一、参考
1、tkinter UI菜单
2、tkinter UI对话框打开、保存文件
3、tkinter 控件介绍
4、读写excel
5、执行文件打开:os.startfile(‘newfile.txt’)
6、发动机激励及悬置模态及振动计算csdn
二、界面

三、代码
# _*_ coding:UTF-8 _*_
import numpy as np
from numpy import sin
from numpy import cos
from numpy import arcsin as asin
from numpy import sqrt
from numpy import tan
from scipy import interpolate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import lti, lsim
def M_sys(m,Ixx,Ixy,Ixz,Iyy,Iyz,Izz):
return np.array([[m,0,0,0,0,0],\
[0,m,0,0,0,0],\
[0,0,m,0,0,0],\
[0,0,0,Ixx,-Ixy,-Ixz],\
[0,0,0,-Ixy,Iyy,-Iyz],\
[0,0,0,-Ixz,-Iyz,Izz]])
def K_sys_byMatrix(k_pi,k_qi,k_ri,theta_pi,phi_pi,psi_pi,theta_qi,phi_qi,psi_qi,theta_ri,phi_ri,psi_ri,Ai,Bi,Ci):
#参数均采用数组格式
n=np.size(Ai)
ki=np.zeros((n,3,3))
Ti=np.zeros_like(ki)
BBi=np.zeros((n,3,6))
KKi=np.zeros((n,6,6))
K=np.zeros((6,6))
for i in range(n):
ki[i]=np.array([[k_pi[i],0,0],\
[0,k_qi[i],0],\
[0,0,k_ri[i]]])
Ti[i]=np.array([[cos(theta_pi[i]),cos(phi_pi[i]),cos(psi_pi[i])],\
[cos(theta_qi[i]),cos(phi_qi[i]),cos(psi_qi[i])],\
[cos(theta_ri[i]),cos(phi_ri[i]),cos(psi_ri[i])]])
BBi[i]=np.array([[1,0,0,0,Ci[i],-Bi[i]],\
[0,1,0,-Ci[i],0,Ai[i]],\
[0,0,1,Bi[i],-Ai[i],0]])
KKi[i]=BBi[i].T@Ti[i].T@ki[i]@Ti[i]@BBi[i]
K=np.sum(KKi,axis=0)
return K
def Energy_DistributionJ(M,Value,Vector_Matrix):
#3维能量分布:(阶次、Dof、Dof)
n=M.shape[0]
KE_klj=np.zeros((n,n,n))
for j in range(n):
Value_j=Value[j] #0维数组:特征值 频率的平方
Vector_r=Vector_Matrix[:,j] #一维数组:行向量
Vector_c=Vector_r.reshape(n,1) #改成二维数组:列向量
KE_klj[j]=0.5*Value_j*M*Vector_c*Vector_r
return KE_klj
def Energy_percent(KE_klj):
n=KE_klj.shape[0]
#KE_klj 3维能量分布:(阶次、Dof、Dof=页、行、列)
#将每行Dof的能量合并缩维,得到(各Dof总能量占比,阶):
Energy_perDof=np.sum(KE_klj,2) #按行合并,第3维压缩掉,成2维数组:矩阵(阶次、各Dof能量)
Energy_AllDof_r=np.sum(Energy_perDof,1) #按行合并,第2维压缩掉,成一维数组:行向量[1阶总能量、2阶总能量、...]
Energy_AllDof_c=Energy_AllDof_r.reshape(n,1) #改成二维数组:列向量[[1阶总能量],[2阶总能量]、...]
