BufferQueueLayer是Android系统中的一个图层,用于管理图像缓冲区的队列。它是SurfaceFlinger系统服务的一部分,负责接收应用程序或系统组件提交的图像缓冲区,并将其显示在屏幕上。onFirstRef是BufferQueueLayer类的一个方法,它是在第一次引用BufferQueueLayer对象时被调用的。在这个方法中,可以进行一些初始化操作,例如创建和配置图像缓冲区队列。
在创建BufferQueueLayer同时会创建一套生产者-消费者模型架构,核心是如下几个类:
BufferQueueLayer:创建了BufferQueue、MonitoredProducer、BufferLayerConsumer
BufferQueue:buffer队列,创建BufferQueueCore,BufferQueueProducer
BufferQueueProducer:生产者
BufferQueueConsumer:消费者
MonitoredProducer:生产者的封装
BufferLayerConsumer:消费者的封装
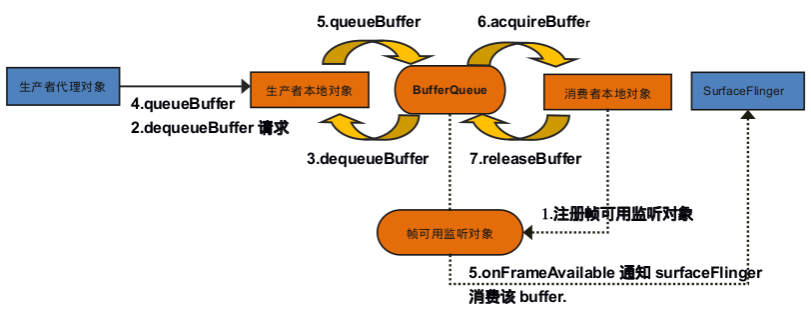
生产者提供图形数据,放入BufferQueue,消费者拿到图形数据进行合成,通常认为生产者为Surface,消费者为SurfaceFlinger,下面我们就分析一下生产者-消费者模型架构的搭建。
我们以BufferQueueLayer的创建为入口分析:
//frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/BufferQueueLayer.cpp
void BufferQueueLayer::onFirstRef() {
BufferLayer::onFirstRef();
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> producer;
sp<IGraphicBufferConsumer> consumer;
//步骤1
BufferQueue::createBufferQueue(&producer, &consumer, true); //创建BufferQueue
//步骤2
mProducer = new MonitoredProducer(producer, mFlinger, this); //创建一个生产者
{
// Grab the SF state lock during this since it's the only safe way to access RenderEngine
Mutex::Autolock lock(mFlinger->mStateLock);
//步骤3
mConsumer =
new BufferLayerConsumer(consumer, mFlinger->getRenderEngine(), mTextureName, this); //创建一个消费者
{
}
//步骤4
mConsumer->setConsumerUsageBits(getEffectiveUsage(0)); //设置缓冲区的类型,会保存到BufferQueueCore中的mConsumerUsageBits变量中
//步骤5
mConsumer->setContentsChangedListener(this); //设置缓冲区内容改变的监听器
mConsumer->setName(mName);
// BufferQueueCore::mMaxDequeuedBufferCount is default to 1
if (!mFlinger->isLayerTripleBufferingDisabled()) {
mProducer->setMaxDequeuedBufferCount(2);
}
if (const auto display = mFlinger->getDefaultDisplayDevice()) {
updateTransformHint(display);
}
if (mFlinger->mLayerExt) {
mLayerType = mFlinger->mLayerExt->getLayerClass(mName.string());
}
}
上面这个函数就是创建SurfaceFlinger生产者-消费者模型的核心代码,我们分步骤分析:
BufferQueue createBufferQueue
步骤1:createBufferQueue,从名字看就能知道是创建BufferQueue,并且将生产者producer和消费者consumer的地址传了过去,显然这两个对象也会在createBufferQueue中创建。
//frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueue.cpp
void BufferQueue::createBufferQueue(sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>* outProducer,
sp<IGraphicBufferConsumer>* outConsumer,
bool consumerIsSurfaceFlinger) {
sp<BufferQueueCore> core(new BufferQueueCore()); //创建BufferQueueCore
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> producer(new BufferQueueProducer(core, consumerIsSurfaceFlinger)); //创建BufferQueueProducer
sp<IGraphicBufferConsumer> consumer(new BufferQueueConsumer(core)); //创建BufferQueueConsumer
*outProducer = producer;
*outConsumer = consumer;
}
可以看到这个函数中并没有创建BufferQueue,而是创建的BufferQueueCore,可见BufferQueue的核心实现其实是依靠BufferQueueCore的,接着又创建了生产者的具体实现类BufferQueueProducer,消费者的具体实现类BufferQueueConsumer,并且这两个类都持有BufferQueueCore的引用,最后outProducer,outConsumer分别指向创建的生产者-消费者,下面分别进行分析:
new BufferQueueCore
创建BufferQueueCore对象,BufferQueueCore的构造方法如下:
//frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueCore.cpp
class BufferQueueCore : public virtual RefBase {
