几个关键类:
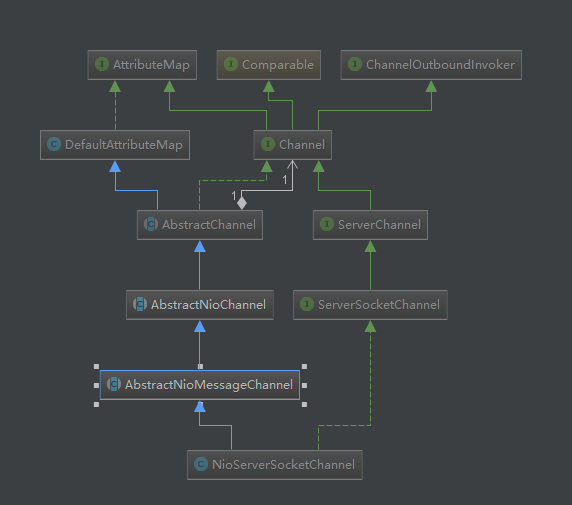
1.NioServerSocketChannel
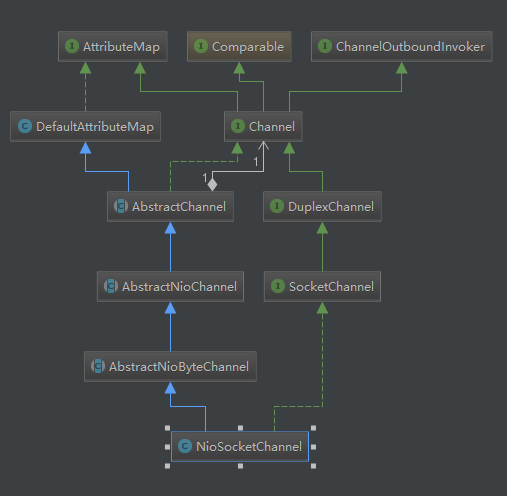
2.NioSocketChannel
两个继承和实现的接口都差不多,功能也差不多
3.ServerBootstrap 和 Bootstrap都继承自AbstractBootstrap功能都是作为入口,构建服务端和客户端
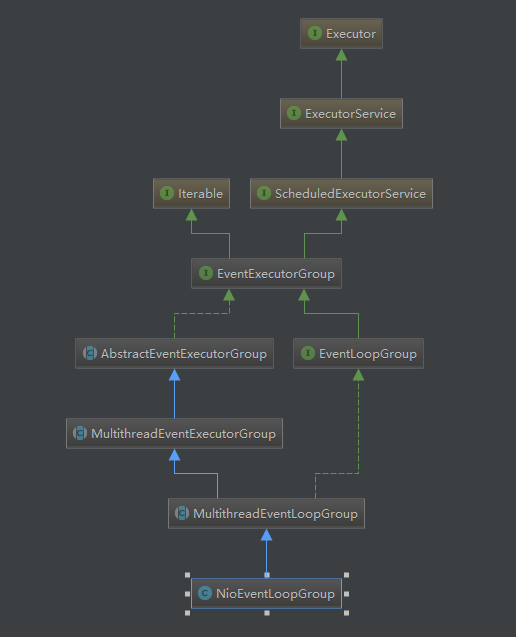
4.NioEventLoopGroup
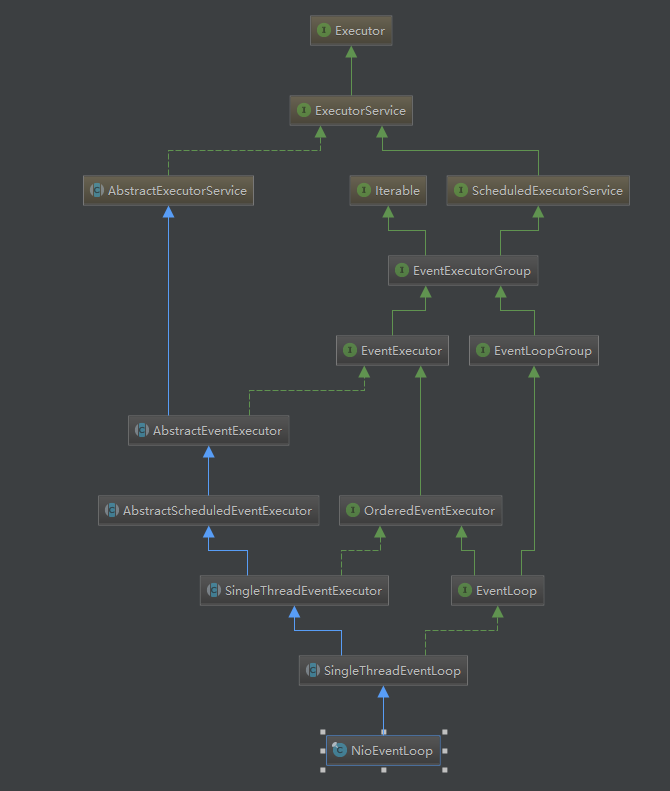
5.NioEventLoop
6.DefaultChannelPipeline
二.初始化流程
创建一个服务端代码
EventLoopGroup bossgroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workgroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossgroup,workgroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new
ProtobufDecoder(SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.getDefaultInstance()));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossgroup.shutdownGracefully();
workgroup.shutdownGracefully();
}group()、channel()、option() 、handler() 、childHandler()都是配置属性信息
整个创建初始化注册是在bind()方法内
public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort) {
return bind(new InetSocketAddress(inetPort));
}
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
validate();
if (localAddress == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");
}
return doBind(localAddress);
}
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}再看一下initAndRegister() 主要是创建server channel和注册selector
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
//创建channel对象
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
//初始化配置
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
//注册channel到selector上








 本文介绍了Netty中的关键类,如NioServerSocketChannel、NioSocketChannel、ServerBootstrap和Bootstrap,并详细阐述了服务端初始化流程,包括group、channel、option、handler和childHandler的配置,以及NioEventLoopGroup、NioEventLoop和DefaultChannelPipeline的作用。在bind()方法内,通过initAndRegister()创建并注册server channel,最终通过AbstractUnsafe在Selector上完成注册,触发pipeline中handler的channelRegistered事件,完成服务器启动流程。
本文介绍了Netty中的关键类,如NioServerSocketChannel、NioSocketChannel、ServerBootstrap和Bootstrap,并详细阐述了服务端初始化流程,包括group、channel、option、handler和childHandler的配置,以及NioEventLoopGroup、NioEventLoop和DefaultChannelPipeline的作用。在bind()方法内,通过initAndRegister()创建并注册server channel,最终通过AbstractUnsafe在Selector上完成注册,触发pipeline中handler的channelRegistered事件,完成服务器启动流程。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 4360
4360

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








