零、文章目录
JavaScript高级一、作用域&解构&箭头函数
1、作用域
(1)局部作用域
-
局部作用域分为
函数作用域和块作用域。 -
**函数作用域:**在函数内部声明的变量所在作用域。
- 函数内部声明的变量,在函数外部无法被访问。
- 不同函数内部声明的变量无法互相访问。
-
**块作用域:**在 JavaScript 中使用 { } 包裹的代码称为代码块,代码块内部声明的变量外部将
有可能无法被访问。- let、const 声明的变量会产生块作用域(推荐),var 不会产生块作用域
- 不同代码块之间的变量无法互相访问
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>局部作用域</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function getSum() {
//函数作用域
const num = 10
console.log(num)
}
console.log(num)//超出作用域报错
for (let i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
//块作用域
console.log(i)
}
console.log(i)//超出作用域报错
</script>
</body>
</html>
(2)全局作用域
<script>标签 和.js文件 的【最外层】就是所谓的全局作用域。- 全局作用域中声明的变量,任何其它作用域都可以访问。
- 为 window 对象动态添加的属性默认也是全局的,不推荐!
- 函数中未使用任何关键字声明的变量为全局变量,不推荐!!!
- 尽可能少的声明全局变量,防止全局
变量被污染
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>全局作用域</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 全局作用域
// 全局变量 name
const name = '小明'
// 函数作用域中访问全局变量
function sayHi() {
// 此处为局部
console.log('你好' + name)
}
// 全局变量x
let x = 10
// 块作用域中访问全局变量
if (true) {
let y = 5
console.log(x + y) // x 是全局的
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
(3)作用域链
嵌套关系的作用域串联起来形成了作用域链,作用域链本质上是底层的变量查找机制。- 在函数被执行时,会
优先查找当前函数作用域中的变量 - 如果当前作用域查找不到则会依次
逐级查找父级作用域直到全局作用域 - 子作用域能够访问父作用域,父级作用域无法访问子级作用域
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>作用域链</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//全局作用域
let a = 1
let b = 2
//局部作用域
function f() {
let a = 1
//局部作用域
function g() {
a = 2
console.log(a)
}
g()
}
f()
</script>
</body>
</html>
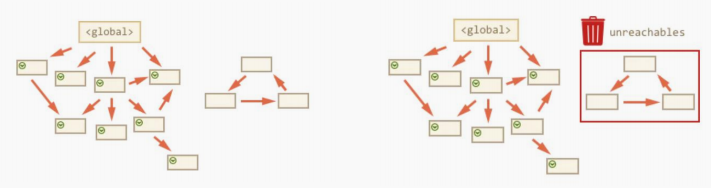
(4)JS垃圾回收机制
-
垃圾回收机制(Garbage Collection)
GC- JS中内存的分配和回收都是自动完成的,内存在不使用的时候会被垃圾回收器自动回收。
- 正因为垃圾回收器的存在,许多人认为JS不用太关心内存管理的问题,但如果不了解JS的内存管理机制,我们同样非常容易成内存泄漏(内存无法被回收)的情况
- 不再用到的内存,没有及时释放,就叫做
内存泄漏
-
JS环境中分配的
内存, 一般有如下生命周期- 内存分配:当我们声明变量、函数、对象的时候,系统会自动为他们分配内存
- 内存使用:即读写内存,也就是使用变量、函数等
- 内存回收:使用完毕,由垃圾回收自动回收不再使用的内存
- 说明:全局变量一般不会回收(关闭页面回收);
-
堆栈空间分配区别:
- 栈(操作系统): 由
操作系统自动分配释放函数的参数值、局部变量等,基本数据类型放到栈里面。 - 堆(操作系统): 一般由程序员分配释放,若程序员不释放,由垃圾回收机制回收。复杂数据类型放到堆里面
- 栈(操作系统): 由
-
两种常见的浏览器垃圾回收算法:
引用计数法 和 标记清除法 -
**引用计数:**IE采用的引用计数算法, 定义“
内存不再使用”,就是看一个对象是否有指向它的引用,没有引用了就回收对象- 跟踪记录被
引用的次数 - 如果被引用了一次,那么就记录次数1,多次引用会
加1 - 加++个引用就
减1 - 如果引用次数是
0,则释放内存
- 跟踪记录被

- 引用计数致命问题:
嵌套引用(循环引用),如果两个对象相互引用,尽管他们已不再使用,垃圾回收器不会进行回收,因为他们的引用次数永远不会是0,导致内存泄露。

- **标记清除法:**现代的浏览器已经不再使用引用计数算法了。现代浏览器通用的大多是基于
标记清除算法的某些改进算法,总体思想都是一致的。- 标记清除算法将“不再使用的对象”定义为“
无法达到的对象”。 - 就是从
根部(在JS中就是全局对象)出发定时扫描内存中的对象。 凡是能从根部到达的对象,都是还需要使用的。 - 那些
无法由根部出发触及到的对象被标记为不再使用,稍后进行回收。
- 标记清除算法将“不再使用的对象”定义为“
(5)闭包
-