BufferQueueCore::BufferQueueCore()
: mMutex(),
mIsAbandoned(false),
mConsumerControlledByApp(false),
mConsumerName(getUniqueName()),
mConsumerListener(),
mConsumerUsageBits(0),
mConsumerIsProtected(false),
mConnectedApi(NO_CONNECTED_API),
mLinkedToDeath(),
mConnectedProducerListener(),
mBufferReleasedCbEnabled(false),
mSlots(),
mQueue(),
mFreeSlots(),
mFreeBuffers(),
mUnusedSlots(),
mActiveBuffers(),
mDequeueCondition(),
mDequeueBufferCannotBlock(false),
mQueueBufferCanDrop(false),
mLegacyBufferDrop(true),
mDefaultBufferFormat(PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888),
mDefaultWidth(1),
mDefaultHeight(1),
mDefaultBufferDataSpace(HAL_DATASPACE_UNKNOWN),
mMaxBufferCount(BufferQueueDefs::NUM_BUFFER_SLOTS),
mMaxAcquiredBufferCount(1),
mMaxDequeuedBufferCount(1),
mBufferHasBeenQueued(false),
mFrameCounter(0),
mTransformHint(0),
mIsAllocating(false),
mIsAllocatingCondition(),
mAllowAllocation(true),
mBufferAge(0),
mGenerationNumber(0),
mAsyncMode(false),
mSharedBufferMode(false),
mAutoRefresh(false),
mSharedBufferSlot(INVALID_BUFFER_SLOT),
mSharedBufferCache(Rect::INVALID_RECT, 0, NATIVE_WINDOW_SCALING_MODE_FREEZE,
HAL_DATASPACE_UNKNOWN),
mLastQueuedSlot(INVALID_BUFFER_SLOT),
mUniqueId(getUniqueId()),
mAutoPrerotation(false),
mTransformHintInUse(0) {
int numStartingBuffers = getMaxBufferCountLocked();
for (int s = 0; s < numStartingBuffers; s++) {
mFreeSlots.insert(s);
}
for (int s = numStartingBuffers; s < BufferQueueDefs::NUM_BUFFER_SLOTS;
s++) {
mUnusedSlots.push_front(s);
}
}
}
new BufferQueueProducer
创建BufferQueueProducer对象,BufferQueueProducer的构造方法如下:
//frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueProducer.cpp
class BufferQueueProducer : public BnGraphicBufferProducer,
private IBinder::DeathRecipient {
BufferQueueProducer::BufferQueueProducer(const sp<BufferQueueCore>& core,
bool consumerIsSurfaceFlinger) :
mCore(core),
mSlots(core->mSlots),
mConsumerName(),
mStickyTransform(0),
mConsumerIsSurfaceFlinger(consumerIsSurfaceFlinger),
mLastQueueBufferFence(Fence::NO_FENCE),
mLastQueuedTransform(0),
mCallbackMutex(),
mNextCallbackTicket(0),
mCurrentCallbackTicket(0),
mCallbackCondition(),
mDequeueTimeout(-1),
mDequeueWaitingForAllocation(false) {}
}
new BufferQueueConsumer
创建BufferQueueConsumer对象,BufferQueueConsumer的构造方法如下:
//frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueConsumer.cpp
class BufferQueueConsumer : public BnGraphicBufferConsumer {
BufferQueueConsumer::BufferQueueConsumer(const sp<BufferQueueCore>& core) :
mCore(core),
mSlots(core->mSlots),
mConsumerName() {}
}
new MonitoredProducer
步骤2:为生产者对象创建一个MonitoredProducer,这个类完全就是生产者的封装类,它里面的所有函数几乎都是通过传递进去的producer来完成的,MonitoredProducer类定义如下:
//frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/MonitoredProducer.cpp
class MonitoredProducer : public BnGraphicBufferProducer {
public:
MonitoredProducer(const sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>& producer,
const sp<SurfaceFlinger>& flinger,
const wp<Layer>& layer);
virtual ~MonitoredProducer();
