unordered_map
一.介绍
1.1介绍
-
unordered_map是C++11正式加入的对hash_map的官方实现(之前标准C++没有hash_map的官方实现,我们使用的STL的hash_map并不是官方的)。
-
从名字可以看出这个结构是无序的,底层设计思想和STL的hash_map一样。元素在内部不以任何特定顺序排序,而是放进桶中。元素放进哪个桶完全依赖于 其键的哈希。这允许对单独元素的快速访问,因为一旦计算哈希,则它准确指代元素所放进的桶。
-
unordered_map搜索、插入和元素移除拥有平均常数时间复杂度。
-
unordered_map 容器在<unordered_map>头文件中,并位于 std 命名空间中。因此,如果想使用该容器,代码中应包含如下语句:#include <unordered_map> using namespace std;
-
模板:template < class Key, //键值对中键的类型
class T, //键值对中值的类型
class Hash = hash<Key>, //容器内部存储键值对所用的哈希函数
class Pred = equal_to<Key>, //判断各个键值对键相同的规则
class Alloc = allocator< pair<const Key,T> > // 指定分配器对象的类型
> class unordered_map;
-
主要使用的也是模板的前2个参数<键,值>: unordered_map<const Key, T> umap;
-
以上 5 个参数中,必须显式给前 2 个参数传值,并且除特殊情况外,最多只需要使用前 4 个参数,各自的含义和功能如表 1 所示。

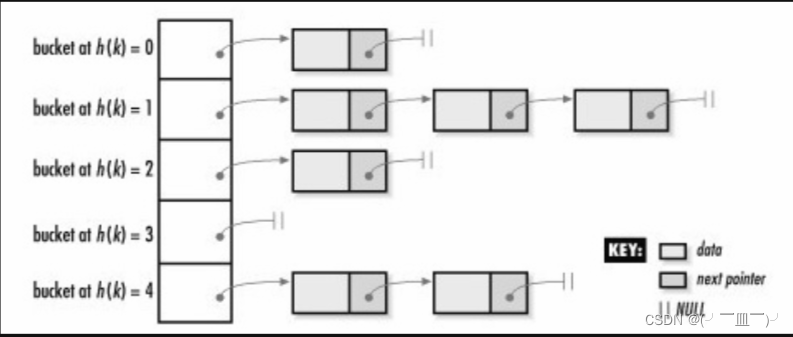
1.2 Hashtable和bucket
由于unordered_map内部采用的hashtable的数据结构存储,所以,每个特定的key会通过一些特定的哈希运算映射到一个特定的位置,我们知道,hashtable是可能存在冲突的(多个key通过计算映射到同一个位置),在同一个位置的元素会按顺序链在后面。所以把这个位置称为一个bucket是十分形象的(像桶子一样,可以装多个元素)。
2.1 迭代器
unordered_map的迭代器是一个指针,指向这个元素,通过迭代器来取得它的值。
unordered_map<Key,T>::iterator it;
(*it).first; // the key value (of type Key)--键
(*it).second; // the mapped value (of type T)--值
(*it); // the "element value" (of type pair<const Key,T>)
it->first; // same as (*it).first (the key value)
it->second; // same as (*it).second (the mapped value)
遍历intHash
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main(){
unordered_map<int, int> intHash;
intHash[1] = 123;
intHash[2] = 456;
intHash[3] = 789;
for (auto it = intHash.begin(); it != intHash.end(); ++it)
cout << " " << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
}
3. 功能函数
3.1 构造函数
unordered_map的构造方式有几种:
- 构造空的容器
- 复制构造
- 范围构造
- 用数组构造
3.1.2示例代码
// constructing unordered_maps
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef
unordered_map<string,string>
stringmap
;
stringmap merge (stringmap a,stringmap b)
//返回临时 unordered_map 容器的函数
{
stringmap temp(a);
temp.insert(b.begin(),b.end());
return temp;
}
int main ()
{
stringmap first; // 空
stringmap second ( {{"apple","red"},{"lemon","yellow"}} ); // 用数组初始
stringmap third;
third["orange"]="orange",third["strawberry"]="red";
stringmap fourth (second); // 复制初始化
stringmap fifth (merge(third,fourth)); // 移动初始化
stringmap sixth (fifth.begin(),fifth.end()); // 范围初始化
cout << "sixth contains:";
for (auto& x: sixth) cout << " " << x.first << ":" << x.second;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
sixth contains: apple:red lemon:yellow orange:orange strawberry:red
3.2 容量操作
3.2.1 size
size_type size() const noexcept;
返回unordered_map的大小
3.2.2 empty
bool empty() const noexcept;
- 为空返回true