简单理解:闭包 = 内层函数 + 外层函数的变量
-
闭包作用:
- 封闭数据,提供操作,外部也可以访问函数内部的变量
- 闭包很有用,因为它允许将函数与其所操作的某些数据(环境)关联起来
-
闭包应用:实现数据的私有,比如,我们要做个统计函数调用次数,函数调用一次,就++
-
闭包可能引起的问题:
内存泄漏
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>闭包</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//外层函数可以使用内层函数的变量
//闭包常见的写法
function outer1() {
let a = 100
function fn() {
console.log(a)
}
return fn
}
outer1()() // 调用函数
// 闭包简化的写法
function outer2() {
let a = 100
//直接返回函数
return function() {
console.log(a)
}
}
outer2()() // 调用函数
// 闭包的应用:实现数据私有, 统计函数调用的次数
// 普通形式
let i = 0 //因为i是全局变量,容易被修改
function count1() {
i++
console.log(`函数被调用了${i}次`)
}
count1()
//闭包形式
function count2() {
let i = 0 //实现数据私有,外部无法直接修改i
function fn() {
i++
console.log(`111函数被调用了${i}次`)
}
return fn
}
count2()()
</script>
</body>
</html>
(6)变量提升
- 变量提升
var声明变量,存在变量提升问题,它允许在变量声明之前即被访问,变量的值为undefined,变量提升出现在相同作用域当中。let/const 声明的变量不存在变量提升问题,未声明即被访问时会报语法错误。实际开发中推荐先声明再访问变量。
- 变量提升流程
- 先把var 变量提升到当前作用域于最前面
- 只提升变量声明, 不提升变量赋值
- 然后依次执行代码
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>变量提升</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.log(num) //undefined
var num = 10
console.log(num) //10
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、函数进阶
(1)函数提升
- 函数提升与变量提升比较类似,是指函数在声明之前即可被调用。
- 函数提升能够使函数的声明调用更灵活。
- 函数提升出现在相同作用域当中。
函数表达式不存在提升的现象。
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>函数提升</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
fn()
function fn() {
console.log('函数提升,声明之前就被调用')
}
fun() //函数表达式必须先声明和赋值后调用,否则报错
var fun = function() {
console.log('函数表达式不存在提升现象')
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
(2)函数参数
-
函数参数的使用细节,能够提升函数应用的灵活度。
-
动态参数:
arguments是函数内部内置的伪数组变量,它包含了调用函数时传入的所有实参- arguments 是一个
伪数组,只存在于函数中 - arguments 的作用是动态获取函数的实参
- 可以通过for循环依次得到传递过来的实参
- arguments 是一个
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>函数动态参数</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function getSum() {
// arguments 动态参数 只存在于 函数里面
// 是伪数组 里面存储的是传递过来的实参
// console.log(arguments) [2,3,4]
let sum = 0
for (let i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
sum += arguments[i]
}
console.log(sum)
}
getSum(2, 3, 4)
getSum(1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 2, 3, 4)
</script>
</body>
</html>
- **剩余参数:**剩余参数允许我们将一个
不定数量的参数表示为一个数组- … 是语法符号,置于最末函数形参之前,用于获取
多余的实参 - 借助 … 获取的剩余实参,是个
真数组
- … 是语法符号,置于最末函数形参之前,用于获取
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>函数剩余参数</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function getSum(a, b, ...arr) {
console.log(arr) // 使用的时候不需要写 ...
