时间:2021.8.26 上午
目录
一、复杂网络
(一)构造网络(加权有向网络)
代码:
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
column1 = []
with open('node-9.txt','r') as f:
line = f.readline() # 读取一行
while line:
txt_data = eval(line) # 可将字符串变为元组
column1.append(txt_data) # 列表增加
line = f.readline() # 读取下一行
#print(column1)
edge = []
with open('edge-9.txt','r') as f:
line = f.readline() # 读取一行
while line:
txt_data = eval(line) # 可将字符串变为元组
edge.append(txt_data) # 列表增加
line = f.readline() # 读取下一行
#print(edge)
G = nx.DiGraph()
G.add_nodes_from(column1)
G.add_weighted_edges_from(edge)
nx.draw_networkx(G,pos=nx.shell_layout(G),node_size=20,node_shape='o',width=1,style='solid',font_size=8)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
#print ( G.nodes())
网络图

(二)度分布
接上面的代码,先导入import numpy as np
度分布直方图代码:
import numpy as np
degree_freq = np.array(nx.degree_histogram(G)).astype('float')
plt.stem(degree_freq)
plt.ylabel("Frequence")
plt.xlabel("Degree")
plt.show()
结果图
(三)算法1:寻路和图搜索算法
1.寻路算法
寻路算法:通过最小化跳(hop)的数量来寻找两个节点之间的最短路径。
-
最短路径(单源最短路径(Single Source Shortest Path/SSSP)、所有配对最短路径(All Pairs Shortest Path / APSP))(更多最短路径问题的介绍:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shortest_path_problem);
-
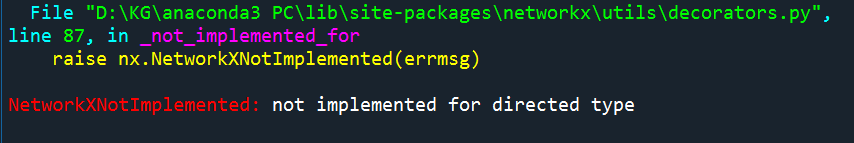
最小权重生成树(minimum spanning tree),应该用于无向图。
-
最短路径代码
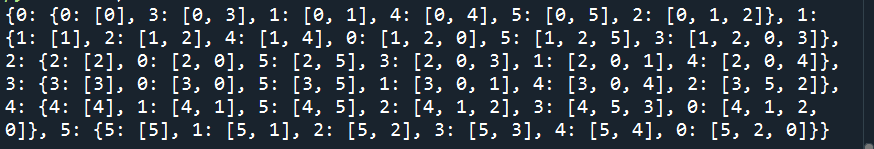
# Returns shortest path between each node返回图中每个节点之间的最小路径的列表
sh= nx.shortest_path(G)
print(sh)
- 最小权重生成树代码
from networkx.algorithms import tree
#最小权重生成树(minimum spanning tree)应该用于无向图 报错
mst = tree.minimum_spanning_edges(G, algorithm='prim', data=False)
edgelist = list(mst)
sorted(edgelist)
结果展示
2.搜索算法
搜索算法:不是给出最短路径,而是根据图的相邻情况或深度来探索图,可用于信息检索。宽度优先搜索(BFS)、深度优先搜索(DFS)。
(四)社区检测
1.Community detection(社群检测)
接数据代码:
from networkx.algorithms import community
import itertools
#社区算法 Girvan Newman 算法
k = 1 # k=1 的意思是我们期望得到 2 个社群
comp = community.girvan_newman(G)
for communities in itertools.islice(comp, k):
print(tuple(sorted(c) for c in communities))
完整代码:
import networkx as nx
import itertools
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from networkx.algorithms import community
column1 = []
with open('node-9.txt','r') as f:
line = f.readline() # 读取一行
while line:
txt_data = eval(line) # 可将字符串变为元组
column1.append(txt_data) # 列表增加
line = f.readline() # 读取下一行
#print(column1)
edge = []
with open('edge-9.txt','r') as f:
line = f.readline() # 读取一行
while line:
txt_data = eval(line) # 可将字符串变为元组
edge.append(txt_data) # 列表增加
line = f.readline() # 读取下一行
#print(edge)
G = nx.DiGraph()
G.add_nodes_from(column1)
G.add_weighted_edges_from(edge)
nx.draw_networkx(G,pos=nx.shell_layout(G),node_size=20,node_shape='o',width=1,style='solid',font_size=8)
plt.show()
#print ( G.nodes())
#社区算法 Girvan Newman 算法
k = 1 # k=1 的意思是我们期望得到 2 个社群
comp = community.girvan_newman(G)
for communities in itertools.islice(comp, k):
print(tuple(sorted(c) for c in communities))
结果:

2.Louvain 算法
需要无向网络
import community
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
column1 = []
with open('node-9.txt','r') as f:
line = f.readline() # 读取一行
while line:
txt_data = eval(line) # 可将字符串变为元组
column1.append(txt_data) # 列表增加
line = f.readline() # 读取下一行
#print(column1)
edge = []
with open('edge-10.txt','r') as f:
line = f.readline() # 读取一行
while line:
txt_data = eval(line) # 可将字符串变为元组
edge.append(txt_data) # 列表增加
line = f.readline() # 读取下一行
#print(edge)
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_nodes_from(column1)
G.add_edges_from(edge)
pos = nx.spring_layout(G)
partition = community.best_partition(G)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.axis('off')
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G, pos, node_size=600, cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu, node_color=list(partition.values()))
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, pos, alpha=0.3)
plt.show(G)
如果是原来的有向加权,可以看到报错
import community
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
column1 = []
with open('node-9.txt','r') as f:
line = f.readline() # 读取一行
while line:
txt_data = eval(line) # 可将字符串变为元组
column1.append(txt_data) # 列表增加
line = f.readline() # 读取下一行
#print(column1)
edge = []
with open('edge-9.txt','r') as f:
line = f.readline() # 读取一行
while line:
txt_data = eval(line) # 可将字符串变为元组
edge.append(txt_data) # 列表增加
line = f.readline() # 读取下一行
#print(edge)
G = nx.DiGraph()
G.add_nodes_from(column1)
G.add_weighted_edges_from(edge)
pos = nx.spring_layout(G)
partition = community.best_partition(G)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.axis('off')
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G, pos, node_size=600, cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu, node_color=list(partition.values()))
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, pos, alpha=0.3)
plt.show(G)
结果报错: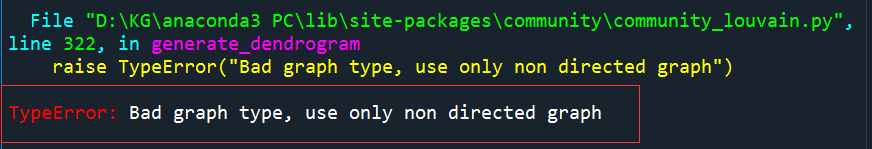
# 参考链接 [社会网络分析——三、图论与图学习](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44194088/article/details/115574600)
总结:问题仍未解决,需要计算点强度,如何正确使用加权网络,利用权重分析图。






















 974
974











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