Energy_percent=100.0*Energy_perDof/Energy_AllDof_c #2维数组:矩阵(阶次、各Dof能量占比)
Energy_percent=Energy_percent.T ########二维数组转置,得到矩阵(各Dof总能量占比,阶)
return Energy_percent
def PointSensor(Yxyzi,x_p,y_p,z_p):
#将刚体质心加速度Yxyzi根据传感器的的坐标转换到Pxyzi:
TransMatrix=np.array([[1,0,0,0,z_p,y_p],\
[0,1,0,z_p,0,x_p],\
[0,0,1,y_p,x_p,0]])
Pxyzi=Yxyzi@TransMatrix.T
return Pxyzi
def EngineSim(mPiston,mConnectingRod,l,lB,R,Ap,IC,offside_cylinder,pr,crank_angle,omega,num_cylinders=6):
#mPiston=430/1000; #kg
#mConnectingRod=440/1000; #kg
#l=140/1000; #m,Connecting rod pin-pin length
#lB=37/1000; #m,Connecting rod pin B-CG lengh
#R=49/1000; #m,Crank radius
#Ap=5800; #mm2,Pistion area
#IC=0.0015; #kg.m2,Connecting rod inertia
#offside_cylinder=0/1000 #气缸与曲轴偏置距 add by lijilin 2020.12.23
#num_cylinders=6
#-------Pressure in combustion chamber-------
#pr=[18,32,32.5,32,20,15,10,8,6,5,3,1.2,0.6,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1.0,2.0,4,9,15,18]
#crank_angle=[0,20,23,26,50,60,70,80,100,110,150,190,200,220,230,250,280,300,330,360,380,400,440,460,480,500,540,600,630,660,690,710,720]
#omega=3000; #rpm speed of engine
pi=np.pi
pr=np.array(pr.tolist()) ##
n=np.size(pr)
pr.resize(n,1)
crank_angle=np.array(crank_angle.tolist()) ##
crank_angle.resize(n,1)
omeg=omega*pi/30
Rl=R/l #define ratio R over l
lA=l-lB
ang=crank_angle*pi/180
#ang=ang.tolist() ##### If you make a numpy array from mixed objects, such as numbers, strings or symbols, you get an object dtype array.
##### np.sin(arr) on such an array is performed by calling [x.sin() for x in arr]
sa=sin(ang)
ca=cos(ang)
s2a=sin(2*ang)
c2a=cos(2*ang)
#beta=asin((Rl*sa));
beta=asin((R*sa-offside_cylinder)/l) #####update by lijilin 2020.12.23
ka=ca+Rl*c2a/cos(beta)+Rl**3*s2a**2/cos(beta)**3/4
#//Piston acceleration:
aP=R*ka*omeg**2
#//onnecting rod angular acceleration:
alpha_c=Rl*omeg**2*sa/cos(beta)
#//Connecting rod GC acceleration:
k3=lA*sa/l
k4=ca+Rl*c2a*lB/cos(beta)/l
agx=-R*omeg**2*k3
agy=-R*omeg**2*k4
ag=sqrt(agx**2+agy**2)
#//Piston pressure force:
Fp=pr*Ap/9.8
#//Piston inertia force:
FIP=-mPiston*aP
#//Resultant piston force:
FPt=Fp+FIP
#//Connection rod inertia forces(N):
FIx=-mConnectingRod*agx
FIy=-mConnectingRod*agy
#//Conneting rod inertia torque(Nm):
TIG=IC*alpha_c
#//Crank-pin bearing forces:
Bx=(-FIP-Fp+lB*FIy/l)*tan(beta)-lA*FIx/l-TIG/l/cos(beta)
By=Fp+FIP-FIy
#//Engine torque:
Te=R*(By*sa-Bx*ca)
#//气缸壁侧压力:
Fw=-FIx-Bx
#倾覆力矩:
T_w=-Fw*(R*ca+l*cos(beta))
T_offside=-By*offside_cylinder
T_all=T_w+T_offside
crank_angle_i=np.linspace(0,719,720)
#"nearest","zero"为阶梯插值
#slinear 线性插值
#"quadratic","cubic" 为2阶、3阶B样条曲线插值
# ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’ and ‘cubic’ refer to a spline interpolation of first, second or third order)
func_interp=interpolate.interp1d(crank_angle[:,0],T_all[:,0],"cubic")
T_all_i=func_interp(crank_angle_i).reshape(720,1)
psi_shift=int(720/num_cylinders)
T_shift=np.zeros((720,num_cylinders))
T_shift[:,0]=T_all_i[:,0]
for i in range(num_cylinders-1):
i=i+1
T_shift[:-psi_shift*i,i]=T_all_i[psi_shift*i:,0]
T_shift[-psi_shift*i+1:,i]=T_all_i[:psi_shift*i-1,0]
T_output=np.sum(T_shift,1)
return [Fp,FIP,FPt,FIx,FIy,crank_angle,TIG,Bx,By,crank_angle,Te,crank_angle,Fw,T_w,T_offside,T_all,crank_angle_i,T_shift,T_output]
#########################UI::###########################
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, dialog
