本文是根据<JAX-WS使用教程.pdf>学习所写笔记
1、JAX-WS概述
JAX-WS 2.0 的全称为 Java API for XML-Based Web services (JAX-WS) 2.0。JAX-WS 2.0 是对 JAX-RPC 1.0 规范的扩展,是 JAX-RPC 1.1 的后续版本, JAX-RPC 2.0标准发布不久后便被重新命名为 JAX-WS 2.0。 JAX-WS 2.0 是面向 Java 5 的开发 Web services 的最新编程标准,它提供了新的编程模型和对以往的 JAX-RPC 方式的 Web services 进行了增强。
JAX-WS2.0 (JSR 224)是Sun新的web services协议栈,是一个完全基于标准的实现。在binding层,使用的是the Java Architecture for XML Binding (JAXB, JSR 222),在parsing层,使用的是the Streaming API for XML (StAX, JSR 173),同时它还完全支持schema规范。
2、创建Web Service
JAX-WS 2.0 有两种开发过程:自顶向下和自底向上。自顶向下方式指通过一个 WSDL 文件来创建Web Service,自底向上是从 Java 类出发创建 Web Service。两种开发过程最终形成的文件包括:
l SEI。一个SEI对应WSDL中Web Service的一个port,在Java中是一个Java接口。
l SEI实现类。
l WSDL和XSD文件。
2.1 从java开始
编写类Hello
代码如下:
package ws;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public class Hello {
@WebMethod
public String say(String name , int age){
return "Hello , I am "+name+", I am "+age+" years old";
}
}
根据这webservice类,生成wsdl和服务端代码
2.1.1 运行wsgen
wsgen -cp ./bin -r ./wsdl -s ./src -d ./bin -wsdl ws.Hello
解释:
- -cp 定义classpath,就是ws.Hello这个类的classes文件存放的地方(如:bin\ws\Hello.class)
- -r 生成 bean的wsdl文件的存放目录,即指定wsdl存放地方
- -s 生成发布Web Service的源代码文件的存放目录(如果方法有抛出异常,则会生成该异常的描述类源文件)
- -d 生成发布Web Service的编译过的二进制类文件的存放目录(该异常的描述类的class文件),即生成的Say和SayResponse的class文件存放处

生成的java代码:
package ws.jaxws;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
@XmlRootElement(name = "say", namespace = "http://ws/")
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "say", namespace = "http://ws/", propOrder = {
"arg0",
"arg1"
})
public class Say {
@XmlElement(name = "arg0", namespace = "")
private String arg0;
@XmlElement(name = "arg1", namespace = "")
private int arg1;
/**
*
* @return
* returns String
*/
public String getArg0() {
return this.arg0;
}
/**
*
* @param arg0
* the value for the arg0 property
*/
public void setArg0(String arg0) {
this.arg0 = arg0;
}
/**
*
* @return
* returns int
*/
public int getArg1() {
return this.arg1;
}
/**
*
* @param arg1
* the value for the arg1 property
*/
public void setArg1(int arg1) {
this.arg1 = arg1;
}
}
应答代码
package ws.jaxws;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
@XmlRootElement(name = "sayResponse", namespace = "http://ws/")
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "sayResponse", namespace = "http://ws/")
public class SayResponse {
@XmlElement(name = "return", namespace = "")
private String _return;
/**
*
* @return
* returns String
*/
public String getReturn() {
return this._return;
}
/**
*
* @param _return
* the value for the _return property
*/
public void setReturn(String _return) {
this._return = _return;
}
}
2.1.2 生成的WSDL和XSD
WSDL
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<!-- Generated by JAX-WS RI at http://jax-ws.dev.java.net. RI's version is JAX-WS RI 2.1.1 in JDK 6. -->
<definitions targetNamespace="http://ws/" name="HelloService" xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" xmlns:tns="http://ws/" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/">
<types>
<xsd:schema>
<xsd:import namespace="http://ws/" schemaLocation="HelloService_schema1.xsd"/>
</xsd:schema>
</types>
<message name="say">
<part name="parameters" element="tns:say"/>
</message>
<message name="sayResponse">
<part name="parameters" element="tns:sayResponse"/>
</message>
<portType name="Hello">
<operation name="say">
<input message="tns:say"/>
<output message="tns:sayResponse"/>
</operation>
</portType>
<binding name="HelloPortBinding" type="tns:Hello">
<soap:binding transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http" style="document"/>