// From IGraphicBufferProducer
virtual status_t requestBuffer(int slot, sp<GraphicBuffer>* buf);
virtual status_t setMaxDequeuedBufferCount(int maxDequeuedBuffers);
virtual status_t setAsyncMode(bool async);
virtual status_t dequeueBuffer(int* slot, sp<Fence>* fence, uint32_t w, uint32_t h,
PixelFormat format, uint64_t usage, uint64_t* outBufferAge,
FrameEventHistoryDelta* outTimestamps);
virtual status_t detachBuffer(int slot);
virtual status_t detachNextBuffer(sp<GraphicBuffer>* outBuffer,
sp<Fence>* outFence);
virtual status_t attachBuffer(int* outSlot,
const sp<GraphicBuffer>& buffer);
virtual status_t queueBuffer(int slot, const QueueBufferInput& input,
QueueBufferOutput* output);
virtual status_t cancelBuffer(int slot, const sp<Fence>& fence);
virtual int query(int what, int* value);
virtual status_t connect(const sp<IProducerListener>& token, int api,
bool producerControlledByApp, QueueBufferOutput* output);
virtual status_t disconnect(int api, DisconnectMode mode);
virtual status_t setSidebandStream(const sp<NativeHandle>& stream);
virtual void allocateBuffers(uint32_t width, uint32_t height,
PixelFormat format, uint64_t usage);
virtual status_t allowAllocation(bool allow);
virtual status_t setGenerationNumber(uint32_t generationNumber);
virtual String8 getConsumerName() const override;
virtual status_t setDequeueTimeout(nsecs_t timeout) override;
virtual status_t setLegacyBufferDrop(bool drop) override;
virtual status_t getLastQueuedBuffer(sp<GraphicBuffer>* outBuffer,
sp<Fence>* outFence, float outTransformMatrix[16]) override;
virtual IBinder* onAsBinder();
virtual status_t setSharedBufferMode(bool sharedBufferMode) override;
virtual status_t setAutoRefresh(bool autoRefresh) override;
virtual void getFrameTimestamps(FrameEventHistoryDelta *outDelta) override;
virtual status_t getUniqueId(uint64_t* outId) const override;
virtual status_t getConsumerUsage(uint64_t* outUsage) const override;
// The Layer which created this producer, and on which queued Buffer's will be displayed.
sp<Layer> getLayer() const;
private:
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> mProducer;
sp<SurfaceFlinger> mFlinger;
// The Layer which created this producer, and on which queued Buffer's will be displayed.
wp<Layer> mLayer;
};
}; // namespace android
new BufferLayerConsumer
步骤3:为生产者对象创建一个BufferLayerConsumer,这个类完全就是消费者的封装类,BufferLayerConsumer类定义如下:
//frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/BufferLayerConsumer.cpp
class BufferLayerConsumer : public ConsumerBase {
public:
static const status_t BUFFER_REJECTED = UNKNOWN_ERROR + 8;
class BufferRejecter {
friend class BufferLayerConsumer;
virtual bool reject(const sp<GraphicBuffer>& buf, const BufferItem& item) = 0;
protected:
virtual ~BufferRejecter() {}
};
struct ContentsChangedListener : public FrameAvailableListener {
virtual void onSidebandStreamChanged() = 0;
};
// BufferLayerConsumer constructs a new BufferLayerConsumer object. The
// tex parameter indicates the name of the RenderEngine texture to which
// images are to be streamed.