import os
import pandas as pd
file_path_engine = ''
file_path_mount = ''
bFigureShow=True
def banben():
dialog.Dialog(None, {'title': '版本', 'text': 'v1-2022-10-17', 'bitmap': 'warning', 'default': 0 ,
'strings': ('OK', 'Cancle')})
def open_file_engine():
'''
打开文件
:return:
'''
global file_path_engine
file_path_engine = filedialog.askopenfilename(title=u'选择文件', initialdir=(os.path.expanduser('C:/')))
text1.delete(1.0, 'end')
text1.insert('insert',file_path_engine) #insert
def open_file_mount():
'''
打开文件
:return:
'''
global file_path_mount
file_path_mount = filedialog.askopenfilename(title=u'选择文件', initialdir=(os.path.expanduser('C:/')))
text2.delete(1.0, 'end')
text2.insert('insert',file_path_mount) #insert
#file_text=text2.get(1.0,'end')
def mount():
'''
计算模态及解耦率
'''
if not file_path_mount:
dialog.Dialog(None, {'title': '悬置文件错误', 'text': '请打开悬置文件', 'bitmap': 'warning', 'default': 0,
'strings': ('OK', 'Cancle')})
return
dataFrame =pd.read_excel(file_path_mount)
data=dataFrame.values[:,:] #二维数组
#x=dataFrame.values[:10,2]
#y=dataFrame.values[:10,1]
###########input###########################################################################
[m,Ixx,Iyy,Izz,Ixy,Iyz,Ixz]=data[2,:7] ##
PG=data[5,:3]/1000
Num_points=data[8,2]
ABC=np.zeros((Num_points,3))
for i in range(Num_points):
ABC[i,:]=data[61+i*3,2:5]/1000
ABC=np.array(ABC)-np.array(PG)
Ai,Bi,Ci=ABC[:,0],ABC[:,1],ABC[:,2]
theta_pi=np.zeros(Num_points)
theta_qi=np.zeros(Num_points)
theta_ri=np.zeros(Num_points)
phi_pi=np.zeros(Num_points)
phi_qi=np.zeros(Num_points)
phi_ri=np.zeros(Num_points)
psi_pi=np.zeros(Num_points)
psi_qi=np.zeros(Num_points)
psi_ri=np.zeros(Num_points)
for i in range(Num_points):
theta_pi[i]=data[83+i*5,2]
theta_qi[i]=data[84+i*5,2]
theta_ri[i]=data[85+i*5,2]
phi_pi[i]=data[83+i*5,3]
phi_qi[i]=data[84+i*5,3]
phi_ri[i]=data[85+i*5,3]
psi_pi[i]=data[83+i*5,4]
psi_qi[i]=data[84+i*5,4]
psi_ri[i]=data[85+i*5,4]
[theta_pi,phi_pi,psi_pi,theta_qi,phi_qi,psi_qi,theta_ri,phi_ri,psi_ri]=\
np.array([theta_pi,phi_pi,psi_pi,theta_qi,phi_qi,psi_qi,theta_ri,phi_ri,psi_ri])*np.pi/180
k_pi=np.zeros(Num_points)
k_qi=np.zeros(Num_points)
k_ri=np.zeros(Num_points)
c_pi=np.zeros(Num_points)
c_qi=np.zeros(Num_points)
c_ri=np.zeros(Num_points)
for i in range(Num_points):
k_pi[i]=data[17+i*3,2]*1000
k_qi[i]=data[17+i*3,3]*1000
k_ri[i]=data[17+i*3,4]*1000
c_pi[i]=data[17+i*3,6]
c_qi[i]=data[17+i*3,7]
c_ri[i]=data[17+i*3,8]
'''
[m,Ixx,Iyy,Izz,Ixy,Ixz,Iyz]=[1224.4,79.385,523.73,491.332,-5.866,-76.403,-4.698]
PG=[0.266249,-0.011964,0.186296]
ABC=[[-0.525,-0.413,0.110],[-0.525,0.413,0.110],[0.675,-0.380,0.151],[0.675,0.380,0.151]]
ABC=np.array(ABC)-np.array(PG)
Ai,Bi,Ci=ABC[:,0],ABC[:,1],ABC[:,2]
theta_pi=[0,0,0,0] #3
theta_qi=[90,90,90,90]
theta_ri=[90,90,90,90] #93
phi_pi=[90,90,90,90]
phi_qi=[0,0,0,0]
phi_ri=[90,90,90,90]
psi_pi=[90,90,90,90] #87
psi_qi=[90,90,90,90]
psi_ri=[0,0,0,0] #3
[theta_pi,phi_pi,psi_pi,theta_qi,phi_qi,psi_qi,theta_ri,phi_ri,psi_ri]=\
np.array([theta_pi,phi_pi,psi_pi,theta_qi,phi_qi,psi_qi,theta_ri,phi_ri,psi_ri])*np.pi/180
k_pi=[1386000,1386000,2745000,2745000]
k_qi=[354000,354000,367500,367500]
k_ri=[1068000,1068000,2025000,2025000]
'''
###########end input###########################################################################
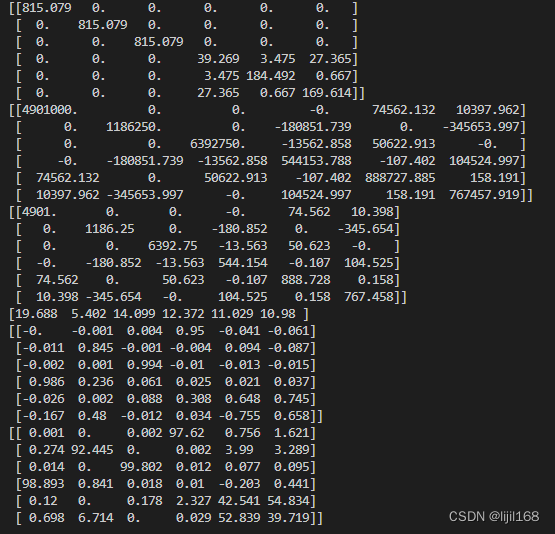
M_sys_value=M_sys(m,Ixx,Ixy,Ixz,Iyy,Iyz,Izz) #M_sys的值不能用M_sys的函数名!!
