前言
本人以笔记的方式来记录学习过程,仅当学习的输出,加深自己学习印象
手写spring的思路
通过手写spring,虽然和源码有差别,但有助于了解整体过程
(1)了解spring启动过程
(2)了解BeanDefinition、BeanPostProcessor的概念
(3)了解Spring依赖注入、Aware回调的工作原理
(4)了解AOP的工作原理
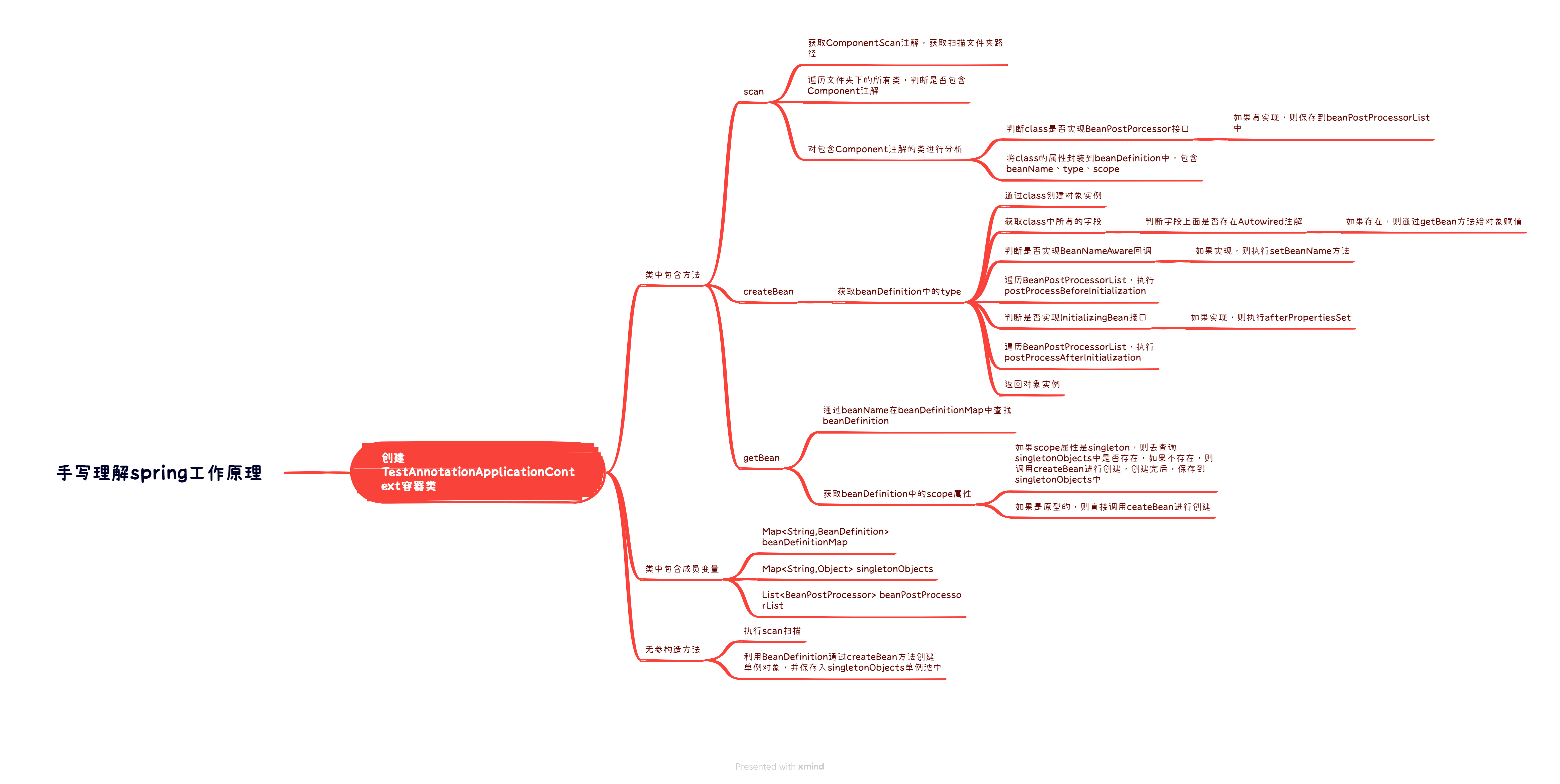
以下是applicationContext的思维导图
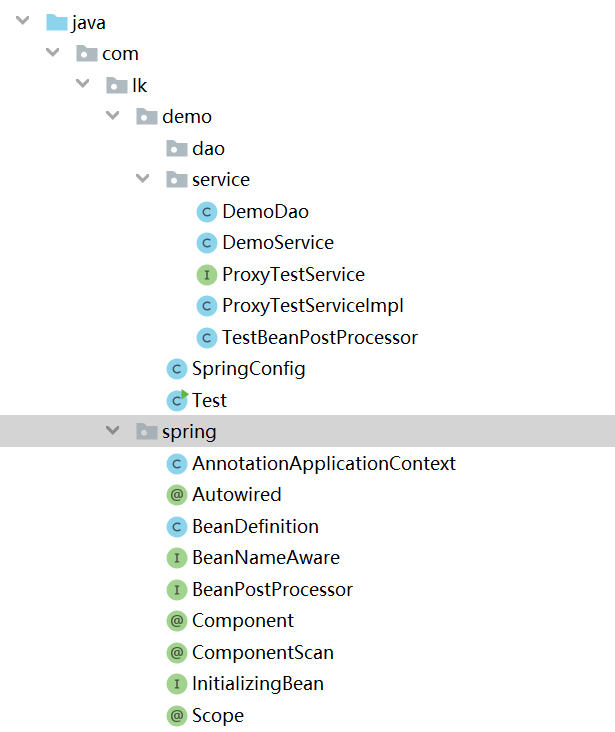
 包目录结构如下:
包目录结构如下:
代码
1. 首先创建spring相关的类
创建AnnotationApplicationContext
package com.lk.spring;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class AnnotationApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
private Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new HashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
private Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new HashMap<String, Object>();
private List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessorList = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
public AnnotationApplicationContext(Class configClass) throws Exception {
this.configClass = configClass;
// 扫描
scan(configClass);
// 创建单例bean
for (Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition> entry : beanDefinitionMap.entrySet()) {
String beanName = entry.getKey();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = entry.getValue();
if ("singleton".equals(beanDefinition.getScope())){
Object bean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
}
private Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception{
Class aClass = beanDefinition.getType();
Object instance = null;
instance = aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// 获取所有Autowired注解的字段,并注入
for (Field field : aClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(instance, getBean(field.getName()));
}
}
// 执行 BeanNameAware 回调
if (instance instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) instance).setBeanName(beanName);
}
// 遍历beanPostProcessor执行postProcessBeforeInitialization
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(instance, beanName);
}
// 如果实现InitializingBean接口,执行afterPropertiesSet初始化方法执行
if (instance instanceof InitializingBean) {
((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertiesSet();
}
// 遍历beanPostProcessor执行postProcessAfterInitialization
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(instance, beanName);
}
// 返回创建好的对象
return instance;
}
public Object getBean(String beanName) throws Exception{
// 获取beanDefinition,判断是否为单例bean
if (!beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
throw new Exception();
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if ("singleton".equals(beanDefinition.getScope())) {
Object bean = singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果单例池中为空,说明还没创建,则调用createBean进行创建,并将创建好的bean放入单例池
if (null == bean) {
bean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);
}
return bean;
} else {
// 原型
Object prototypeBean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
return prototypeBean;
}
}
private void scan(Class configClass) throws Exception {
if (configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)){
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScan.value();
String newPath = path.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println(newPath);
ClassLoader classLoader = AnnotationApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
URL resources = classLoader.getResource(newPath);
File file = new File(resources.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()){
for (File f : file.listFiles()) {
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println(absolutePath);
absolutePath = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("com"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
absolutePath = absolutePath.replace("\\", ".");
Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(absolutePath);
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
// 判断是否实现接口BeanPostProcessor,如果是,则需要保存到beanPostProcessorList中
if (BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(aClass)) {
BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor) aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
beanPostProcessorList.add(beanPostProcessor);