<operation name="say">
<soap:operation soapAction=""/>
<input>
<soap:body use="literal"/>
</input>
<output>
<soap:body use="literal"/>
</output>
</operation>
</binding>
<service name="HelloService">
<port name="HelloPort" binding="tns:HelloPortBinding">
<soap:address location="REPLACE_WITH_ACTUAL_URL"/>
</port>
</service>
</definitions>
XSD
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<xs:schema version="1.0" targetNamespace="http://ws/" xmlns:tns="http://ws/" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="say" type="tns:say"/>
<xs:element name="sayResponse" type="tns:sayResponse"/>
<xs:complexType name="say">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="arg0" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="arg1" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="sayResponse">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="return" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
2.1.3 目录结构
目录结构

2.2 从WSDL开始
2.2.1 运行wsimport
使用上面生成的WSDL来反向生成Java代码。生成后,不需要进行改动。
wsimport -d ./bin -s ./src -p test.ws D:\MyEclipseNGCRMWorkspace\jax-ws\wsdl\HelloService.wsdl
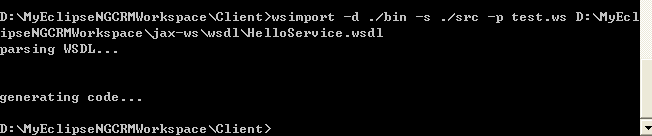
目录结构
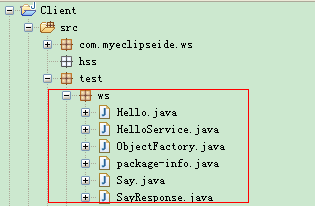
2.2.2 生成的java代码
Hello.java
package test.ws;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebResult;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlSeeAlso;
import javax.xml.ws.RequestWrapper;
import javax.xml.ws.ResponseWrapper;
/**
* This class was generated by the JAX-WS RI.
* JAX-WS RI 2.1.1 in JDK 6
* Generated source version: 2.1
*
*/
@WebService(name = "Hello", targetNamespace = "http://ws/")
@XmlSeeAlso({
ObjectFactory.class
})
public interface Hello {
/**
*
* @param arg1
* @param arg0
* @return
* returns java.lang.String
*/
@WebMethod
@WebResult(targetNamespace = "")
@RequestWrapper(localName = "say", targetNamespace = "http://ws/", className = "test.ws.Say")
@ResponseWrapper(localName = "sayResponse", targetNamespace = "http://ws/", className = "test.ws.SayResponse")
public String say(
@WebParam(name = "arg0", targetNamespace = "")
String arg0,
@WebParam(name = "arg1", targetNamespace = "")
int arg1);
}
HelloService.java
package test.ws;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceClient;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature;
/**
* This class was generated by the JAX-WS RI.
* JAX-WS RI 2.1.1 in JDK 6
* Generated source version: 2.1
*
*/
@WebServiceClient(name = "HelloService", targetNamespace = "http://ws/", wsdlLocation = "file:/D:/MyEclipseNGCRMWorkspace/jax-ws/wsdl/HelloService.wsdl")
public class HelloService
extends Service
{
private final static URL HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION;
static {
URL url = null;
try {
url = new URL("file:/D:/MyEclipseNGCRMWorkspace/jax-ws/wsdl/HelloService.wsdl");
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION = url;
}
public HelloService(URL wsdlLocation, QName serviceName) {
super(wsdlLocation, serviceName);
}
public HelloService() {
super(HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION, new QName("http://ws/", "HelloService"));
}
/**
*
* @return
* returns Hello
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloPort")
public Hello getHelloPort() {
return (Hello)super.getPort(new QName("http://ws/", "HelloPort"), Hello.class);
}
/**
*
* @param features
* A list of {@link javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature} to configure on the proxy. Supported features not in the <code>features</code> parameter will have their default values.