}
getSum(2, 3)
getSum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
</script>
</body>
</html>
-
动态参数
VS剩余参数- 动态参数是伪数组
- 剩余参数是真数组
- 开发中,还是提倡多使用 剩余参数。
-
展开运算符:展开运算符(…),将一个数组进行展开
- 不会修改原数组
- 典型运用场景: 求数组最大值(最小值)、合并数组等
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>展开运算符</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3]
// 展开运算符 可以展开数组
console.log(...arr1)//1 2 3
// 1 求数组最大值
console.log(Math.max(...arr1)) // 3
console.log(Math.min(...arr1)) // 1
// 2. 合并数组
const arr2 = [3, 4, 5]
const arr = [...arr1, ...arr2]
console.log(arr)//1 2 3 3 4 5
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 展开运算符
VS剩余参数- 剩余参数:函数参数使用,得到真数组
- 展开运算符:数组中使用,数组展开
(3)箭头函数
- **目的:**引入箭头函数的目的是更简短的函数写法并且不绑定this,箭头函数的语法比函数表达式更简洁
- **使用场景:**箭头函数更适用于那些本来
需要匿名函数的地方
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>箭头函数</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//普通函数
const fn1 = function () {
console.log(123)
}
//箭头函数 基本语法
const fn2 = () => {
console.log(123)
}
//只有一个形参的时候,可以省略小括号
const fn3 = (x) => {
console.log(x)
}
const fn4 = x => {
console.log(x)
}
// 只有一行代码的时候,我们可以省略大括号
const fn5 = x => console.log(x)
//只有一行代码的时候,可以省略return
const fn6 = x => x + x
//箭头函数可以直接返回一个对象
const fn = (uname) => ({ uname: uname })
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 箭头函数参数:箭头函数没有 arguments 动态参数,但是有剩余参数 …args
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>箭头函数的参数</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 1. 利用箭头函数来求和
const getSum = (...arr) => {
let sum = 0
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i]
}
return sum
}
const result = getSum(2, 3, 4)
console.log(result) // 9
</script>
</body>
</html>
- **箭头函数 this:**在箭头函数出现之前,每一个新函数根据它是被
如何调用的来定义这个函数的this值。箭头函数不会创建自己的this,它只会从自己的作用域链的上一层沿用this。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>箭头函数的this</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//以前this的指向:谁调用的这个函数,this 就指向谁
console.log(this) // window
// 普通函数
function fn1() {
console.log(this) // window
}
window.fn1()
//对象方法里面的this
const obj1 = {
name: 'andy',
sayHi: function() {
console.log(this) // obj1
}
}
obj1.sayHi()
//箭头函数的this是上一层作用域的this指向
const fn2 = () => {
console.log(this) // window
}
window.fn2()
//对象方法箭头函数 this
const obj2 = {
uname: 'pink老师',
sayHi: () => {
console.log(this) //window 上一层作用域就是window
}
}
obj2.sayHi()
//复杂一些情况
const user = {
uname: 'pink老师',
sayHi: function() {
console.log(this) // user 调用的是user,this指向user
let i = 10
const count = () => {
console.log(this) // user 上一层作用域就是sayHi的作用域,调用者user就是user
}
count()
}
}
user.sayHi()
</script>
</body>
</html>
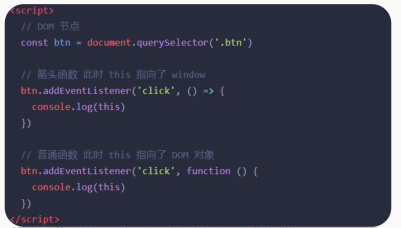
- **DOM事件回调函数不推荐使用箭头函数:**在开发中,事件回调函数使用箭头函数时,this 为全局的 window,
因此DOM事件回调函数不推荐使用箭头函数
3、解构赋值
- 解构赋值是一种快速为变量赋值的简洁语法,本质上仍然是为变量赋值。
(1)数组解构
- **定义:**数组解构赋值是将数组的单元值
快速批量赋值给一系列变量的简洁语法 - **基本语法:**赋值运算符 = 左侧的 [] 用于批量声明变量,右侧数组的单元值将被赋值给左侧的变量
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>数组解构</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 数组解构 赋值
const [max, min, avg] = [100, 60, 80]
console.log(max) // 100
console.log(avg) // 80
// 交换2个变量的值
let a = 1
let b = 2;
[b, a] = [a, b]
console.log(a, b)//2 1
</script>
</body>
</html>
- js 前面必须加分号情况
- 立即执行函数
- 数组解构
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>必须加分号的两种情况</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 1. 立即执行函数