BufferLayerConsumer(const sp<IGraphicBufferConsumer>& bq, renderengine::RenderEngine& engine,
uint32_t tex, Layer* layer);
// Sets the contents changed listener. This should be used instead of
// ConsumerBase::setFrameAvailableListener().
void setContentsChangedListener(const wp<ContentsChangedListener>& listener);
// updateTexImage acquires the most recently queued buffer, and sets the
// image contents of the target texture to it.
//
// This call may only be made while RenderEngine is current.
//
// This calls doFenceWait to ensure proper synchronization unless native
// fence is supported.
//
// Unlike the GLConsumer version, this version takes a functor that may be
// used to reject the newly acquired buffer. It also does not bind the
// RenderEngine texture until bindTextureImage is called.
status_t updateTexImage(BufferRejecter* rejecter, nsecs_t expectedPresentTime,
bool* autoRefresh, bool* queuedBuffer, uint64_t maxFrameNumber);
// See BufferLayerConsumer::bindTextureImageLocked().
status_t bindTextureImage();
// setReleaseFence stores a fence that will signal when the current buffer
// is no longer being read. This fence will be returned to the producer
// when the current buffer is released by updateTexImage(). Multiple
// fences can be set for a given buffer; they will be merged into a single
// union fence.
void setReleaseFence(const sp<Fence>& fence);
bool releasePendingBuffer();
sp<Fence> getPrevFinalReleaseFence() const;
// See GLConsumer::getTransformMatrix.
void getTransformMatrix(float mtx[16]);
// getTimestamp retrieves the timestamp associated with the texture image
// set by the most recent call to updateTexImage.
//
// The timestamp is in nanoseconds, and is monotonically increasing. Its
// other semantics (zero point, etc) are source-dependent and should be
// documented by the source.
int64_t getTimestamp();
// getDataSpace retrieves the DataSpace associated with the texture image
// set by the most recent call to updateTexImage.
ui::Dataspace getCurrentDataSpace();
// getCurrentHdrMetadata retrieves the HDR metadata associated with the
// texture image set by the most recent call to updateTexImage.
const HdrMetadata& getCurrentHdrMetadata() const;
// getFrameNumber retrieves the frame number associated with the texture
// image set by the most recent call to updateTexImage.
//
// The frame number is an incrementing counter set to 0 at the creation of
// the BufferQueue associated with this consumer.
uint64_t getFrameNumber();
bool getTransformToDisplayInverse() const;
// must be called from SF main thread
const Region& getSurfaceDamage() const;
// Merge the given damage region into the current damage region value.
void mergeSurfaceDamage(const Region& damage);
// getCurrentApi retrieves the API which queues the current buffer.
int getCurrentApi() const;
// See GLConsumer::setDefaultBufferSize.
status_t setDefaultBufferSize(uint32_t width, uint32_t height);
// setFilteringEnabled sets whether the transform matrix should be computed
// for use with bilinear filtering.
void setFilteringEnabled(bool enabled);
// getCurrentBuffer returns the buffer associated with the current image.
// When outSlot is not nullptr, the current buffer slot index is also
// returned. Simiarly, when outFence is not nullptr, the current output
// fence is returned.
sp<GraphicBuffer> getCurrentBuffer(int* outSlot = nullptr, sp<Fence>* outFence = nullptr) const;
// getCurrentCrop returns the cropping rectangle of the current buffer.
Rect getCurrentCrop() const;
// getCurrentTransform returns the transform of the current buffer.
uint32_t getCurrentTransform() const;
// getCurrentScalingMode returns the scaling mode of the current buffer.
uint32_t getCurrentScalingMode() const;
// getCurrentFence returns the fence indicating when the current buffer is
// ready to be read from.
sp<Fence> getCurrentFence() const;
// getCurrentFence returns the FenceTime indicating when the current
// buffer is ready to be read from.
std::shared_ptr<FenceTime> getCurrentFenceTime() const;
// setConsumerUsageBits overrides the ConsumerBase method to OR
// DEFAULT_USAGE_FLAGS to usage.
status_t setConsumerUsageBits(uint64_t usage);
void onBufferAvailable(const BufferItem& item) EXCLUDES(mImagesMutex);
protected:
// abandonLocked overrides the ConsumerBase method to clear
// mCurrentTextureImage in addition to the ConsumerBase behavior.