K_sys=K_sys_byMatrix(k_pi,k_qi,k_ri,theta_pi,phi_pi,psi_pi,theta_qi,phi_qi,psi_qi,theta_ri,phi_ri,psi_ri,Ai,Bi,Ci)
C_sys=K_sys_byMatrix(c_pi,c_qi,c_ri,theta_pi,phi_pi,psi_pi,theta_qi,phi_qi,psi_qi,theta_ri,phi_ri,psi_ri,Ai,Bi,Ci)
Value, Vector_Matrix = np.linalg.eig(np.linalg.inv(M_sys_value)@K_sys)
#np.set_printoptions(formatter={'float': '{: 0.3f}'.format})
np.set_printoptions(precision=3, suppress=True)
print(M_sys_value)
print(K_sys)
print(C_sys)
print(np.sqrt(Value)/2/np.pi)
print(Vector_Matrix)
#print(Vector_Matrix.T@M_sys@Vector_Matrix)
#print(Vector_Matrix.T@K_sys@Vector_Matrix)
KE_klj=Energy_DistributionJ(M_sys_value,Value,Vector_Matrix)
print(Energy_percent(KE_klj))
return [M_sys_value,K_sys,C_sys,Ai,Bi,Ci]
def engine():
'''
计算发动机激励
'''
if not file_path_engine:
dialog.Dialog(None, {'title': '发动机文件错误', 'text': '请打开发动机文件', 'bitmap': 'warning', 'default': 0,
'strings': ('OK', 'Cancle')})
return
dataFrame =pd.read_excel(file_path_engine)
data=dataFrame.values[:,:] #二维数组
#x=dataFrame.values[:10,2]
#y=dataFrame.values[:10,1]
#######################begin:计算发动机激励#################################
#-----input-----
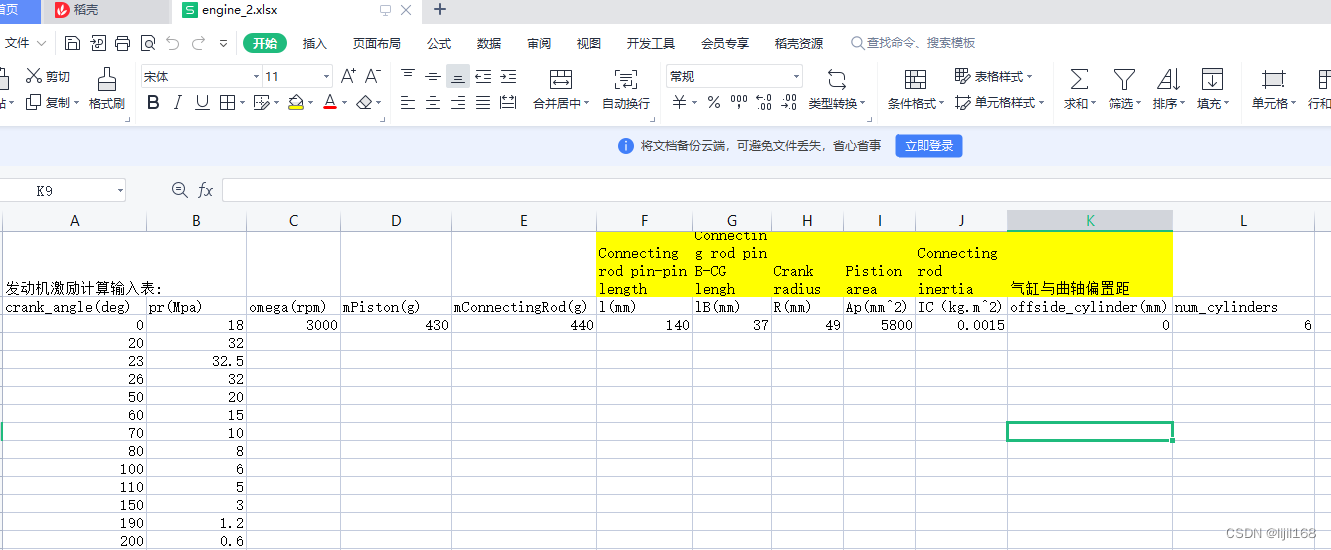
mPiston=data[1,3]/1000 #kg
mConnectingRod=data[1,4]/1000 #kg
l=data[1,5]/1000 #m,Connecting rod pin-pin length
lB=data[1,6]/1000 #m,Connecting rod pin B-CG lengh
R=data[1,7]/1000 #m,Crank radius
Ap=data[1,8] #mm2,Pistion area
IC=data[1,9] #kg.m2,Connecting rod inertia
offside_cylinder=data[1,10]/1000 #气缸与曲轴偏置距 add by lijilin 2020.12.23
num_cylinders=data[1,11]
omega=data[1,2]
#-------Pressure in combustion chamber--------
pr=data[1:,1]
crank_angle=data[1:,0]
'''
