K-Nearest Neighbor KNN算法
如果一个样本在特征空间中的K个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的样本中的大多数属于某一个类别,则该样本也属于这个类别。
所选择的邻居都是已经正确分类的对象。
如果K=3,则绿色圆形的类别与红色三角形相同
如果K=5,则绿色圆形的类别与蓝色正方形相同
The choice of distance is a
hyperparameter.
K的选择: 不同问题不同对待,一般是尝试很多不同的K值,找到最好的。
- Choose hyperparameters that work best on the data.

BAD:K=1 always works perfectly on training data
- Split data into train and test, choose hyperparameters that work best on test data.

BAD: test set is a proxy for the generalization performance, using only at the end.
(交叉验证)用四个fold作为训练,一个fold作为验证,循环。
距离选择:
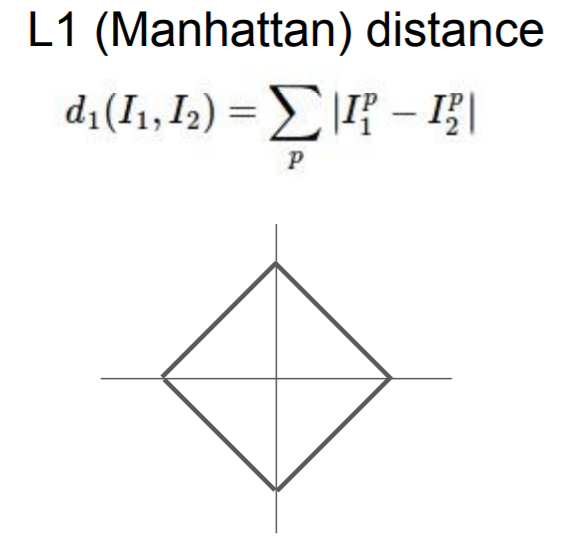
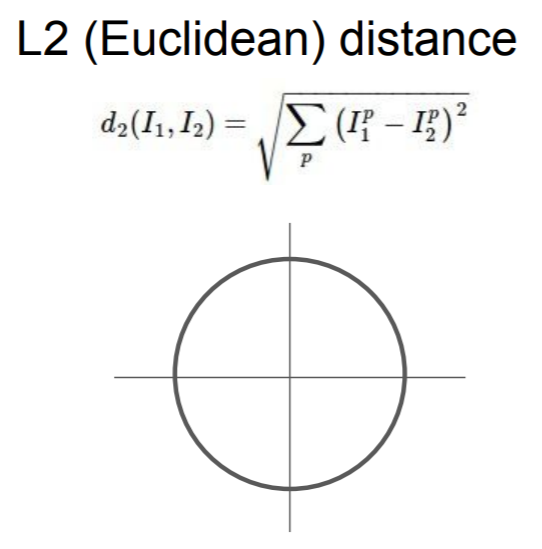
K-Nearest Neighbor on images
never used.
效率低
并不提供详细的信息
KNN算法matlab实现(一次预测一个点)
function ytest = KNN(X, y, Xtest, k)
% X = [1,3; 2,2; 1,1; 3,1; 3,0.5; 2,0.5]
% y = [0;0;1;1;1;1]
% Xtest = [1,2]
% k =3 k =5
m = size(X,1);
n = size(X,2);
mtest = size(Xtest,1);
dis = zeros(m,1);
for i = 1:m,
temp = 0;
for j = 1:n
temp = temp + (Xtest(1,j) - X(i,j))^2;
end;
temp = temp.^0.5;
dis(i,1) = temp;
end;
ordered_dis = sort(dis);
disp(ordered_dis);
max_dis = ordered_dis(k);
index = find(dis<=max_dis);
num = size(index,1);
tar_y = y(index);
count = zeros(num,1);
for i = 1:num,
count(i) = size(find(tar_y == tar_y(i)),1);
end;
tar_index = find(count==max(count));
ytest = tar_y(tar_index(1));
Python实现
import numpy
def KNN(X, y, Xtest, k):
m = X.shape[0]
n = X.shape[1]
print(m)
print(n)
ytest = 0
temp = (numpy.tile(Xtest, (m, 1)) - X)**2
dis = []
for z in range(m):
s = 0
for l in range(n):
s = s + temp[z][l]
dis.append(s ** 0.5)
print(dis)
index = numpy.argsort(dis)
index = index[0:k]
print(index)
tar_y = []
for i in index:
tar_y.append(y[i])
print(tar_y)
count = 0
class_index = 0
for j in tar_y:
print('j =',j)
if count < tar_y.count(j):
count = tar_y.count(j)
print(count)
ytest = tar_y[class_index]
class_index = class_index + 1
return ytest
X = numpy.array([[1, 3], [2, 2], [1, 1], [3, 1], [3, 0.5], [2, 0.5]])
y = [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]
k = 3
Xtest = [1, 2]
ytest = KNN(X, y, Xtest, k)
print(ytest)























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








