学习网址:https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/mnist/beginners
MNIST是一个手写数组集,具体信息可以看 Yann LeCun's website: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/(deeplearning三大巨头之一)
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)"""Functions for downloading and reading MNIST data."""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import gzip
import os
import tempfile
import numpy
from six.moves import urllib
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist import read_data_sets
主要就是导入数据而已,可以略过去
def read_data_sets(train_dir,
fake_data=False,
one_hot=False,
dtype=dtypes.float32,
reshape=True,
validation_size=5000):
if fake_data:
def fake():
return DataSet([], [], fake_data=True, one_hot=one_hot, dtype=dtype)
train = fake()
validation = fake()
test = fake()
return base.Datasets(train=train, validation=validation, test=test)
TRAIN_IMAGES = 'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
TRAIN_LABELS = 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
TEST_IMAGES = 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
TEST_LABELS = 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
local_file = base.maybe_download(TRAIN_IMAGES, train_dir,
SOURCE_URL + TRAIN_IMAGES)
with open(local_file, 'rb') as f:
train_images = extract_images(f)
local_file = base.maybe_download(TRAIN_LABELS, train_dir,
SOURCE_URL + TRAIN_LABELS)
with open(local_file, 'rb') as f:
train_labels = extract_labels(f, one_hot=one_hot)
local_file = base.maybe_download(TEST_IMAGES, train_dir,
SOURCE_URL + TEST_IMAGES)
with open(local_file, 'rb') as f:
test_images = extract_images(f)
local_file = base.maybe_download(TEST_LABELS, train_dir,
SOURCE_URL + TEST_LABELS)
with open(local_file, 'rb') as f:
test_labels = extract_labels(f, one_hot=one_hot)
if not 0 <= validation_size <= len(train_images):
raise ValueError(
'Validation size should be between 0 and {}. Received: {}.'
.format(len(train_images), validation_size))
validation_images = train_images[:validation_size]
validation_labels = train_labels[:validation_size]
train_images = train_images[validation_size:]
