2.7 Proxy
代理模式为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。 在需要用比较通用和复杂的对象指针代替简单的的指针的时候,使用代理模式。有四种常用的情况:
1、远程代理,也就是为一个对象在不同的地址空间提供局部代表。这样可以隐藏一个对象存在于不同地址空间的事实。
2、虚拟代理,是根据需要创建开销很大的对象。通过它来存放实例化需要很长时间的真实对象。
3、安全代理,用来控制真实对象访问的权限。
4、智能指针,取代了简单的指针,它在访问对象时执行一些附加操作。
参与者:
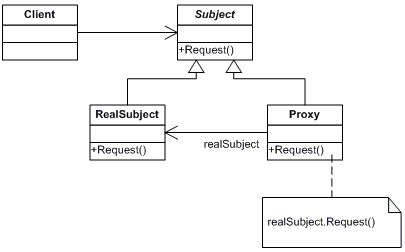
Proxy
— 保存一个引用使得代理可以访问实体。若RealSubject和Subject的接口相同,proxy会引用Subject。
— 提供一个与Subject的接口相同的接口,这样代理就可以用来代替实体。
— 控制对实体的存取,并可能负责创建和删除它。
— 其它功能依赖于代理的类型。
Subject
— 定义RealSubject和Proxy的共用接口,这样就可以在任何使用RealSubject的地方都可以使用Proxy。
RealSubject
— 定义Proxy所代表的实体。
思想:作为C++工程师,免不了要管理内存,内存管理也是C++中的难点,而智能指针采用引用计数的办法很方便的帮我们管理了内
存的使用,极大方便了我们的工作效率。而智能指针的这种用法其实就是代理模式的一种,他帮我们控制了该对象的内存使用。代理
模式就是为其他对象提供一种代理来控制对这个对象的访问。
场景:需要注意体会他和Decorator的需别。Proxy是继承需要修饰的类,而Decorator用的是包含的方式。Proxy模式,或者准确地
说DynamicProxy模式,是现代AOP框架实现中的一种常用方式。典型的实现如Spring,JBoss以及CastleProject中的Aspect。
实现:继承,并在过载方法中添加需要的修饰功能。
实例:
(1) 远程代理
大话设计模式里面的例子:小王想追求小娟,但他不认识小娟。但他的朋友小林认识小娟,所以他通过让小林帮忙送礼物的方式追求小娟。
这里的小林就是我们的代理!
首先,我们实现一个女孩类:
class Girl{ public: Girl(char* name = ""):mName(name){} char* getName() { return mName; } private: char* mName; };
送礼物的接口:
class GiveGift { public: virtual void GiveDolls() = 0; virtual void GiveFlowers() = 0; virtual void GiveChocolate() = 0; };
送礼物实例类(小王)
class Puisuit : public GiveGift { public: Puisuit(Girl mm):mGirl(mm){} virtual void GiveDolls() { cout<<"送"<<mGirl.getName()<<"玩具!"<<endl; } virtual void GiveFlowers() { cout<<"送"<<mGirl.getName()<<"鲜花!"<<endl; } virtual void GiveChocolate() { cout<<"送"<<mGirl.getName()<<"巧克力!"<<endl; } private: Girl mGirl; };
送礼物代理类(小林)
class Proxy : public GiveGift { public: Proxy(Girl mm) { mPuisuit = new Puisuit(mm); } virtual void GiveDolls() { mPuisuit->GiveDolls(); } virtual void GiveFlowers() { mPuisuit->GiveFlowers(); } virtual void GiveChocolate() { mPuisuit->GiveChocolate(); } private: Puisuit* mPuisuit; };
客户端代码:
#include <iostream> #include "Proxy.h" using namespace std; int main() { Girl mm("小娟"); Proxy pro(mm); pro.GiveChocolate(); pro.GiveDolls(); pro.GiveFlowers(); return 0; }
(2)虚拟代理
考虑一个可以在文档中嵌入图形对象的文档编辑器。有些图形对象的创建开销很大。但是打开文档必须很迅速,因此我们在打开文档时应避免一次性创建所有开销
很大的对象。这里就可以运用代理模式,在打开文档时,并不打开图形对象,而是打开图形对象的代理以替代真实的图形。待到真正需要打开图形时,仍由代理负
责打开。
简单实现如下:
- class Image
- {
- public:
- Image(string name): m_imageName(name) {}
- virtual ~Image() {}
- virtual void Show() {}
- protected:
- string m_imageName;
- };
- class BigImage: public Image
- {
- public:
- BigImage(string name):Image(name) {}
- ~BigImage() {}
- void Show() { cout<<"Show big image : "<<m_imageName<<endl; }
- };
- class BigImageProxy: public Image
- {
- private:
- BigImage *m_bigImage;
- public:
- BigImageProxy(string name):Image(name),m_bigImage(0) {}
- ~BigImageProxy() { delete m_bigImage; }
- void Show()
- {
- if(m_bigImage == NULL)
- m_bigImage = new BigImage(m_imageName);
- m_bigImage->Show();
- }
- };
客户调用:
- int main()
- {
- Image *image = new BigImageProxy("proxy.jpg"); //代理
- image->Show(); //需要时由代理负责打开
- delete image;
- return 0;
- }
在这个例子属于虚代理的情况,下面给两个智能引用的例子。一个是C++中的auto_ptr,另一个是smart_ptr。自己实现了一下。先给出auto_ptr的代码实现
- template<class T>
- class auto_ptr {
- public:
- explicit auto_ptr(T *p = 0): pointee(p) {}
- auto_ptr(auto_ptr<T>& rhs): pointee(rhs.release()) {}
- ~auto_ptr() { delete pointee; }
- auto_ptr<T>& operator=(auto_ptr<T>& rhs)
- {
- if (this != &rhs) reset(rhs.release());
- return *this;
- }
- T& operator*() const { return *pointee; }
- T* operator->() const { return pointee; }