virtual void abandonLocked() EXCLUDES(mImagesMutex);
// dumpLocked overrides the ConsumerBase method to dump BufferLayerConsumer-
// specific info in addition to the ConsumerBase behavior.
virtual void dumpLocked(String8& result, const char* prefix) const;
// See ConsumerBase::acquireBufferLocked
virtual status_t acquireBufferLocked(BufferItem* item, nsecs_t presentWhen,
uint64_t maxFrameNumber = 0) override
EXCLUDES(mImagesMutex);
bool canUseImageCrop(const Rect& crop) const;
struct PendingRelease {
PendingRelease() : isPending(false), currentTexture(-1), graphicBuffer() {}
bool isPending;
int currentTexture;
sp<GraphicBuffer> graphicBuffer;
};
// This releases the buffer in the slot referenced by mCurrentTexture,
// then updates state to refer to the BufferItem, which must be a
// newly-acquired buffer. If pendingRelease is not null, the parameters
// which would have been passed to releaseBufferLocked upon the successful
// completion of the method will instead be returned to the caller, so that
// it may call releaseBufferLocked itself later.
status_t updateAndReleaseLocked(const BufferItem& item,
PendingRelease* pendingRelease = nullptr)
EXCLUDES(mImagesMutex);
// Binds mTexName and the current buffer to TEXTURE_EXTERNAL target.
// If the bind succeeds, this calls doFenceWait.
status_t bindTextureImageLocked();
private:
// Utility class for managing GraphicBuffer references into renderengine
class Image {
public:
Image(const sp<GraphicBuffer>& graphicBuffer, renderengine::RenderEngine& engine);
virtual ~Image();
const sp<GraphicBuffer>& graphicBuffer() { return mGraphicBuffer; }
private:
// mGraphicBuffer is the buffer that was used to create this image.
sp<GraphicBuffer> mGraphicBuffer;
// Back-reference into renderengine to initiate cleanup.
renderengine::RenderEngine& mRE;
DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(Image);
};
// freeBufferLocked frees up the given buffer slot. If the slot has been
// initialized this will release the reference to the GraphicBuffer in
// that slot. Otherwise it has no effect.
//
// This method must be called with mMutex locked.
virtual void freeBufferLocked(int slotIndex) EXCLUDES(mImagesMutex);
// IConsumerListener interface
void onDisconnect() override;
void onSidebandStreamChanged() override;
void addAndGetFrameTimestamps(const NewFrameEventsEntry* newTimestamps,
FrameEventHistoryDelta* outDelta) override;
// computeCurrentTransformMatrixLocked computes the transform matrix for the
// current texture. It uses mCurrentTransform and the current GraphicBuffer
// to compute this matrix and stores it in mCurrentTransformMatrix.
// mCurrentTextureImage must not be nullptr.
void computeCurrentTransformMatrixLocked();
// doFenceWaitLocked inserts a wait command into the RenderEngine command
// stream to ensure that it is safe for future RenderEngine commands to
// access the current texture buffer.
status_t doFenceWaitLocked() const;
// getCurrentCropLocked returns the cropping rectangle of the current buffer.
Rect getCurrentCropLocked() const;
// The default consumer usage flags that BufferLayerConsumer always sets on its
// BufferQueue instance; these will be OR:d with any additional flags passed
// from the BufferLayerConsumer user. In particular, BufferLayerConsumer will always
// consume buffers as hardware textures.
static const uint64_t DEFAULT_USAGE_FLAGS = GraphicBuffer::USAGE_HW_TEXTURE;
// mCurrentTextureBuffer is the buffer containing the current texture. It's
// possible that this buffer is not associated with any buffer slot, so we
// must track it separately in order to support the getCurrentBuffer method.
std::shared_ptr<Image> mCurrentTextureBuffer;
// mCurrentCrop is the crop rectangle that applies to the current texture.
// It gets set each time updateTexImage is called.
Rect mCurrentCrop;
// mCurrentTransform is the transform identifier for the current texture. It
// gets set each time updateTexImage is called.
uint32_t mCurrentTransform;
// mCurrentScalingMode is the scaling mode for the current texture. It gets
// set each time updateTexImage is called.
uint32_t mCurrentScalingMode;
// mCurrentFence is the fence received from BufferQueue in updateTexImage.
sp<Fence> mCurrentFence;
// The FenceTime wrapper around mCurrentFence.
std::shared_ptr<FenceTime> mCurrentFenceTime{FenceTime::NO_FENCE};
// mCurrentTransformMatrix is the transform matrix for the current texture.