(function () { })();
(function () { })();
// 2. 使用数组的时候
const str = 'pink';
[1, 2, 3].map(function (item) {
console.log(item)
})
let a = 1
let b = 2;
[b, a] = [a, b]
console.log(a, b)
</script>
</body>
</html>
-
数组解构细节
-
**变量多,单元值少的情况:**多余的变量将被赋值为
undefined -
变量少 单元值多的情况:多余的值丢弃
-
**利用剩余参数解决变量少单元值多的情况:**剩余参数返回的还是一个数组,但剩余参数只能置于最末位
-
**防止有undefined传递单元值的情况,可以设置默认值:**允许初始化变量的默认值,且只有单元值为
undefined时默认值才会生效 -
按需导入,忽略某些返回值
-
支持多维数组的解构
-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>数组解构细节</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 1.变量多,单元值少的情况:多余的变量将被赋值为 undefined
const [a1, b1, c1, d1] = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(a1) // 1
console.log(b1) // 2
console.log(c1) // 3
console.log(d1) // undefined
// 2.变量少 单元值多的情况:多余的值丢弃
const [a2, b2] = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(a2) // 1
console.log(b2) // 2
// 3.利用剩余参数解决变量少单元值多的情况:剩余参数返回的还是一个数组,但剩余参数只能置于最末位
const [a3, b3, ...c3] = [1, 2, 3, 4]
console.log(a3) // 1
console.log(b3) // 2
console.log(c3) // [3, 4] 真数组
// 4.防止有undefined传递单元值的情况,可以设置默认值:允许初始化变量的默认值,且只有单元值为 undefined 时默认值才会生效
const [a4 = 1, b4 = 2] = []
console.log(a4) // 1
console.log(b4) // 2
// 5.按需导入,忽略某些返回值
const [a5, b5, , d5] = [1, 2, 3, 4]
console.log(a5) // 1
console.log(b5) // 2
console.log(d5) // 4
// 6.支持多维数组的解构
const [a6, b6, c6] = [1, 2, [3, 4]]
console.log(a6) // 1
console.log(b6) // 2
console.log(c6) // [3,4]
const [a7, b7, [c7, d7]] = [1, 2, [3, 4]]
console.log(a7) // 1
console.log(b7) // 2
console.log(c7) // 3
console.log(d7) // 4
</script>
</body>
</html>
(2)对象解构
- **定义:**对象解构是将对象属性和方法
快速批量赋值给一系列变量的简洁语法 - **基本语法:**赋值运算符 = 左侧的 {} 用于批量声明变量,右侧对象的属性值将被赋值给左侧的变量
- 对象中找不到与变量名一致的属性时变量值为
undefined - **给新的变量名赋值:**可以从一个对象中提取变量并同时修改新的变量名
- 还可以给数组对象解构
- 对象中找不到与变量名一致的属性时变量值为
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>对象解构</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 普通对象
const user = {
uname: 'zhangsan',
age: 18
}
// 解构的语法
const {
uname,
age,
sex
} = user
// 等价于 const uname = user.uname const age = user.age
// 要求属性名和变量名必须一致
console.log(uname) //zhangsan
console.log(age) //18
//对象中找不到与变量名一致的属性时变量值为 undefined
console.log(sex) //undefined
// 对象解构可以给新的变量名赋值 旧变量名: 新变量名
const {
uname: myname,
age: myage
} = user
console.log(myname)
console.log(myage)
// 解构数组对象
const pig = [{
puname: '佩奇',
page: 6
}]
const [{
puname,
page
}] = pig
console.log(puname)
console.log(page)
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 多级对象解构
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>多级对象解构</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const person = [{
name: '佩奇',
family: {
mother: '猪妈妈',
father: '猪爸爸',
sister: '乔治'
},
age: 6
}]
const [{
name,
family: {
mother,
father,
sister
}
}] = person
console.log(name) //佩奇
console.log(mother) //猪妈妈
console.log(father) //猪爸爸
console.log(sister) //乔治
</script>
</body>
</html>
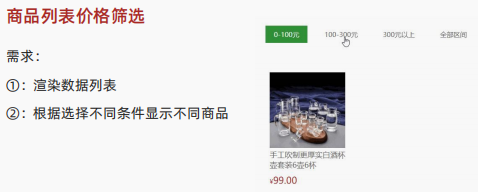
(3)商品列表案例

-
forEach() 方法用于调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传递给回调函数
- forEach 主要是遍历数组。
- 参数当前数组元素是必须要写的, 索引号可选。
-
核心思路:有多少条数据,就渲染多少模块,然后 生成对应的 html结构标签, 赋值给 list标签即可
- 利用forEach 遍历数据里面的数据
- 拿到数据,利用字符串拼接生成结构添加到页面中
- 注意:传递参数的时候,可以使用对象解构