- T* get() const { return pointee; }
- T* release()
- {
- T *oldPointee = pointee;
- pointee = 0;
- return oldPointee;
- }
- void reset(T *p = 0)
- {
- if (pointee != p) {
- delete pointee;
- pointee = p;
- }
- }
- private:
- T *pointee;
- };
分配的对象提供异常安全。因为它用一个对象存储需要被自动释放的资源,然后依靠对象的析构函数来释放资源。这样客户就不需要关注资源的释放,由auto_ptr
对象自动完成。实现中的一个关键就是重载了解引用操作符和箭头操作符,从而使得auto_ptr的使用与真实指针类似。
(3)安全代理
游戏中,通过代理来控制不同vip玩家的游戏权限。
基本操作接口
class Play { public: virtual void Play1() = 0; virtual void Play2() = 0; virtual void Play3() = 0; };
操作类:
class Player:public Play { public: void Play1() { cout<<"战役"<<endl; } void Play2() { cout<<"军团"<<endl; } void Play3() { cout<<"神器"<<endl; } };
不同vip玩家的代理:
class ProxyPlayerVip0:Play { public: ProxyPlayerVip0() { mPlayer = new Player; } void Play1() { mPlayer->Play1(); } void Play2() { cout<<"没有权限"<<endl; } void Play3() { cout<<"没有权限"<<endl; } private: Play* mPlayer; }; class ProxyPlayerVip1:Play { public: ProxyPlayerVip1() { mPlayer = new Player; } void Play1() { mPlayer->Play1(); } void Play2() { mPlayer->Play2(); } void Play3() { cout<<"没有权限"<<endl; } private: Play* mPlayer; };
客户端代码:
ProxyPlayerVip0 pro5;
pro5.Play1();
pro5.Play2();
pro5.Play3();
ProxyPlayerVip1 pro1;
pro1.Play1();
pro1.Play2();
pro1.Play3();
结果:
战役
没有权限
没有权限
战役
军团
没有权限
(4)智能指针
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include <assert.h>
- #define KSAFE_DELETE(p) \
- if (p) \
- { \
- delete p; \
- p = NULL; \
- }
- class KRefCount
- {
- public:
- KRefCount():m_nCount(0){}
- public:
- void AddRef(){m_nCount++;}
- int Release(){return --m_nCount;}
- void Reset(){m_nCount=0;}
- private:
- int m_nCount;
- };
- template <typename T>
- class KSmartPtr
- {
- public:
- KSmartPtr(void)
- : m_pData(NULL)
- {
- m_pReference = new KRefCount();
- m_pReference->AddRef();
- }
- KSmartPtr(T* pValue)
- : m_pData(pValue)
- {
- m_pReference = new KRefCount();
- m_pReference->AddRef();
- }
- KSmartPtr(const KSmartPtr<T>& sp)
- : m_pData(sp.m_pData)
- , m_pReference(sp.m_pReference)
- {
- m_pReference->AddRef();
- }
- ~KSmartPtr(void)
- {
- if (m_pReference && m_pReference->Release() == 0)
- {
- KSAFE_DELETE(m_pData);
- KSAFE_DELETE(m_pReference);
- }
- }
- inline T& operator*()
- {
- return *m_pData;
- }
- inline T* operator->()
- {
- return m_pData;
- }
- KSmartPtr<T>& operator=(const KSmartPtr<T>& sp)
- {
- if (this != &sp)
- {
- if (m_pReference && m_pReference->Release() == 0)
- {
- KSAFE_DELETE(m_pData);
- KSAFE_DELETE(m_pReference);
- }
- m_pData = sp.m_pData;
- m_pReference = sp.m_pReference;
- m_pReference->AddRef();
- }
- return *this;
- }
- KSmartPtr<T>& operator=(T* pValue)
- {
- if (m_pReference && m_pReference->Release() == 0)
- {
- KSAFE_DELETE(m_pData);
- KSAFE_DELETE(m_pReference);
- }
- m_pData = pValue;
- m_pReference = new KRefCount;
- m_pReference->AddRef();
- return *this;
- }
- T* Get()
- {
- T* ptr = NULL;
- ptr = m_pData;
- return ptr;
- }
- void Attach(T* pObject)
- {
- if (m_pReference->Release() == 0)
- {
- KSAFE_DELETE(m_pData);
- KSAFE_DELETE(m_pReference);
- }
- m_pData = pObject;
- m_pReference = new KRefCount;
- m_pReference->AddRef();
- }
- T* Detach()
- {
- T* ptr = NULL;
- if (m_pData)
- {
- ptr = m_pData;
- m_pData = NULL;
- m_pReference->Reset();
- }
- return ptr;
- }
- private:
- KRefCount* m_pReference;
- T* m_pData;
- }
重构成本:低。























 9557
9557

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








