
return;
//执行command的func函数
ret = cur_command->func(cur_command->nargs, cur_command->args);
INFO("command '%s' r=%d\n", cur_command->args[0], ret);
}下面是service属性中flag的介绍,经常见到的是
disabled,表示不会随着class一起启动,即不受class_start影响,需要显示start service名字,
oneshot,表示退出后不需要init再去重启,
critical,崩溃的次数多了系统就进入recovery了。
#define SVC_DISABLED 0x01 /* do not autostart with class */
#define SVC_ONESHOT 0x02 /* do not restart on exit */
#define SVC_RUNNING 0x04 /* currently active */
#define SVC_RESTARTING 0x08 /* waiting to restart */
#define SVC_CONSOLE 0x10 /* requires console */
#define SVC_CRITICAL 0x20 /* will reboot into recovery if keeps crashing */
#define SVC_RESET 0x40 /* Use when stopping a process, but not disabling
so it can be restarted with its class */
#define SVC_RC_DISABLED 0x80 /* Remember if the disabled flag was set in the rc script */
#define SVC_RESTART 0x100 /* Use to safely restart (stop, wait, start) a service */结构体关系图
下面是init.rc解析完成后的简单关系图,






















 1737
1737

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








