To compile and launch DPVS, pls check README.md for this project.
Terminology
About the concepts of Full-NAT (FNAT), DR, Tunnel, toa, OSPF/ECMP and keepalived, pls refer LVS and Alibaba/LVS.
Note DPVS support FNAT, DR, Tunnel, SNAT forwarding modes, and each mode can be configured as one-arm or two-arm topology, with or without OSFP/ECMP/keepalived. There're too many combinations, I cannot list all the examples here. Let's just give some popular working models used in our daily work.
One-arm and two-arm
The term two-arm means, you have clients in one side of load-balancer (LB) and servers (RS) in another side, then LB forwards packets between its two logical network interfaces. For example, WAN-to-LAN load balancing.
On the other hand, one-arm means all clients and servers are in same side of load-balancer, LB forwards traffic through the same logical network interface.
Logical interface (or device) could be physical
DPDKinterface, orDPVSvirtual devices like bonding, vlan and tunnel devices.
To make things easier, we do not consider virtual devices for now. Thus, two-arm topology need
- two DPDK interfaces loaded with
igb_uiodriver, and /etc/dpvs.confshould also be configured with two interfaces. Pls refer the fileconf/dpvs.conf.sample.
$ dpdk-devbind --status Network devices using DPDK-compatible driver ============================================ 0000:06:00.0 'Ethernet Controller 10-Gigabit X540-AT2' drv=igb_uio unused=uio_pci_generic 0000:06:00.1 'Ethernet Controller 10-Gigabit X540-AT2' drv=igb_uio unused=uio_pci_generic
For one-arm, only one DPDK intreface needed, and you can refer conf/dpvs.conf.single-nic.sample.
KNI Device
Like LVS, DPVS can be deployed as different sort of Cluster models for High-Available (HA) purpose. Both OSPF/ECMP and Master/Backup models are supported. OSPF/ECMP model need package quagga and its zebra and ospfd programs. And master/back model need Keepalived.
Considering DPDK application manages the networking interface completely (except the extra control NIC if exist), Linux Kernel and programs run on Kernel TCP/IP stack cannot receive packets from DPDK interface directly. To make Linux programs like sshd, zebra/ospfd and keepalived work, DPDK kni device is used. Then the Linux programs can working on kni device with Linux TCP/IP stack. Actually, DPVS passes the packets, which it's not interested in, to kni device. For instance, OSPF/VRRP/ssh packets. So that the programs "working" on Linux stack are able to handle them.
We do not want to port
ospfd/keepalieved/sshdto DPDK environment, beacause TCP and Socket layer is needed. And the work load is another reason.

Note, keepalived is modified by DPVS project to support some specific parameters. The codes is resident in tools/keepalived and the executable is bin/keepalived. And ospfd/sshd is the standard version.
Let's start from Full-NAT example first, it's not the easiest but really popular.
【免费订阅,永久学习】学习地址:
LinuxC/C++服务器开发/架构师 面试题、学习资料、教学视频和学习路线图(资料包括C/C++,Linux,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis、MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK等),或点击这里加qun免费领取,关注我持续更新哦! !
【免费订阅,永久学习】学习地址:
Dpdk/网络协议栈/vpp/OvS/DDos/NFV/虚拟化/高性能专家-学习视频教程-腾讯课堂


Full-NAT Mode
Simple Full-NAT (two-arm)
This is a simple example for FullNAT (FNAT), forwarding between two interfaces. Assuming one is WAN interface (dpdk1) and another is LAN interface (dpdk0).
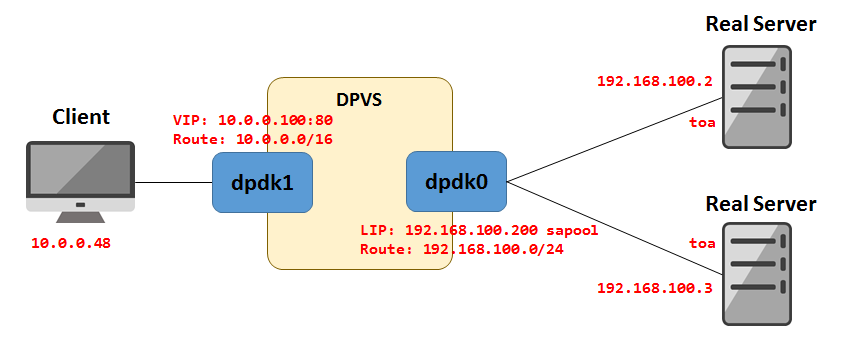
The setting including:
- ip-addresses and routes for DPDK LAN/WAN network.
- VIP on WAN interface (
dpdk1) FNATservice (vip:vport) and relatedRSFNATmode need at least one LIP on LAN interface (dpdk0)
#!/bin/sh - # add VIP to WAN interface ./dpip addr add 10.0.0.100/32 dev dpdk1 # route for WAN/LAN access # add routes for other network or default route if needed. ./dpip route add 10.0.0.0/16 dev dpdk1 ./dpip route add 192.168.100.0/24 dev dpdk0 # add service <VIP:vport> to forwarding, scheduling mode is RR. # use ipvsadm --help for more info. ./ipvsadm -A -t 10.0.0.100:80 -s rr # add two RS for service, forwarding mode is FNAT (-b) ./ipvsadm -a -t 10.0.0.100:80 -r 192.168.100.2 -b ./ipvsadm -a -t 10.0.0.100:80 -r 192.168.100.3 -b # add at least one Local-IP (LIP) for FNAT on LAN interface ./ipvsadm --add-laddr -z 192.168.100.200 -t 10.0.0.100:80 -F dpdk0
And you can use the commands below to check what's just set:
$ ./dpip addr show
inet 10.0.0.100/32 scope global dpdk1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.100.200/32 scope global dpdk0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever sa_used 0 sa_free 1032176








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 1338
1338











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








