2 神经网络前向传播
神经网络是一种很古老的算法,它最初产生的目的是制造能模拟大脑的机器。20世纪八九十年代比较火,后来支持向量机的兴起而逐渐衰落。21世纪第一个十年后期,由于计算机处理能力的显著提高,神经网络又火起来。
科学家希望模拟人的大脑,不同的接收器官(比如眼睛、鼻子、耳朵)接收信号,经过多个不同神经元处理,形成最终的信息

神经网络包含:一个输入层、一个输出层、多个隐藏层
如下图3层神经网络包含:一个输入层、一个隐藏层、一个输出层。前向传播过程见下图

2.1 作业介绍
在本练习的前一部分中,您实现了多类逻辑回归来识别手写数字。然而,逻辑回归只是一个线性分类器,不能形成更复杂的假设
在本部分练习中,您将使用与前面相同的训练集实现一个神经网络来识别手写数字。神经网络将能够表示形成非线性假设的复杂模型。这周,你们将使用我们已经训练过的神经网络的参数。您的目标是实现x前向传播算法来使用我们的权重进行预测。在下周的练习中,您将编写学习神经网络参数的反向传播算法。
2.2 导入模型和数据
导入模块
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as scio
import displayData as dd # 绘制手写图形函数
import predict as pd # 预测函数
初始化数据
plt.ion()
# Setup the parameters you will use for this part of the exercise
input_layer_size = 400 # 20x20 input images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = 25 # 25 hidden layers
num_labels = 10 # 10 labels, from 0 to 9
# Note that we have mapped "0" to label 10
导入数据
data = scio.loadmat('ex3data1.mat')
X = data['X']
y = data['y'].flatten()
m = y.size
2.3 绘制数字图片函数(displayData.py)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def display_data(x):
(m, n) = x.shape # 训练样本维度 (100, 400)
# Set example_width automatically if not passed in
example_width = np.round(np.sqrt(n)).astype(int) # 数字图片宽 20
example_height = (n / example_width).astype(int) # 数字图片高 20
# Compute the number of items to display
display_rows = np.floor(np.sqrt(m)).astype(int) # 训练样本行数:10
display_cols = np.ceil(m / display_rows).astype(int) # 训练样本列数:10
# Between images padding
pad = 1 # 数字图片前后左右间隔为1px
# Setup blank display 显示样例图片范围
display_array = - np.ones((pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad),
pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad)))
# Copy each example into a patch on the display array
curr_ex = 0
for j in range(display_rows):
for i in range(display_cols):
if curr_ex > m:
break
# Copy the patch
# Get the max value of the patch
max_val = np.max(np.abs(x[curr_ex]))#不明白为啥要除最大值,没看出差异
# 开始一个个画出数字图
display_array[pad + j * (example_height + pad) + np.arange(example_height),
pad + i * (example_width + pad) + np.arange(example_width)[:, np.newaxis]] = \
x[curr_ex].reshape((example_height, example_width)) / max_val
curr_ex += 1
if curr_ex > m:
break
# Display image
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(display_array, cmap='gray', extent=[-1, 1, -1, 1])
plt.axis('off')
随机选择100数字图,并显示效果
# Randomly select 100 data points to display
rand_indices = np.random.permutation(range(m))
selected = X[rand_indices[0:100], :]
dd.display_data(selected)

2.4 加载提供已训练好参数的theta
data = scio.loadmat('ex3weights.mat')
theta1 = data['Theta1']
theta2 = data['Theta2']
显示theta
print('theta1.shape: ',theta1.shape, '\ntheta2.shape: ', theta2.shape)
theta1.shape: (25, 401)
theta2.shape: (10, 26)
2.5 用神经网络训练的参数预测手写数字
sigmoid公式
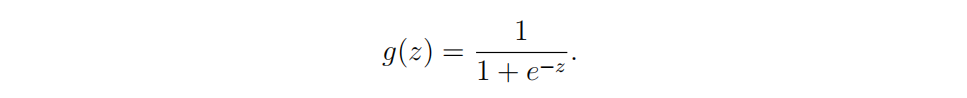
sidmoid函数
def sigmoid(z):
g = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
return g
from sigmoid import *
def predict(theta1, theta2, x):
# Useful values
m = x.shape[0]
num_labels = theta2.shape[0]
# You need to return the following variable correctly
p = np.zeros(m)
a1 = np.c_[np.ones(m), x]
z2 = np.dot(a1, theta1.T)
a2 = np.c_[np.ones(m),sigmoid(z2)]
z3 = np.dot(a2, theta2.T)
a3 = sigmoid(z3)
p = np.argmax(a3, axis=1) + 1
return p
调用预测函数预测并打印预测准确百分比,神经网络预测准确率97.52,较多分类逻辑回归要高好多
pred = predict(theta1, theta2, X)
print('Training set accuracy: {}'.format(np.mean(pred == y)*100))
Training set accuracy: 97.52
def getch():
import termios
import sys, tty
def _getch():
fd = sys.stdin.fileno()
old_settings = termios.tcgetattr(fd)
try:
tty.setraw(fd)
ch = sys.stdin.read(1)
finally:
termios.tcsetattr(fd, termios.TCSADRAIN, old_settings)
return ch
return _getch()
# Randomly permute examples
rp = np.random.permutation(range(m))
for i in range(m):
print('Displaying Example image')
example = X[rp[i]]
example = example.reshape((1, example.size))
dd.display_data(example)
pred = pd.predict(theta1, theta2, example)
print('Neural network prediction: {} (digit {})'.format(pred, np.mod(pred, 10)))
s = input('Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit: ')
if s == 'q':
break
Displaying Example image
Neural network prediction: [0.] (digit [0.])
Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit:
Displaying Example image
Neural network prediction: [0.] (digit [0.])
Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit:
Displaying Example image
Neural network prediction: [0.] (digit [0.])
Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit:
Displaying Example image
Neural network prediction: [0.] (digit [0.])
Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit:
Displaying Example image
Neural network prediction: [0.] (digit [0.])
Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit:
Displaying Example image
Neural network prediction: [0.] (digit [0.])
Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit:
Displaying Example image
Neural network prediction: [0.] (digit [0.])
Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit:
Displaying Example image
Neural network prediction: [0.] (digit [0.])
Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit: q


前一篇 吴恩达机器学习 EX3 作业 第一部分多分类逻辑回归 手写数字
后一篇 吴恩达机器学习 EX4 作业 神经网络反向传播 手写数字






















 1387
1387











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








