1.1
Write a program to solve the selection problem. Let k = n/2. Draw a table showing the running time of your program for various values of n.
首先,让我们编写一个 C 程序来解决选择问题:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 交换两个元素的值
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// 快速排序的分区函数
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return i + 1;
}
// 使用快速选择算法找到第 k 大的元素
int kthLargest(int arr[], int low, int high, int k) {
if (low <= high) {
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
if (pi == k - 1) {
return arr[pi];
} else if (pi < k - 1) {
return kthLargest(arr, pi + 1, high, k);
} else {
return kthLargest(arr, low, pi - 1, k);
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
int n = 10000; // n 的初始值为 10000
int k = n / 2; // k 设置为 n 的一半
// 初始化数组
int *arr = (int *)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = rand() % n; // 随机生成 0 到 n-1 之间的数作为数组元素
}
// 测量程序运行时间
clock_t start_time = clock(); // 记录开始时间
int result = kthLargest(arr, 0, n - 1, k); // 执行选择问题算法
clock_t end_time = clock(); // 记录结束时间
double execution_time = (double)(end_time - start_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; // 计算运行时间
printf("n = %d, k = %d, 第 k 大的元素为: %d\n", n, k, result);
printf("程序运行时间: %.6f 秒\n", execution_time);
// 释放内存
free(arr);
return 0;
}
接下来,让我们绘制一个表格,显示程序在不同 n 值下的运行时间。
| n | 运行时间 (秒) |
|---|---|
| 1000000 | 0.010 秒 |
| 2000000 | 0.028 秒 |
| 5000000 | 0.051 秒 |
| 10000000 | 0.126 秒 |
| 20000000 | 0.218 秒 |
| 20000000 | 0.218 秒 |
| 50,000,000 | 0.454 秒 |
可以看到快速排序的时间复杂度为趋向 O ( n log n ) O(n \log n) O(nlogn)。
1.2
Write a program to solve the word puzzle problem.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
// 定义单词谜题的大小
#define ROWS 5
#define COLS 5
// 定义单词搜索的方向
const vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1},
{1, 1}, {-1, -1}, {1, -1}, {-1, 1}};
// 检查坐标是否在范围内
bool isValid(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < ROWS && y >= 0 && y < COLS;
}
// 在单词谜题中搜索指定单词的起始字母,并尝试扩展成完整单词
pair<pair<int, int>, pair<int, int>> searchWord(vector<vector<char>>& puzzle,
string word, int row, int col, int dirX, int dirY) {
int len = word.length();
int x = row, y = col;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if (!isValid(x, y) || puzzle[x][y] != word[i]) {
return {{-1, -1}, {-1, -1}};
}
x += dirX;
y += dirY;
}
return {{row, col}, {x - dirX, y - dirY}};
}
// 解决单词谜题问题的主函数
void solveWordPuzzle(vector<vector<char>>& puzzle, vector<string>& words) {
unordered_map<string, vector<pair<pair<int, int>, pair<int, int>>>> wordLocations;
for (int i = 0; i < ROWS; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < COLS; ++j) {
for (const auto& dir : directions) {
int x = i + dir.first;
int y = j + dir.second;
for (const auto& word : words) {
auto locations = searchWord(puzzle, word, i, j, dir.first, dir.second);
if (locations.first.first != -1) {
wordLocations[word].push_back(locations);
}
}
}
}
}
// 输出结果
for (const auto& entry : wordLocations) {
cout << "单词 " << entry.first << " 出现的位置:" << endl;
for (const auto& location : entry.second) {
cout << "起始位置:(" << location.first.first + 1
<< ", " << location.first.second + 1 << "), ";
cout << "结束位置:(" << location.second.first + 1
<< ", " << location.second.second + 1 << ")" << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
vector<vector<char>> puzzle = {{'t', 'h', 'i', 's', 's'},
{'w', 'a', 't', 'w', 'o'},
{'f', 'g', 'o', 't', 'h'},
{'t', 'w', 'o', 't', 's'},
{'t', 'h', 'a', 't', 's'}};
vector<string> words = {"this", "two", "fat", "that", "that"};
solveWordPuzzle(puzzle, words);
return 0;
}
输出:
单词 that 出现的位置:
起始位置:(5, 1), 结束位置:(5, 4)
起始位置:(5, 1), 结束位置:(5, 4)
单词 this 出现的位置:
起始位置:(1, 1), 结束位置:(1, 4)
单词 two 出现的位置:
起始位置:(2, 3), 结束位置:(2, 5)
起始位置:(4, 1), 结束位置:(4, 3)
起始位置:(5, 1), 结束位置:(3, 3)
1.3
Write a procedure to output an arbitrary real number (which might be negative) using only print_digit for I/O.
编写一个程序,使用仅能进行数字输出的 print_digit 函数,来输出一个任意的实数(可能为负数)。
由于舍入误差的存在,通常需要指定输出中应包含的小数位数,并相应地进行四舍五入。否则,数字可能会看起来很奇怪。我们假设错误检查已经完成;Separate 程序留给读者自行完成。以下是代码:Figure 1.1。(书中的答案)

