1、tfrecord文件格式介绍
tfrecord文件格式,是深度学习框架tensorflow专用的一种文件格式,其底层使用protobuf,TensorFlow(python)也提供了api用于读取和写入tfrecord,非常方便,而对于golang语言,目前没有成熟的包可以使用,调研过一个nivida的开源库,这个库已经三四年没有更新,在读取tfrecord上存在问题,所以go语言,至今没有找到合适的包可以操作tfrecord。
一个tfrecord文件是有多个example组成,一个example是有多个key-value对构成的结构:

2、tfrecord文件操作
测试环境:
python:3.8
TensorFlow:2.13
系统:Ubuntu2004
2.1 生成tfrecord
#!/usr/bin/python3.10
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def _bytes_feature(value):
if isinstance(value, type(tf.constant(0))):
value = value.numpy()
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
def _float_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[value]))
def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]))
def _int64_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=value))
def _bytes_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value.astype(np.float32).tobytes()]))
def serialize_example(f0, f1, f2, f3, f4):
features = {
'a': _int64_feature(f0),
'b': _int64_list_feature(f1),
'c': _bytes_feature(f2),
'd': _float_feature(f3),
'e': _bytes_list_feature(f4)
}
example_proto = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature=features))
return example_proto.SerializeToString()
def main():
filename = 'tf.tfrecord'
with tf.io.TFRecordWriter(filename) as writer:
for i in range(10):
example = serialize_example(1, [1, 1, 9], b'tfrecord', 1.4, np.array([1, 2, 3]))
writer.write(example)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
上面代码共写了10个example到文件里,运行上面 代码之前,需要安装tensorflow:

TensorFlow安装完成后,运行上面python代码:
执行完成后,生成tf.tfrecord文件,下面我们会尝试读取一下生成的这个文件。
2.2 读取tfrecord
上面2.1生成了一个tfrecord文件,我们就来读取这个文件,首先这个tfrecord一共包含10个example,每个example包含5个key,可以对照第一章节的图示进行理解,读取代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python3.10
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
feature_desc = {
'a': tf.io.FixedLenFeature((), tf.int64, default_value=0),
'b': tf.io.FixedLenFeature((3), tf.int64, default_value=[-1, -1, -1]),
'c': tf.io.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value=''),
'd': tf.io.FixedLenFeature((), tf.float32, default_value=0.0),
'e': tf.io.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string)
}
def main():
filename = '/root/python/tfrecord/tf.tfrecord'
examples = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(filename)
for example in examples:
feature = tf.io.parse_single_example(example, feature_desc)
print('a=', feature['a'].numpy())
print('b=', feature['b'].numpy())
print('c=', feature['c'].numpy().decode('utf-8'))
print('d=', feature['d'].numpy())
print('e=', tf.io.decode_raw(feature['e'], tf.float32))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
代码运行结果:

3、获取tfrecord文件特征属性
当某些时候,我们不知道tfrecord的特征属性时,也就是不知道文件里的feature格式时,我们可以用下面的方法将feature的key值、value等信息打印出来:
#!/usr/bin/python3.10
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def getTFRecordFormat(files):
# 加载TFRecord数据
ds = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(files)
ds = ds.batch(1)
ds = ds.prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
for batch_data in ds.take(1):
for serialized_example in batch_data:
example_proto = tf.train.Example.FromString(serialized_example.numpy())
for key, feature in example_proto.features.feature.items():
ftype = None
fvalue = None
if feature.HasField('bytes_list'):
ftype = 'bytes_list'
fvalue = (feature.bytes_list.value)
elif feature.HasField('float_list'):
ftype = 'float_list'
fvalue = (feature.float_list.value)
elif feature.HasField('int64_list'):
ftype = 'int64_list'
fvalue = (feature.int64_list.value)
if ftype:
result = '{0} : {1} {2}'.format(key, ftype, fvalue)
print(result)
def main():
filename = '/root/python/tfrecord/tf.tfrecord'
getTFRecordFormat(filename)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
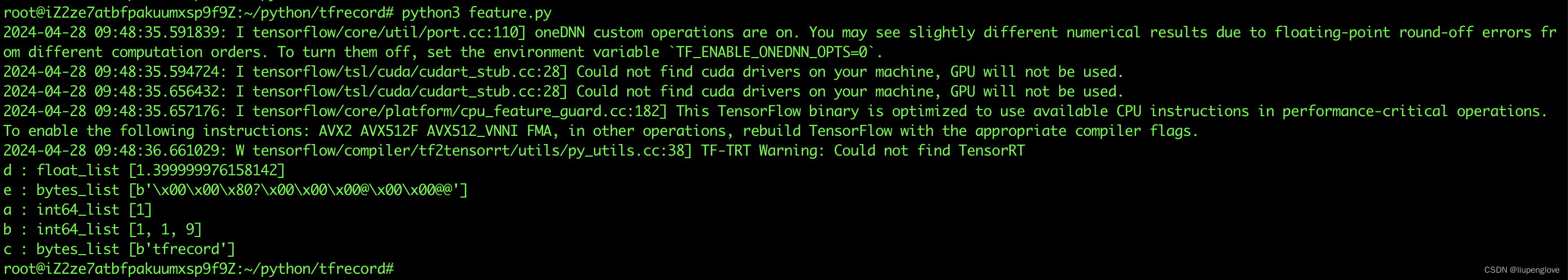
代码运行记录:
4、为什么使用tfrecord
TFRecord文件格式在机器学习和深度学习应用中具有多个优势,这也是为什么它被广泛采用的原因。以下是TFRecord文件格式的主要优点:
- 高效的数据存储与读取:TFRecord使用二进制格式来存储数据,相比于文本格式(如CSV或JSON),它更加紧凑,因此可以节省存储空间。此外,二进制格式的数据读取速度也更快,这对于大规模数据集的训练和推理过程尤为重要。
- 多样化的数据类型支持:TFRecord可以支持多种数据类型,包括整数、浮点数、字符串等,这使得它非常适合存储各种类型的训练数据。无论是图像、文本还是其他类型的数据,都可以方便地存储为TFRecord格式。
- 方便的数据预处理:通过将数据转换为TFRecord格式,可以方便地进行数据预处理操作,如数据增强、归一化等。这些操作可以在数据加载阶段进行,从而避免了在训练过程中重复进行预处理,提高了训练效率。
- 易于扩展与并行处理:TFRecord文件可以轻松地扩展以适应更大的数据集。此外,由于其紧凑的二进制格式和高效的数据读取机制,TFRecord文件也支持并行处理,可以充分利用多核CPU或GPU的并行计算能力。
- 跨平台兼容性:TFRecord文件使用Protocol Buffers进行编码,这是一种跨平台的序列化结构数据格式。因此,TFRecord文件可以在不同的操作系统和编程环境中使用,具有良好的兼容性。
综上所述,TFRecord文件格式在机器学习和深度学习中具有高效、灵活、易于扩展和跨平台兼容等优点,使得它成为处理大规模数据集的首选格式之一。







 本文详细介绍了TensorFlow中的TFRecord文件格式,包括其结构、Python和Go语言的操作示例,以及TFRecord在机器学习中的优势,如高效存储、多样化数据类型支持和跨平台兼容性。
本文详细介绍了TensorFlow中的TFRecord文件格式,包括其结构、Python和Go语言的操作示例,以及TFRecord在机器学习中的优势,如高效存储、多样化数据类型支持和跨平台兼容性。

















 754
754

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