* @return
* returns Hello
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloPort")
public Hello getHelloPort(WebServiceFeature... features) {
return (Hello)super.getPort(new QName("http://ws/", "HelloPort"), Hello.class, features);
}
}
ObjectFactory.java
package test.ws;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElementDecl;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRegistry;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
/**
* This object contains factory methods for each
* Java content interface and Java element interface
* generated in the test.ws package.
* <p>An ObjectFactory allows you to programatically
* construct new instances of the Java representation
* for XML content. The Java representation of XML
* content can consist of schema derived interfaces
* and classes representing the binding of schema
* type definitions, element declarations and model
* groups. Factory methods for each of these are
* provided in this class.
*
*/
@XmlRegistry
public class ObjectFactory {
private final static QName _Say_QNAME = new QName("http://ws/", "say");
private final static QName _SayResponse_QNAME = new QName("http://ws/", "sayResponse");
/**
* Create a new ObjectFactory that can be used to create new instances of schema derived classes for package: test.ws
*
*/
public ObjectFactory() {
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link Say }
*
*/
public Say createSay() {
return new Say();
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link SayResponse }
*
*/
public SayResponse createSayResponse() {
return new SayResponse();
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link JAXBElement }{@code <}{@link Say }{@code >}}
*
*/
@XmlElementDecl(namespace = "http://ws/", name = "say")
public JAXBElement<Say> createSay(Say value) {
return new JAXBElement<Say>(_Say_QNAME, Say.class, null, value);
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link JAXBElement }{@code <}{@link SayResponse }{@code >}}
*
*/
@XmlElementDecl(namespace = "http://ws/", name = "sayResponse")
public JAXBElement<SayResponse> createSayResponse(SayResponse value) {
return new JAXBElement<SayResponse>(_SayResponse_QNAME, SayResponse.class, null, value);
}
}
package-info.java
@javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlSchema(namespace = "http://ws/")
package test.ws;
Say.java
package test.ws;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
/**
* <p>Java class for say complex type.
*
* <p>The following schema fragment specifies the expected content contained within this class.
*
* <pre>
* <complexType name="say">
* <complexContent>
* <restriction base="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}anyType">
* <sequence>
* <element name="arg0" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string" minOccurs="0"/>
* <element name="arg1" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}int"/>
* </sequence>
* </restriction>
* </complexContent>
* </complexType>
* </pre>
*
*
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "say", propOrder = {
"arg0",
"arg1"
})
public class Say {
protected String arg0;
protected int arg1;
/**
* Gets the value of the arg0 property.
*
* @return
* possible object is
* {@link String }
*
*/
public String getArg0() {
return arg0;
}
/**
* Sets the value of the arg0 property.
*
* @param value
* allowed object is
* {@link String }
*
*/
public void setArg0(String value) {
this.arg0 = value;
}
/**
* Gets the value of the arg1 property.
*
*/
public int getArg1() {
return arg1;
}
/**
* Sets the value of the arg1 property.
*
*/
public void setArg1(int value) {
this.arg1 = value;
}
}
SayResponse.java
package test.ws;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
/**
* <p>Java class for sayResponse complex type.
*
* <p>The following schema fragment specifies the expected content contained within this class.
*
* <pre>
* <complexType name="sayResponse">
* <complexContent>
* <restriction base="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}anyType">
* <sequence>
* <element name="return" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string" minOccurs="0"/>
* </sequence>
* </restriction>
* </complexContent>
* </complexType>
* </pre>
*
*
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "sayResponse", propOrder = {
"_return"
})
public class SayResponse {
@XmlElement(name = "return")
protected String _return;
/**
* Gets the value of the return property.
*
* @return
* possible object is
* {@link String }
*
*/
public String getReturn() {
return _return;
}
/**
* Sets the value of the return property.