#######################begin:计算发动机激励#################################
#-----input-----
mPiston=430/1000; #kg
mConnectingRod=440/1000; #kg
l=140/1000; #m,Connecting rod pin-pin length
lB=37/1000; #m,Connecting rod pin B-CG lengh
R=49/1000; #m,Crank radius
Ap=5800; #mm2,Pistion area
IC=0.0015; #kg.m2,Connecting rod inertia
offside_cylinder=0/1000 #气缸与曲轴偏置距 add by lijilin 2020.12.23
num_cylinders=6
omega=3000
#-------Pressure in combustion chamber--------
pr=[18,32,32.5,32,20,15,10,8,6,5,3,1.2,0.6,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1.0,2.0,4,9,15,18];
crank_angle=[0,20,23,26,50,60,70,80,100,110,150,190,200,220,230,250,280,300,330,360,380,400,440,460,480,500,540,600,630,660,690,710,720];
'''
[Fp,FIP,FPt,FIx,FIy,crank_angle,TIG,Bx,By,crank_angle,Te,crank_angle,Fw,\
T_w,T_offside,T_all,crank_angle_i,T_shift,T_output]=EngineSim(mPiston,mConnectingRod,l,lB,R,Ap,IC,offside_cylinder,pr,crank_angle,omega,num_cylinders)
#-----output------
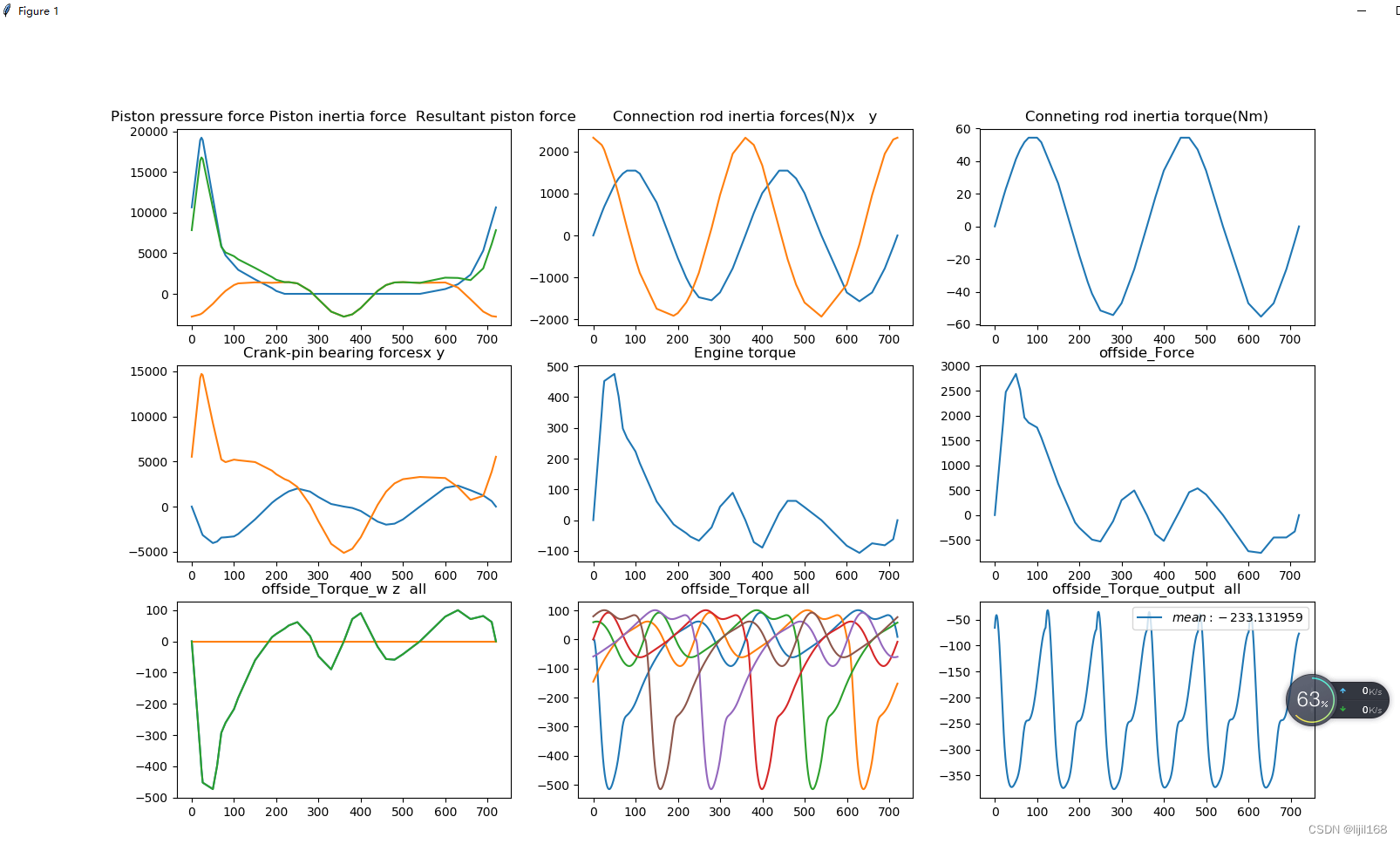
plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))
plt.subplot(3,3,1)
plt.plot(crank_angle,np.c_[Fp,FIP,FPt]);#活塞气压力 惯性力 合力
plt.title('Piston pressure force Piston inertia force Resultant piston force')
plt.subplot(3,3,2)
plt.plot(crank_angle,np.c_[FIx,FIy]);#连杆惯性力x y
plt.title('Connection rod inertia forces(N)x y')
plt.subplot(3,3,3)
plt.plot(crank_angle,TIG);#惯性力矩
plt.title('Conneting rod inertia torque(Nm)')
plt.subplot(3,3,4)
plt.plot(crank_angle,np.c_[Bx,By]);#曲柄销力x y
plt.title('Crank-pin bearing forcesx y')
plt.subplot(3,3,5)
plt.plot(crank_angle,Te);#发动机力矩
plt.title('Engine torque')
plt.subplot(3,3,6)
plt.plot(crank_angle,Fw);#气缸侧压
