题目
Description
Astronomers often examine star maps where stars are represented by points on a plane and each star has Cartesian coordinates. Let the level of a star be an amount of the stars that are not higher and not to the right of the given star. Astronomers want to know the distribution of the levels of the stars.
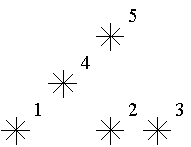
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
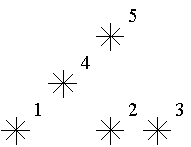
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
Input
The first line of the input file contains a number of stars N (1<=N<=15000). The following N lines describe coordinates of stars (two integers X and Y per line separated by a space, 0<=X,Y<=32000). There can be only one star at one point of the plane. Stars are listed in ascending order of Y coordinate. Stars with equal Y coordinates are listed in ascending order of X coordinate.
Output
The output should contain N lines, one number per line. The first line contains amount of stars of the level 0, the second does amount of stars of the level 1 and so on, the last line contains amount of stars of the level N-1.
Sample Input
5 1 1 5 1 7 1 3 3 5 5
Sample Output
1 2 1 1 0
题目大意:
在坐标上有n个星星,如果某个星星坐标为(x, y), 它的左下位置为:(x0,y0),x0<=x 且y0<=y。如果左下位置有a个星星,就表示这个星星属于level x
按照y递增,如果y相同则x递增的顺序给出n个星星,求出所有level水平的数量。
注意:题目求的是 每个等级星星的个数。并不是第i个星星的等级。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define RANGE 32005
int c[RANGE],level[15001];
int lowbit( int x )
{
return x&(-x);
}
void add( int i )
{
while( i<=RANGE )
{
++c[i];
i+=lowbit(i); //从下往上更新,更新每一个点c[i],因为已经输入了一个点,所以在后面的点看来,左面或者下面已经有一个了
}
}
int sum( int i ) //前i项求和,从第一相开始求
{
int sum=0;
while( i>0 )
{
sum+=c[i];
i-=lowbit(i); //从右往左加,注意看图
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int n,i,x,y;
while( ~scanf("%d",&n) )
{
memset(level,0,sizeof(level));
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
for ( i=0; i<n; i++ )
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
level[sum(++x)]++;
add(x);
}
for( i=0; i<n; i++ )
printf("%d\n",level[i]);
}
return 0;
}<strong>
</strong>
知识点:
树状数组
假设数组a[1..n],那么查询a[1]+...+a[n]的时间是log级别的,而且是一个在线的数据结构,支持随时修改某个元素的值,复杂度也为log级别。
来观察这个图:
令这棵树的结点编号为C1,C2...Cn。令每个结点的值为这棵树的值的总和,那么容易发现:
C1 = A1
C2 = A1 + A2
C3 = A3
C4 = A1 + A2 + A3 + A4
C5 = A5
C6 = A5 + A6
C7 = A7
C8 = A1 + A2 + A3 + A4 + A5 + A6 + A7 + A8
...
C16 = A1 + A2 + A3 + A4 + A5 + A6 + A7 + A8 + A9 + A10 + A11 + A12 + A13 + A14 + A15 + A16
这里有一个有趣的性质:
设节点编号为x,那么这个节点管辖的区间为2^k(其中k为x二进制末尾0的个数)个元素。因为这个区间最后一个元素必然为Ax,
所以很明显:Cn = A(n – 2^k + 1) + ... + An
算这个2^k有一个快捷的办法,定义一个函数如下即可:
|
1
2
3
|
int
lowbit(
int
x){
return
x&(x^(x–1));
}
|
利用机器补码特性,也可以写成:
|
1
2
3
|
int
lowbit(
int
x){
return
x&-x;
}
|
当想要查询一个SUM(n
)(求a[n]的和),可以依据如下算法即可:
step1: 令sum = 0,转第二步;
step2: 假如n <= 0,算法结束,返回sum值,否则sum = sum + Cn,转第三步;
step3: 令n = n – lowbit(n),转第二步。
可以看出,这个算法就是将这一个个区间的和全部加起来,为什么是效率是log(n)的呢?以下给出证明:
n = n – lowbit(n)这一步实际上等价于将n的二进制的最后一个1减去。而n的二进制里最多有log(n)个1,所以查询效率是log(n)的。
那么修改呢,修改一个节点,必须修改其所有祖先,最坏情况下为修改第一个元素,最多有log(n)的祖先。
所以修改算法如下(给某个结点i加上x):
step1: 当i > n时,算法结束,否则转第二步;
step2: Ci = Ci + x, i = i + lowbit(i)转第一步。
i = i +lowbit(i)这个过程实际上也只是一个把末尾1补为0的过程。
对于
数组求和来说树状数组简直太快了!
注:
求lowbit(x)的建议公式:
lowbit(x):=x and -x;
或lowbit(x):=x and (x xor (x - 1));
lowbit(x)即为2^k的值。



























 454
454











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