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>商品列表案例</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.list {
width: 990px;
margin: 0 auto;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
padding-top: 100px;
}
.item {
width: 240px;
margin-left: 10px;
padding: 20px 30px;
transition: all .5s;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.item:nth-child(4n) {
margin-left: 0;
}
.item:hover {
box-shadow: 0px 0px 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
transform: translate3d(0, -4px, 0);
cursor: pointer;
}
.item img {
width: 100%;
}
.item .name {
font-size: 18px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
color: #666;
}
.item .price {
font-size: 22px;
color: firebrick;
}
.item .price::before {
content: "¥";
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="list">
</div>
<script>
const goodsList = [{
id: '4001172',
name: '称心如意手摇咖啡磨豆机咖啡豆研磨机',
price: '289.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/84a59ff9c58a77032564e61f716846d6.jpg',
}, {
id: '4001594',
name: '日式黑陶功夫茶组双侧把茶具礼盒装',
price: '288.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/3346b7b92f9563c7a7e24c7ead883f18.jpg',
}, {
id: '4001009',
name: '竹制干泡茶盘正方形沥水茶台品茶盘',
price: '109.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/2d942d6bc94f1e230763e1a5a3b379e1.png',
}, {
id: '4001874',
name: '古法温酒汝瓷酒具套装白酒杯莲花温酒器',
price: '488.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/44e51622800e4fceb6bee8e616da85fd.png',
}, {
id: '4001649',
name: '大师监制龙泉青瓷茶叶罐',
price: '139.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/4356c9fc150753775fe56b465314f1eb.png',
}, {
id: '3997185',
name: '与众不同的口感汝瓷白酒杯套组1壶4杯',
price: '108.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/8e21c794dfd3a4e8573273ddae50bce2.jpg',
}, {
id: '3997403',
name: '手工吹制更厚实白酒杯壶套装6壶6杯',
price: '99.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/af2371a65f60bce152a61fc22745ff3f.jpg',
}, {
id: '3998274',
name: '德国百年工艺高端水晶玻璃红酒杯2支装',
price: '139.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/8896b897b3ec6639bbd1134d66b9715c.jpg',
}, ]
// 1. 声明一个字符串变量
let str = ''
// 2. 遍历数据
goodsList.forEach(item => {
// console.log(item) // 可以得到每一个数组元素 对象 {id: '4001172'}
// const {id} = item 对象解构
const {
name,
price,
picture
} = item
str += `
<div class="item">
<img src=${picture} alt="">
<p class="name">${name}</p>
<p class="price">${price}</p>
</div>
`
})
// 3.生成的 字符串 添加给 list
document.querySelector('.list').innerHTML = str
</script>
</body>
</html>
4、综合案例
-
filter() 方法创建一个新的数组,新数组中的元素是通过检查指定数组中符合条件的所有元素,不会影响原数组
- **返回值:**返回数组,包含了符合条件的所有元素。如果没有符合条件的元素则返回空数组
- **参数:**currentValue 必须写, index 可选
-
核心思路:
- 页面初始渲染:利用forEach 遍历数据里面的数据,并渲染数据列表
- 点击不同需求显示不同的数据:根据 filter 选择不同条件显示不同商品
- 点击采取事件委托方式 .filter
- 利用过滤函数 filter 筛选出符合条件的数据,因为生成的是一个数组,传递给渲染函数即可
- 筛选条件是根据点击的 data-index 来判断
- 可以使用对象解构,把 事件对象 解构
- 因为全部区间不需要筛选,直接 把goodList渲染即可
- 初始化需要渲染页面,点击不同的需求,还会重新渲染页面,所以渲染做成一个
函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>价格筛选案例</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.list {
width: 990px;
margin: 0 auto;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.item {
width: 240px;
margin-left: 10px;
padding: 20px 30px;
transition: all .5s;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.item:nth-child(4n) {
margin-left: 0;
}
.item:hover {