*
* @param value
* allowed object is
* {@link String }
*
*/
public void setReturn(String value) {
this._return = value;
}
}
创建SEI类
实现Hello接口,并添加@WebService注释,并至少为@WebService添加endpointInterface属性。
package test.ws;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService(serviceName = "HelloService", portName = "HelloPort", endpointInterface = "test.ws.Hello", targetNamespace = "http://ws/")
public class HelloSEI implements Hello {
@Override
public String say(String arg0, int arg1) {
return "Hello , I am "+arg0+", I am "+arg1+" years old";
}
}
生成服务端要领:定义一个发布接口类,该接口类实现portType里定义的接口,重写该方法即可。在WebService里定义的serviceName = "HelloService"是服务,protName是服务里定义的端口,endpointInterface是指发布的接口,该接口即是实现的接口,即在portType里定义的操作类接口,targetNamespace是定义的域名,跟wsdl相关,建议修改wsdl里的域名,自定义域名即可.
2.3发布Web Service
2.3.1在应用程序中发布
JDK6提供了发布Web Service的简便方法: Endpoint.publish("http://localhost:8080/HelloService", new Hello());
如果是从WSDL生成的Web Service,则为, Endpoint.publish("http://localhost:8080/HelloService", new HelloSEI());
代码如下:
package test;
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
import test.ws.HelloSEI;
public class TestHello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Endpoint.publish("http://localhost:8080/HelloService", new HelloSEI());
}
}
2.3.2在Web应用程序中发布
利用SUN公司提供的辅助包,可以将Web Service发布为Web应用程序。
2.3.2.1 依赖包
l activation.jar
l FastInfoset.jar
l http.jar
l jaxb-impl.jar
l jaxws-rt.jar
l mimepull.jar
l resolver.jar
l stax-ex.jar
l streambuffer.jar
2.3.2.1发布步骤
1) 修改web.xml,添加
<listener> <listener-class> com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.servlet.WSServletContextListener</listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>Hello</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.servlet.WSServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/HelloService</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> 为每一个WebService声明一个com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.servlet.WSServlet。
2) 在WEB-INF目录下新建sun-jaxws.xml文件,内容如下,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <endpoints version="2.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jax-ws/ri/runtime"> <endpoint implementation="ws.server.fromjava.Hello" name="Hello" url-pattern="/HelloService" /> </endpoints> 将ws.server.fromjava.Hello声明为Web Service。
如果是从WSDL生成的Web Service,则为,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <endpoints version="2.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jax-ws/ri/runtime"> <endpoint implementation="ws.server.fromjava.HelloSEI" name="Hello" url-pattern="/HelloService" /> </endpoints>
2.4 创建Web Service客户端
客户端开发的通常过程是从已有的WSDL出发,创建辅助类JAXB对象和Service代理类,然后基于这些类开发自己的客户端应用。
2.4.1同步调用方式的客户端
2.4.1.1 开发步骤
1) 运行wsimport命令,生成客户端代码;
2) 修改生成的Java代码中的WSDL地址。
2.4.1.2 运行wsimport
wsimport -d ./bin -s ./src -p test.ws D:\MyEclipseNGCRMWorkspace\jax-ws\wsdl\HelloService.wsdl
src是生成的源代码的存放路径。 bin是生成的class文件的存放路径。HelloService.wsdl是Web Service WSDL的路径。
详情请参考2.2节
2.4.1.3 修改生成的Java代码
编辑HelloService.java,将
package test.ws;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceClient;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature;
/**
* This class was generated by the JAX-WS RI.
* JAX-WS RI 2.1.1 in JDK 6
* Generated source version: 2.1
*
*/
@WebServiceClient(name = "HelloService", targetNamespace = "http://ws/", wsdlLocation = "file:/D:/MyEclipseNGCRMWorkspace/jax-ws/wsdl/HelloService.wsdl")
public class HelloService
extends Service
{
private final static URL HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION;
static {
URL url = null;
try {
url = new URL("file:/D:/MyEclipseNGCRMWorkspace/jax-ws/wsdl/HelloService.wsdl");
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION = url;
}
public HelloService(URL wsdlLocation, QName serviceName) {
super(wsdlLocation, serviceName);
}
public HelloService() {
super(HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION, new QName("http://ws/", "HelloService"));
}
/**
*
* @return
* returns Hello
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloPort")
public Hello getHelloPort() {
return (Hello)super.getPort(new QName("http://ws/", "HelloPort"), Hello.class);
}
/**
*
* @param features
* A list of {@link javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature} to configure on the proxy. Supported features not in the <code>features</code> parameter will have their default values.