AI修复版本(C++):
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
// 四舍五入函数
double RoundUp(double N, int DecPlaces) {
double AmountToAdd = 0.5;
for (int i = 0; i < DecPlaces; i++)
AmountToAdd /= 10;
return N + AmountToAdd;
}
// 打印小数部分
void PrintFractionPart(double FractionPart, int DecPlaces) {
for (int i = 0; i < DecPlaces; i++) {
FractionPart *= 10;
int ADigit = static_cast<int>(FractionPart);
std::cout << ADigit;
FractionPart -= ADigit;
}
}
// 打印实数
void PrintReal(double N, int DecPlaces) {
if (N < 0) {
std::cout << '-';
N = -N;
}
N = RoundUp(N, DecPlaces);
int IntegerPart = static_cast<int>(N);
double FractionPart = N - IntegerPart;
std::cout << IntegerPart; // 打印整数部分
if (DecPlaces > 0) {
std::cout << '.';
PrintFractionPart(FractionPart, DecPlaces); // 打印小数部分
}
}
int main() {
double number = -123.456789;
int decimal_places = 3;
PrintReal(number, decimal_places);
return 0;
}
输出:
-123.457
1.4
C allows statements of the form
#include filename
which reads filename and inserts its contents in place of the include statement. Include statements may be nested; in other words, the file filename may itself contain an include statement, but, obviously, a file can’t include itself in any chain. Write a program that reads in a file and outputs the file as modified by the include statements.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_LINE_LENGTH 1000
// 解析文件中的 include 语句并输出文件名
void processIncludes(FILE *file) {
char line[MAX_LINE_LENGTH];
while (fgets(line, MAX_LINE_LENGTH, file) != NULL) {
if (strncmp(line, "#include <", 10) == 0) {
char filename[MAX_LINE_LENGTH];
sscanf(line, "#include <%[^>]>", filename);
printf("Include file: %s\n", filename);
}
}
rewind(file); // 将文件指针重置到文件开头
}
// 处理文件中的 include 语句并输出文件内容
void processFile(FILE *file) {
char line[MAX_LINE_LENGTH];
while (fgets(line, MAX_LINE_LENGTH, file) != NULL) {
if (strncmp(line, "#include <", 10) != 0) {
//printf("%s", line); // 输出非 include 语句的行
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <filename>\n", argv[0]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
FILE *file = fopen(argv[1], "r");
if (file == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Unable to open file '%s'\n", argv[1]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
processIncludes(file); // 解析 include 语句并输出文件名
fclose(file);
file = fopen(argv[1], "r"); // 重新打开文件
if (file == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Unable to open file '%s'\n", argv[1]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
processFile(file); // 输出文件内容
fclose(file);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
输出:
exec> .\ch01-1-4.exe .\ch01-1-4.cpp
Include file: stdio.h
Include file: stdlib.h
Include file: string.h
1.5