box-shadow: 0px 0px 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
transform: translate3d(0, -4px, 0);
cursor: pointer;
}
.item img {
width: 100%;
}
.item .name {
font-size: 18px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
color: #666;
}
.item .price {
font-size: 22px;
color: firebrick;
}
.item .price::before {
content: "¥";
font-size: 14px;
}
.filter {
display: flex;
width: 990px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 50px 30px;
}
.filter a {
padding: 10px 20px;
background: #f5f5f5;
color: #666;
text-decoration: none;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.filter a:active,
.filter a:focus {
background: #05943c;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="filter">
<a data-index="1" href="javascript:;">0-100元</a>
<a data-index="2" href="javascript:;">100-300元</a>
<a data-index="3" href="javascript:;">300元以上</a>
<a href="javascript:;">全部区间</a>
</div>
<div class="list">
</div>
<script>
// 2. 初始化数据
const goodsList = [{
id: '4001172',
name: '称心如意手摇咖啡磨豆机咖啡豆研磨机',
price: '289.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/84a59ff9c58a77032564e61f716846d6.jpg',
}, {
id: '4001594',
name: '日式黑陶功夫茶组双侧把茶具礼盒装',
price: '288.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/3346b7b92f9563c7a7e24c7ead883f18.jpg',
}, {
id: '4001009',
name: '竹制干泡茶盘正方形沥水茶台品茶盘',
price: '109.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/2d942d6bc94f1e230763e1a5a3b379e1.png',
}, {
id: '4001874',
name: '古法温酒汝瓷酒具套装白酒杯莲花温酒器',
price: '488.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/44e51622800e4fceb6bee8e616da85fd.png',
}, {
id: '4001649',
name: '大师监制龙泉青瓷茶叶罐',
price: '139.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/4356c9fc150753775fe56b465314f1eb.png',
}, {
id: '3997185',
name: '与众不同的口感汝瓷白酒杯套组1壶4杯',
price: '108.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/8e21c794dfd3a4e8573273ddae50bce2.jpg',
}, {
id: '3997403',
name: '手工吹制更厚实白酒杯壶套装6壶6杯',
price: '100.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/af2371a65f60bce152a61fc22745ff3f.jpg',
}, {
id: '3998274',
name: '德国百年工艺高端水晶玻璃红酒杯2支装',
price: '139.00',
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/8896b897b3ec6639bbd1134d66b9715c.jpg',
}, ]
// 1. 渲染函数 封装
function render(arr) {
// 声明空字符串
let str = ''
// 遍历数组
arr.forEach(item => {
// 解构
const {
name,
picture,
price
} = item
str += `
<div class="item">
<img src=${picture} alt="">
<p class="name">${name}</p>
<p class="price">${price}</p>
</div>
`
})
// 追加给list
document.querySelector('.list').innerHTML = str
}
// 页面一打开就需要渲染
render(goodsList)
// 2. 过滤筛选
document.querySelector('.filter').addEventListener('click', e => {
// e.target.dataset.index e.target.tagName
const {
tagName,
dataset
} = e.target
// 判断
if (tagName === 'A') {
// arr 返回的新数组
let arr = goodsList
if (dataset.index === '1') {
arr = goodsList.filter(item => item.price > 0 && item.price <= 100)
} else if (dataset.index === '2') {
arr = goodsList.filter(item => item.price >= 100 && item.price <= 300)
} else if (dataset.index === '3') {
arr = goodsList.filter(item => item.price >= 300)
}
// 渲染函数
render(arr)
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>























 322
322











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