plt.title('offside_Force')
plt.subplot(3,3,7)
plt.plot(crank_angle,np.c_[T_w,T_offside,T_all])
plt.title('offside_Torque_w z all')
plt.subplot(3,3,8)
plt.plot(crank_angle_i,T_shift[:,:])
plt.title('offside_Torque all')
plt.subplot(3,3,9)
plt.plot(crank_angle_i,T_output,label='$mean: %f$' %np.mean(T_output)) ####
plt.title('offside_Torque_output all')
plt.legend()
if bFigureShow:
plt.show() ###
return [crank_angle_i,T_output,omega]
#######################end:计算发动机激励#################################
##############begin:建立状态空间方程并用发动机倾覆力矩激励进行仿真 state space function########################
def ForceResponse():
'''
计算悬置振动
'''
#plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] #用来正常显示中文标签
#plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False #用来正常显示负号
global bFigureShow
bFigureShow=False
#------------悬置系统结构参数数据:---------
[M,K,C,Ai,Bi,Ci]=mount()
#------------使用计算的发动机倾覆力矩激励数据:---------
[crank_angle_i,T_output,omega]=engine()
n=6
G=np.r_[np.c_[C,M],np.c_[M,np.zeros((n,n))]] #G=[C,M;M,O]
H=np.r_[np.c_[K,np.zeros((n,n))],np.c_[np.zeros((n,n)),-M]] #H=[K,O;O,-M]
ssA=-np.linalg.inv(G)@H;
ssB=np.linalg.inv(G)@np.row_stack([np.eye(n),np.zeros((n,n))]); #G dX +H X =E u => dX="-G\H" X +"G\E" u
#ssB=[zeros(n),inv(M);inv(M),-inv(M)^2]*[eye(n);zeros(n)];
#ssC=[-M\K,-M\C];
ssC=np.column_stack([-np.linalg.inv(M)@K,-np.linalg.inv(M)@C])
ssD=np.linalg.inv(M); #设输出Y= d^2X=[-M\K,-M\C]*[X,dX]+[M]\U
sys=lti(ssA,ssB,ssC,ssD)
#------------从文件中读入发动机倾覆力矩激励数据:---------
#data = pd.read_csv('testdata.txt', header=None, )
#data.head(10)
#Fs=data.values[0]
#y=data.values[1:]
#t=np.linspace(0,1/Fs[0]*(np.size(y)-1), num=np.size(y)) #Fs[0]才是采样频率的值!!!