* @return
* returns Hello
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloPort")
public Hello getHelloPort(WebServiceFeature... features) {
return (Hello)super.getPort(new QName("http://ws/", "HelloPort"), Hello.class, features);
}
}
修改为,
package test.ws;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceClient;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature;
/**
* This class was generated by the JAX-WS RI.
* JAX-WS RI 2.1.1 in JDK 6
* Generated source version: 2.1
*
*/
@WebServiceClient(name = "HelloService", targetNamespace = "http://ws/")
public class HelloService
extends Service
{
private final static URL HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION;
public HelloService(URL wsdlLocation){ //wsdl地址由构造函数提供,非指定
super(wsdlLocation, new QName("http://ws/", "HelloService"));
}
static {
URL url = null;
try {
url = new URL("file:/D:/MyEclipseNGCRMWorkspace/jax-ws/wsdl/HelloService.wsdl");
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION = url;
}
public HelloService(URL wsdlLocation, QName serviceName) {
super(wsdlLocation, serviceName);
}
public HelloService() {
super(HELLOSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION, new QName("http://ws/", "HelloService"));
}
/**
*
* @return
* returns Hello
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloPort")
public Hello getHelloPort() {
return (Hello)super.getPort(new QName("http://ws/", "HelloPort"), Hello.class);
}
/**
*
* @param features
* A list of {@link javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature} to configure on the proxy. Supported features not in the <code>features</code> parameter will have their default values.
* @return
* returns Hello
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloPort")
public Hello getHelloPort(WebServiceFeature... features) {
return (Hello)super.getPort(new QName("http://ws/", "HelloPort"), Hello.class, features);
}
}
即删除WSDL具体地址。
2.4.1.4 调用Web Service
代码如下:
package test;
import java.net.URL;
import test.ws.HelloService;
public class TestHelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/HelloService?wsdl");
HelloService server = new HelloService(url);
String s = server.getHelloPort().say("liangbinny", 24);
System.out.println(s);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
或者是
package ws.client;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import ws.server.Hello;
import ws.server.HelloService;
public class TestHelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/hello?wsdl");
//域名和服务
QName qName = new QName("http://www.liangbinny.com/","HelloService");
HelloService server = new HelloService(url,qName);
Hello hello = server.getHelloPort();
String s = hello.say("liangbinny", 24);
System.out.println(s);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
调用客户端要领:HelloService server = new HelloService(url,qName);(先new service),然后server.getHelloPort()(获取服务里的端口,得到的端口类即portType里定义的操作类),最后hello.say("liangbinny", 24);(得到portType里的操作类后,就得到各种方法了).
2.5 SOAP headers
2.5.1 客户端添加SOAP headers
代码如下:
package test;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import test.ws.Hello;
import test.ws.HelloService;
import com.sun.xml.ws.api.message.Headers;
import com.sun.xml.ws.developer.WSBindingProvider;
public class TestHelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/HelloService?wsdl");
HelloService server = new HelloService(url);
Hello hello = server.getHelloPort();
WSBindingProvider bp = (WSBindingProvider) hello;
bp.setOutboundHeaders(Headers.create(new QName("username"),
"liangbinny"), Headers.create(new QName("password"),
"123456"));
String s = server.getHelloPort().say("liangbinny", 24);
System.out.println(s);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.5.2 访问SOAP headers
2.5.2.1 服务器端
@WebService public class FooService { @Resource WebServiceContext context; @WebMethod public void sayHelloTo(String name) { HeaderList hl = context.getMessageContext().get( JAXWSProperties.INBOUND_HEADER_LIST_PROPERTY); Header h = hl.get(MYHEADER); } private static final QName MYHEADER = new QName("myNsUri", "myHeader"); } }
2.5.2.2 客户端
HelloPort port = helloService.getHelloPort(); // or something like that... port.sayHelloTo("duke"); HeaderList hl = port.getResponseContext().get(JAXWSProperties.INBOUND_HEADER_LIST_PROPERTY); Header h = hl.get(MYHEADER);





















 1097
1097











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