train_labels = train_labels[validation_size:]
train = DataSet(train_images, train_labels, dtype=dtype, reshape=reshape)
validation = DataSet(validation_images,
validation_labels,
dtype=dtype,
reshape=reshape)
test = DataSet(test_images, test_labels, dtype=dtype, reshape=reshape)
return base.Datasets(train=train, validation=validation, test=test)The MNIST data is split into three parts: 55,000 data points of training data (mnist.train), 10,000 points of test data (mnist.test), and 5,000 points of validation data (mnist.validation). This split is very important: it's essential in machine learning that we have separate data which we don't learn from so that we can make sure that what we've learned actually generalizes!
这里面有三个数据集:training,cross validation(cv)和test,这是机器学习里面的一些常识,training由于训练,cv用于交叉验证,一般来说是找cv最好的作为最终输出,test是最终的测试结果了。
A one-hot vector is a vector which is 0 in most dimensions, and 1 in a single dimension.
You can picture our softmax regression as looking something like the following, although with a lot more xs. For each output, we compute a weighted sum of the xs, add a bias, and then apply softmax.
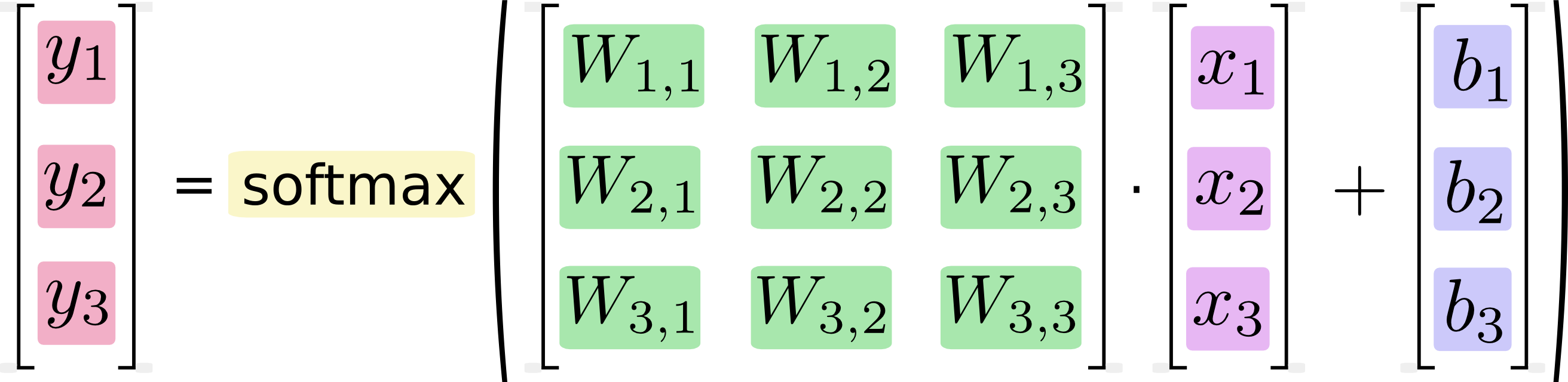
If we write that out as equations, we get:
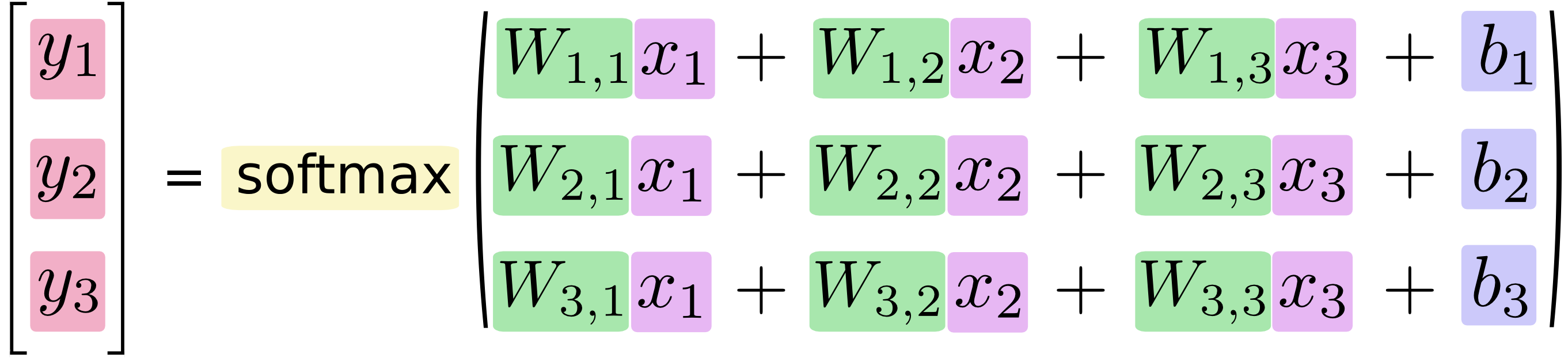
We can "vectorize" this procedure, turning it into a matrix multiplication and vector addition. This is helpful for computational efficiency. (It's also a useful way to think.)
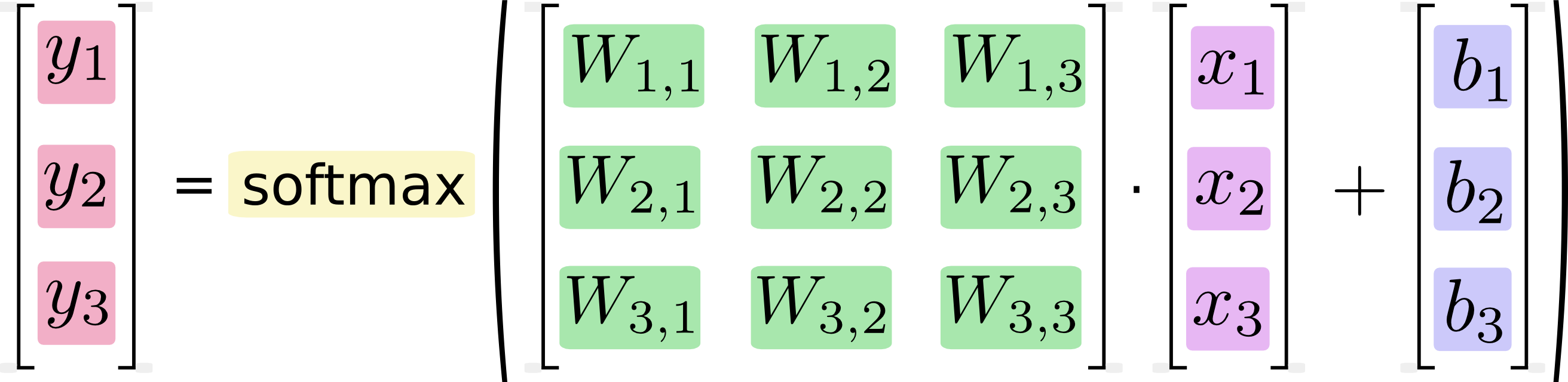
More compactly, we can just write:看一下input_data文件
<a href="http://private.codecogs.com/eqnedit.php?latex=y&space;=&space;\text{softmax}(Wx&space;+&space;b)" target="_blank"><img src="http://latex.codecogs.com/gif.latex?y&space;=&space;\text{softmax}(Wx&space;+&space;b)" title="y = \text{softmax}(Wx + b)" /></a>
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b)
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for _ in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels}))
这里的模型非常简单,看一下神经网络基本能搞定























 821
821

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