t=crank_angle_i/360/omega*60
y=T_output
y.resize(np.size(y))
y1=(y-np.mean(y)) ###########
U=np.zeros((np.size(y),6))
U[:,3]=y1
X0=np.zeros((n*2)) #X0=zeros(2*n,1);%X0=[x1_0,...,dx1_0,...]
tout,Y,X=lsim(sys,U,t,X0)
#-------计算悬置点的加速度:
Pxyzi1=PointSensor(Y,Ai[0],Bi[0],Ci[0])
Pxyzi2=PointSensor(Y,Ai[1],Bi[1],Ci[1])
Pxyzi3=PointSensor(Y,Ai[2],Bi[2],Ci[2])
Pxyzi4=PointSensor(Y,Ai[3],Bi[2],Ci[2]) ##
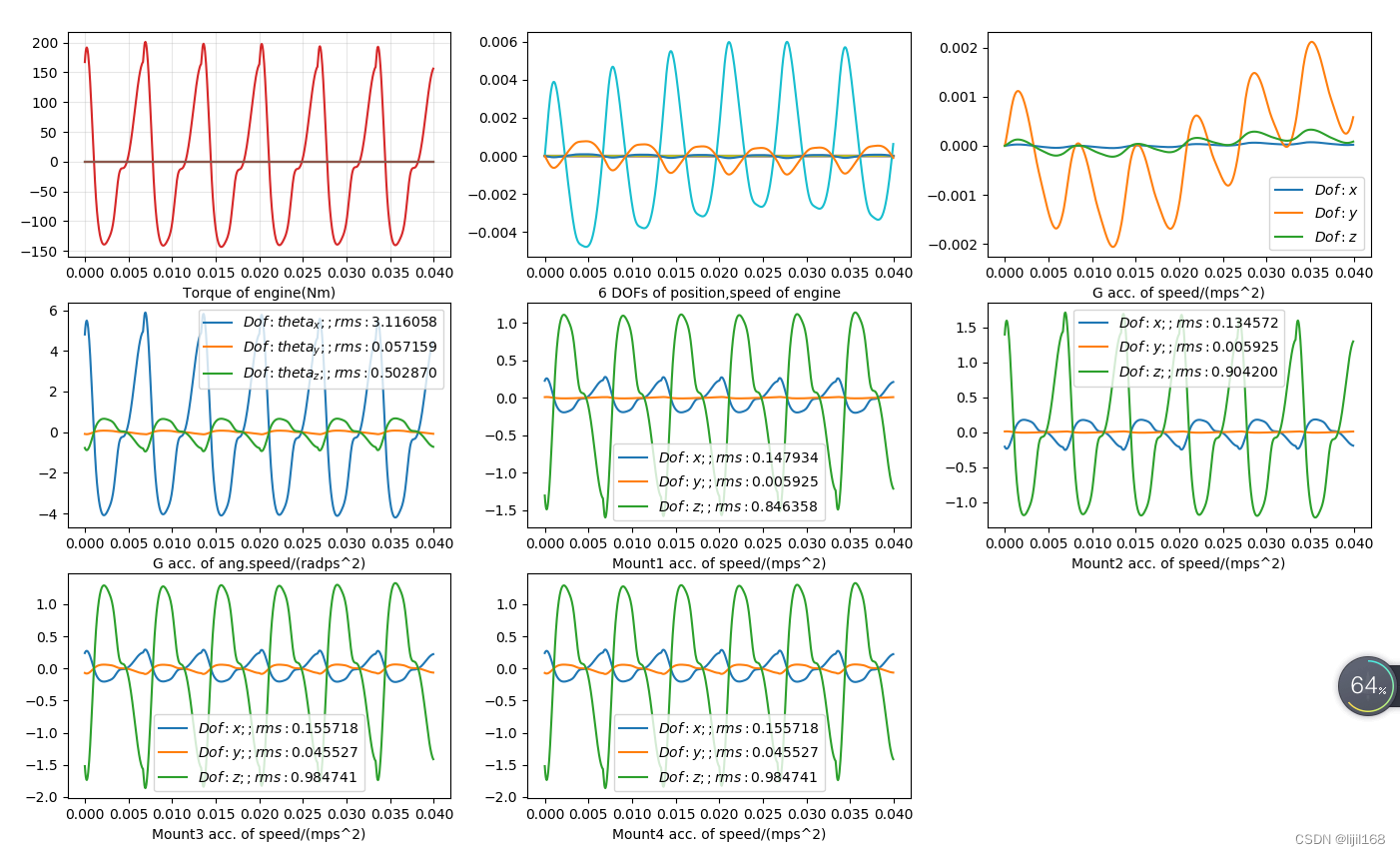
plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))
plt.subplot(3,3,1)
plt.plot(t,U) #######
plt.xlabel('Torque of engine(Nm)')
#grid on
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.subplot(3,3,2)
plt.plot(t,X) ######
plt.xlabel('6 DOFs of position,speed of engine')
plt.subplot(3,3,3)
for i in range(3):
plt.plot(t,Y[:,i],label='$Dof:%s$' % ["x","y","z","theta_x","theta_y","theta_z"][i])
plt.xlabel('G acc. of speed/(mps^2)')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(3,3,4)
for i in [3,4,5]:
plt.plot(t,Y[:,i],label='$Dof:%s;;rms: %f$' %(["x","y","z","theta_x","theta_y","theta_z"][i],np.std(Y[:,i])))
plt.xlabel('G acc. of ang.speed/(radps^2)')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(3,3,5)
for i in range(3):
plt.plot(t,Pxyzi1[:,i],label='$Dof:%s;;rms: %f$' %(["x","y","z"][i],np.std(Pxyzi1[:,i])))
plt.xlabel('Mount1 acc. of speed/(mps^2)')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(3,3,6)
for i in range(3):
plt.plot(t,Pxyzi2[:,i],label='$Dof:%s;;rms: %f$' %(["x","y","z"][i],np.std(Pxyzi2[:,i])))