}
// 如果是普通bean,则创建beanDefinition,并保存到beanDefinitionMap中
Component component = aClass.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = component.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)) {
// 如果没有指定beanName,则默认以类名首字母小写作为beanName
beanName = Introspector.decapitalize(aClass.getSimpleName());
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanName(beanName);
beanDefinition.setType(aClass);
// 判断类是否为单例
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
Scope scopeAnnotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
String scope = scopeAnnotation.value();
if (!"prototype".equals(scope) && !"singleton".equals(scope)) {
scope = "singleton";
}
beanDefinition.setScope(scope);
} else {
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
}
}
}
}
}
创建BeanDefinition
package com.lk.spring;
public class BeanDefinition {
private Class type;
private String scope;
private String beanName;
public Class getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Class type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
public String getBeanName() {
return beanName;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
this.beanName = beanName;
}
}
创建Autowired
package com.lk.spring;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Autowired {
}
创建BeanNameAware
package com.lk.spring;
public interface BeanNameAware {
void setBeanName(String name);
}
创建BeanPostProcessor
package com.lk.spring;
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName){
return bean;
}
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
}
创建Component
package com.lk.spring;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}
创建ComponentScan
package com.lk.spring;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ComponentScan {
String value() default "";
}
创建InitializingBean
package com.lk.spring;
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet();
}
创建Scope
package com.lk.spring;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Scope {
String value() default "";
}
创建测试类
1. 创建sringConfig
package com.lk.demo;
import com.lk.spring.Component;
import com.lk.spring.ComponentScan;
@ComponentScan("com.lk.demo.service")
public class SpringConfig {
}
2.创建DemoService
package com.lk.demo.service;
import com.lk.spring.Autowired;
import com.lk.spring.Component;
@Component
public class DemoService {
@Autowired
private DemoDao demoDao;
public void demo() {
System.out.println(111);
System.out.println(demoDao);
}
}
3.创建DemoDao
package com.lk.demo.service;
import com.lk.spring.Component;
@Component
public class DemoDao {
}
4.创建ProxyTestService
package com.lk.demo.service;
public interface ProxyTestService {
}
5.创建ProxyTestServiceImpl
package com.lk.demo.service;
import com.lk.spring.Component;
@Component("proxyTestService")
public class ProxyTestServiceImpl implements ProxyTestService {
}
6.创建TestBeanPostProcessor
package com.lk.demo.service;
import com.lk.spring.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.lk.spring.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
@Component
public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
// 创建代理对象
if ("proxyTestService".equals(beanName)) {
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(TestBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行代理逻辑");
return method.invoke(bean, args);
}
});
return proxyInstance;
}
return bean;
}
}
7.创建Test用于最终测试
package com.lk.demo;
import com.lk.demo.service.DemoService;
import com.lk.demo.service.ProxyTestService;
import com.lk.spring.AnnotationApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
System.out.println(12121);
AnnotationApplicationContext annotationApplicationContext = new AnnotationApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
DemoService demoService = (DemoService) annotationApplicationContext.getBean("demoService");
demoService.demo();
ProxyTestService proxyTestService = (ProxyTestService) annotationApplicationContext.getBean("proxyTestService");
System.out.println(proxyTestService);
}
}




















 814
814

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