- 不为空返回false,和用size() == 0判断一样。
3.3 元素操作
3.3.1 find
iterator find ( const key_type& k );
查找key所在的元素。
- 找到:返回元素的迭代器。通过迭代器的second属性获取值
- 没找到:返回unordered_map::end--umap.end()
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main(){
unordered_map<int, string> strHash;
strHash[12] = "123";
strHash[25] = "456";
strHash[39] = "789";
unordered_map<int, string>::iterator it = strHash.begin();
it = strHash.find(25);//查找结果
if(it != strHash.end()){
cout <<"key:"<<it->first<<",value:"<< it->second << endl;//键值的表示
}else
{
cout << "not find" << endl;
}
}
判断存在次数:
count函数
unordered_map<int, string> strHash
if(strHash.count(0)==0)
{
cout<<"not exist"<<endl;
}
else if(strHash.count(0)>0)
{
cout<<"exist"<<endl;
}
3.3.2 insert
插入有几种方式:
- 复制插入(复制一个已有的pair的内容)
- 数组插入(直接插入一个二维数组)
- 范围插入(复制一个起始迭代器和终止迭代器中间的内容)
- 数组访问模式插入(和数组的[]操作很相似)
具体的例子可以看后面示例代码。
3.3.3 at
mapped_type& at ( const key_type& k );
查找key所对应的值
- 如果存在:返回key对应的值,可以直接修改,和[]操作一样。
- 如果不存在:抛出 out_of_range 异常.
mymap.at(“Mars”) = 3396;----/mymap[“Mars”] = 3396
3.3.4 erase
擦除元素也有几种方式:
-
通过位置(迭代器)iterator erase ( const_iterator position );
-
通过key
size_type erase ( const key_type& k );
-
通过范围(两个迭代器)
iterator erase ( const_iterator first, const_iterator last );
3.5 clear
void clear() noexcept
3.3.6 swap
void swap ( unordered_map& ump );
交换两个unordered_map(注意,不是交换特定元素,是整个交换两个map中的所有元素)
tmp.swap(umap);
swap(tmp, umap);
3.3.7 示例代码
// unordered_map::insert
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
void display(unordered_map<string,double> myrecipe,string str)
{
cout << str << endl;
for (auto& x: myrecipe)
cout << x.first << ": " << x.second << endl;
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
unordered_map<string,double>
myrecipe,
mypantry = {{"milk",2.0},{"flour",1.5}};
/****************插入*****************/
pair<string,double> myshopping ("baking powder",0.3);
myrecipe.insert (myshopping); // 复制插入
myrecipe.insert (make_pair<string,double>("eggs",6.0)); // 移动插入
myrecipe.insert (mypantry.begin(), mypantry.end()); // 范围插入
myrecipe.insert ({{"sugar",0.8},{"salt",0.1}}); // 初始化数组插入(可以用二维一次插入多个元素,也可以用一维插入一个元素)
umap.insert(make_pair(4, 4));
umap.insert(
pair
<
int
,
int
>(4, 4));
myrecipe["coffee"] = 10.0; //数组形式插入
display(myrecipe,"myrecipe contains:");
/****************查找*****************/
unordered_map<string,double>::const_iterator got = myrecipe.find ("coffee");
if ( got == myrecipe.end() )
cout << "not found";
else
cout << "found "<<got->first << " is " << got->second<<"
";
/****************修改*****************/
myrecipe.at("coffee") = 9.0;
myrecipe["milk"] = 3.0;
display(myrecipe,"After modify myrecipe contains:");