plt.xlabel('Mount2 acc. of speed/(mps^2)')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(3,3,7)
for i in range(3):
plt.plot(t,Pxyzi3[:,i],label='$Dof:%s;;rms: %f$' %(["x","y","z"][i],np.std(Pxyzi3[:,i])))
plt.xlabel('Mount3 acc. of speed/(mps^2)')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(3,3,8)
for i in range(3):
plt.plot(t,Pxyzi4[:,i],label='$Dof:%s;;rms: %f$' %(["x","y","z"][i],np.std(Pxyzi4[:,i])))
plt.xlabel('Mount4 acc. of speed/(mps^2)')
plt.legend()
bFigureShow=True ##当计算振动后,再显示绘图
plt.show()
wnd = tk.Tk()
menuBar = tk.Menu(wnd)
fMenu = tk.Menu(menuBar)
fMenu.add_command(label="打开发动机文件",command=open_file_engine)
fMenu.add_command(label="打开悬置文件",command=open_file_mount)
fMenu.add_command(label="退出",command=wnd.quit)
aMenu = tk.Menu(menuBar)
aMenu.add_command(label="版本信息",command=banben)
menuBar.add_cascade(label="文件", menu=fMenu)
menuBar.add_cascade(label="关于", menu=aMenu)
wnd["menu"] = menuBar
wnd.title('MountSys')
wnd.geometry('500x500') # 窗口尺寸
text1 = tk.Text(wnd, width=50, height=2, bg='orange', font=('Arial', 12))
text1.pack()
text2 = tk.Text(wnd, width=50, height=2, bg='yellow', font=('Arial', 12))
text2.pack()
bt1 = tk.Button(wnd, text='计算发动机激励', width=15, height=2, command=engine)
bt1.pack()
bt2 = tk.Button(wnd, text='计算模态', width=15, height=2, command=mount)
bt2.pack()
bt3 = tk.Button(wnd, text='计算振动', width=15, height=2, command=ForceResponse)
bt3.pack()
wnd.mainloop()
























 564
564











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