// It gets computed by computeTransformMatrix each time updateTexImage is
// called.
float mCurrentTransformMatrix[16];
// mCurrentTimestamp is the timestamp for the current texture. It
// gets set each time updateTexImage is called.
int64_t mCurrentTimestamp;
// mCurrentDataSpace is the dataspace for the current texture. It
// gets set each time updateTexImage is called.
ui::Dataspace mCurrentDataSpace;
// mCurrentHdrMetadata is the HDR metadata for the current texture. It
// gets set each time updateTexImage is called.
HdrMetadata mCurrentHdrMetadata;
// mCurrentFrameNumber is the frame counter for the current texture.
// It gets set each time updateTexImage is called.
uint64_t mCurrentFrameNumber;
// Indicates this buffer must be transformed by the inverse transform of the screen
// it is displayed onto. This is applied after BufferLayerConsumer::mCurrentTransform.
// This must be set/read from SurfaceFlinger's main thread.
bool mCurrentTransformToDisplayInverse;
// The portion of this surface that has changed since the previous frame
Region mCurrentSurfaceDamage;
int mCurrentApi;
uint32_t mDefaultWidth, mDefaultHeight;
// mFilteringEnabled indicates whether the transform matrix is computed for
// use with bilinear filtering. It defaults to true and is changed by
// setFilteringEnabled().
bool mFilteringEnabled;
renderengine::RenderEngine& mRE;
// mTexName is the name of the RenderEngine texture to which streamed
// images will be bound when bindTexImage is called. It is set at
// construction time.
const uint32_t mTexName;
// The layer for this BufferLayerConsumer
const wp<Layer> mLayer;
wp<ContentsChangedListener> mContentsChangedListener;
// mCurrentTexture is the buffer slot index of the buffer that is currently
// bound to the RenderEngine texture. It is initialized to INVALID_BUFFER_SLOT,
// indicating that no buffer slot is currently bound to the texture. Note,
// however, that a value of INVALID_BUFFER_SLOT does not necessarily mean
// that no buffer is bound to the texture. A call to setBufferCount will
// reset mCurrentTexture to INVALID_BUFFER_SLOT.
int mCurrentTexture;
// Shadow buffer cache for cleaning up renderengine references.
std::shared_ptr<Image> mImages[BufferQueueDefs::NUM_BUFFER_SLOTS] GUARDED_BY(mImagesMutex);
// Separate mutex guarding the shadow buffer cache.
// mImagesMutex can be manipulated with binder threads (e.g. onBuffersAllocated)
// which is contentious enough that we can't just use mMutex.
mutable std::mutex mImagesMutex;
// A release that is pending on the receipt of a new release fence from
// presentDisplay
PendingRelease mPendingRelease;
}
步骤4:setConsumerUsageBits设置缓冲区的类型,会保存到BufferQueueCore中的mConsumerUsageBits变量中。
BufferLayerConsumer setContentsChangedListener
步骤5:通过setContentsChangedListener给消费者设置一个缓冲区内容变化的监听器:
// frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/BufferLayerConsumer.cpp
void BufferLayerConsumer::setContentsChangedListener(const wp<ContentsChangedListener>& listener) {
setFrameAvailableListener(listener);
Mutex::Autolock lock(mMutex);
mContentsChangedListener = listener;
}
生产者dequeue一块buffer,应用程序进行绘制,绘制完成后queue此块buffer,此时生产者调用BufferQueueCore的mConsumerListener的onFrameAvailable回调函数,mConsumerListener其实是BufferQueue::ProxyConsumerListener,BufferQueue::ProxyConsumerListener在创建时又接收了ConsumerBase,所以调用到了ConsumerBase的onFrameAvailable中,ConsumerBase这里面又有一个成员变量mFrameAvailableListener,类型为BufferQueueLayer,所以最终是调用到了BufferQueueLayer的具体实现onFrameAvailable中,对这块已经绘制好的buffer进一步处理。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