/****************擦除*****************/
myrecipe.erase(myrecipe.begin()); //通过位置
myrecipe.erase("milk"); //通过key
display(myrecipe,"After erase myrecipe contains:");
/****************交换*****************/
myrecipe.swap(mypantry);
display(myrecipe,"After swap with mypantry, myrecipe contains:");
/****************清空*****************/
myrecipe.clear();
display(myrecipe,"After clear, myrecipe contains:");
return 0;
}
输出结果:
myrecipe contains:
salt: 0.1
milk: 2
flour: 1.5
coffee: 10
eggs: 6
sugar: 0.8
baking powder: 0.3
found coffee is 10
After modify myrecipe contains:
salt: 0.1
milk: 3
flour: 1.5
coffee: 9
eggs: 6
sugar: 0.8
baking powder: 0.3
After erase myrecipe contains:
flour: 1.5
coffee: 9
eggs: 6
sugar: 0.8
baking powder: 0.3
After swap with mypantry, myrecipe contains:
flour: 1.5
milk: 2
After clear, myrecipe contains:
3.4 迭代器和bucket操作
3.4.1 begin
iterator begin() noexcept;
local_iterator begin ( size_type n );
-
begin() : 返回开始的迭代器(和你的输入顺序没关系,因为它的无序的)
-
begin(int n) : 返回n号bucket的第一个迭代器
3.4.2 end
iterator end() noexcept;
local_iterator end( size_type n );
-
end(): 返回结束位置的迭代器
-
end(int n) : 返回n号bucket的最后一个迭代器
3.4.3 bucket
size_type bucket ( const key_type& k ) const;
返回通过哈希计算key所在的bucket(注意:这里仅仅做哈希计算确定bucket,并不保证key一定存在bucket中!)
3.4.4 bucket_count
size_type bucket_count() const noexcept;
返回bucket的总数
3.4.5 bucket_size
size_type bucket_size ( size_type n ) const;
返回第i个bucket的大小(这个位置的桶子里有几个元素,注意:函数不会判断n是否在count范围内)
3.4.6 示例代码
// unordered_map::bucket_count
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int
main()
{
unordered_map
<
string
,
string
> mymap =
{
{
"house"
,
"maison"
},
{
"apple"
,
"pomme"
},
{
"tree"
,
"arbre"
},
{
"book"
,
"livre"
},
{
"door"
,
"porte"
},
{
"grapefruit"
,
"pamplemousse"
}
};
/************begin和end迭代器***************/
cout
<<
"mymap contains:"
;
for
(
auto
it = mymap.begin(); it
!=
mymap.end();
++
it)
cout
<<
" "
<<
it
->
first
<<
":"
<<
it
->
second;
cout
<<
endl;
/************bucket操作***************/
unsigned
n = mymap.bucket_count();
cout
<<
"mymap has "
<<
n
<<
" buckets. "
<<
endl;
for
(
unsigned
i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cout
<<
"bucket #"
<<
i
<<
"'s size:"
<<
mymap.bucket_size(i)
<<
" contains: "
;
for
(
auto
it = mymap.begin(i); it
!=
mymap.end(i);
++
it)
cout
<<
"["
<<
it
->
first
<<
":"
<<
it
->
second
<<
"] "
;
cout
<<
endl;
}
cout
<<
"key:'apple' is in bucket #"
<<
mymap.bucket(
"apple"
)
<<
endl;
cout
<<
"key : 'computer' is in bucket #"
<<
mymap.bucket(
"computer"
)
<<
endl;
return
0;
}
输出结果:























 1755
1755

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