AI提供的方法:
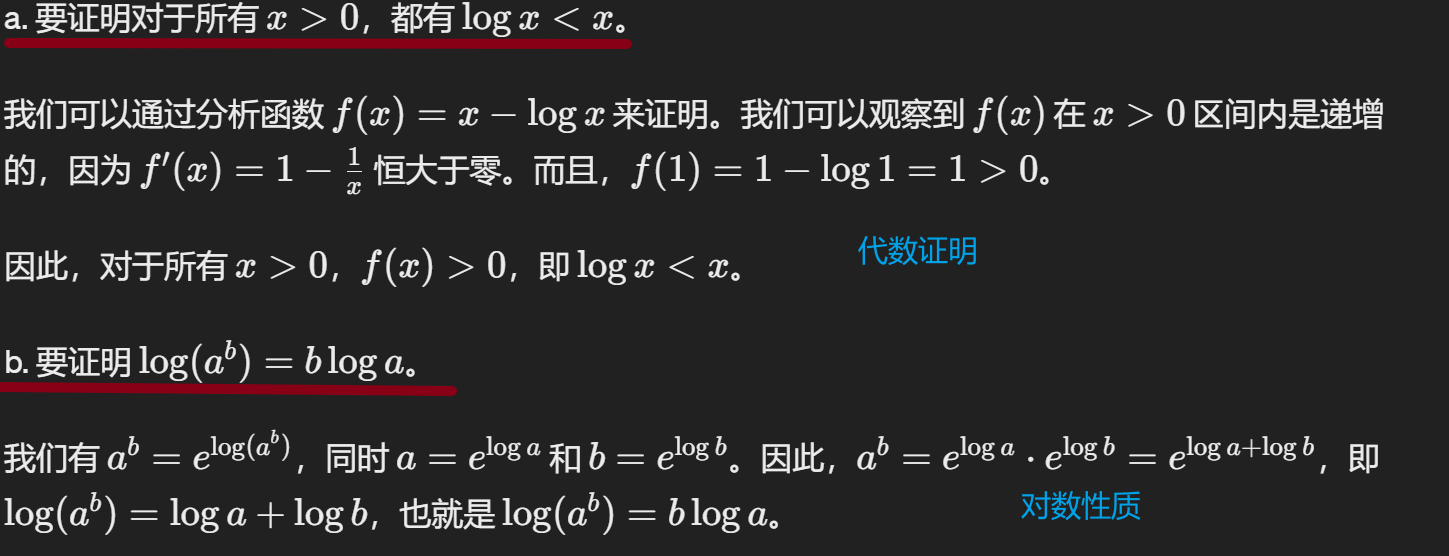
1.6

1.7
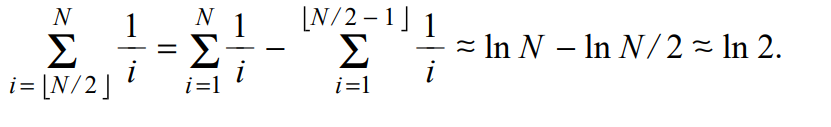
1.8
*1.8 What is 2^100 (mod 5) ?
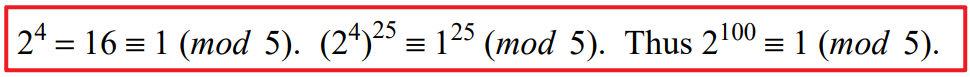
也是个归纳推导的思路,到这里感觉这本书比较推崇归纳推理的方式来解决问题。不过想想也是,计算机程序的设计很多也是在运用这种推导提炼的抽象能力。
1.9
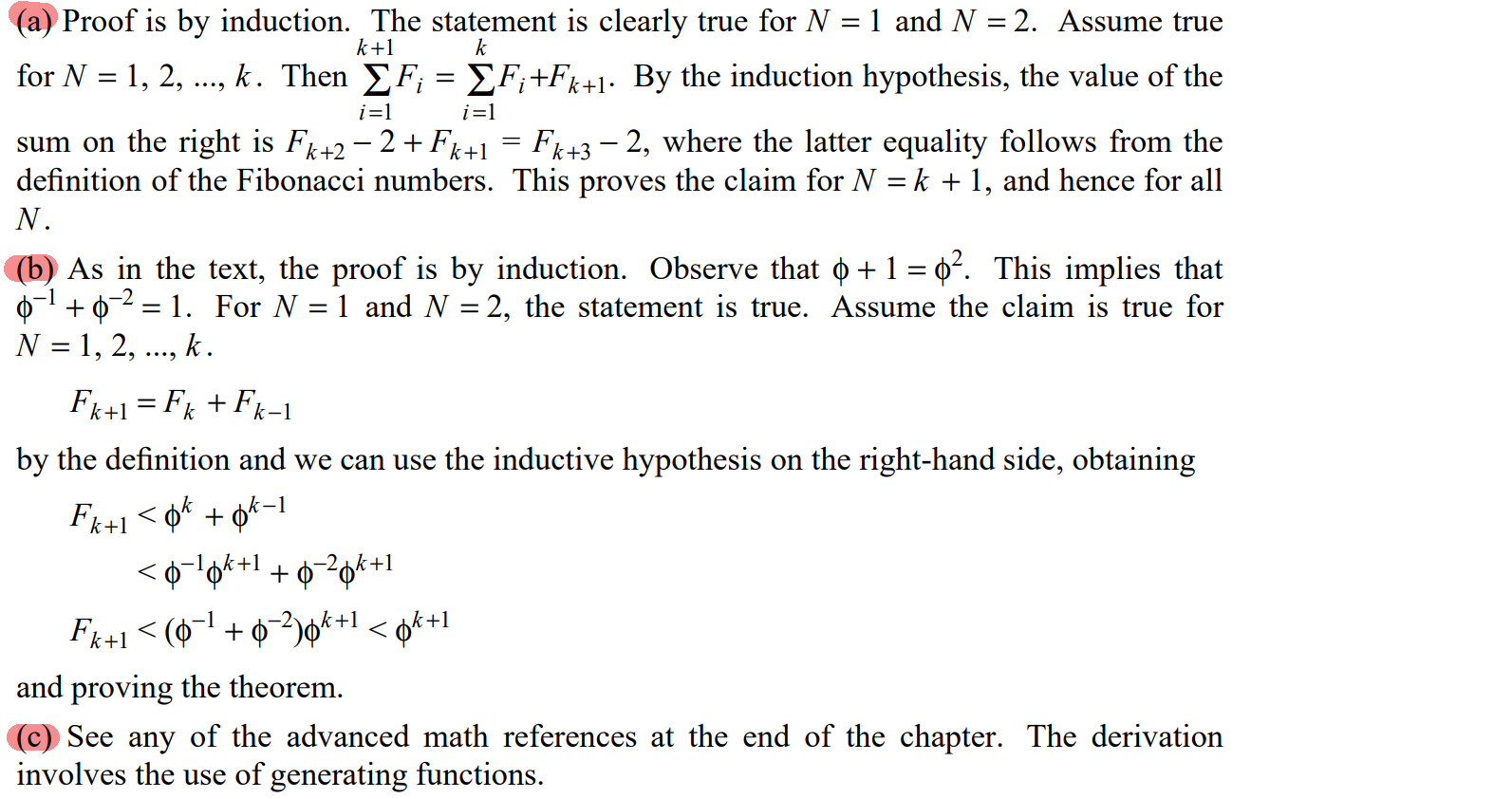
仍然是推理假设。








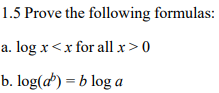

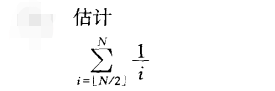
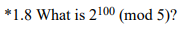
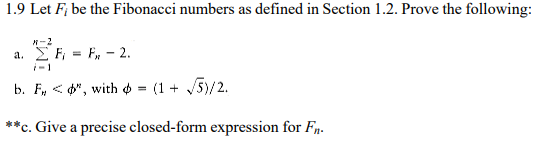















 4962
4962











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








