代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define DEFAULT_SIZE 5
typedef struct StaticLinkedNode {
char data;
int next;
} *NodePtr;
//用于表示静态链表中的一个节点
typedef struct StaticLinkedList {
NodePtr nodes;//用于存储所有节点的数组
int* used;//用于记录每个节点是否被使用
} *ListPtr;
//用于表示整个静态链表
ListPtr initLinkedList() {
ListPtr tempPtr = (ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedList));
tempPtr->nodes = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->used = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->nodes[0].data = '\0';
tempPtr->nodes[0].next = -1;
tempPtr->used[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i++) {
tempPtr->used[i] = 0;
}
return tempPtr;
}
void printList(ListPtr paraListPtr) {
int p = 0;
while (p != -1) {
printf("%c", paraListPtr->nodes[p].data);
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}
void insertElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar, int paraPosition) {
int p, q, i;
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i < paraPosition; i++) {
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
if (p == -1) {
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.\r\n", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
for (i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i++) {
if (paraListPtr->used[i] == 0) {
printf("Space at %d allocated.\r\n", i);
paraListPtr->used[i] = 1;
q = i;
break;
}
}
if (i == DEFAULT_SIZE) {
printf("No space.\r\n");
return;
}
paraListPtr->nodes[q].data = paraChar;
printf("linking\r\n");
paraListPtr->nodes[q].next = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = q;
}
void deleteElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar) {
int p, q;
p = 0;
while ((paraListPtr->nodes[p].next != -1) && (paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].data != paraChar)) {
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
if (paraListPtr->nodes[p].next == -1) {
printf("Cannot delete %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
q = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].next;
paraListPtr->used[q] = 0;//相当于free(q)
}
void appendInsertDeleteTest() {
ListPtr tempList = initLinkedList();
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
printList(tempList);
printf("Deleting 'e'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
printf("Deleting 'a'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printf("Deleting 'o'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'x', 1);
printList(tempList);
}
void main() {
appendInsertDeleteTest();
}代码说明
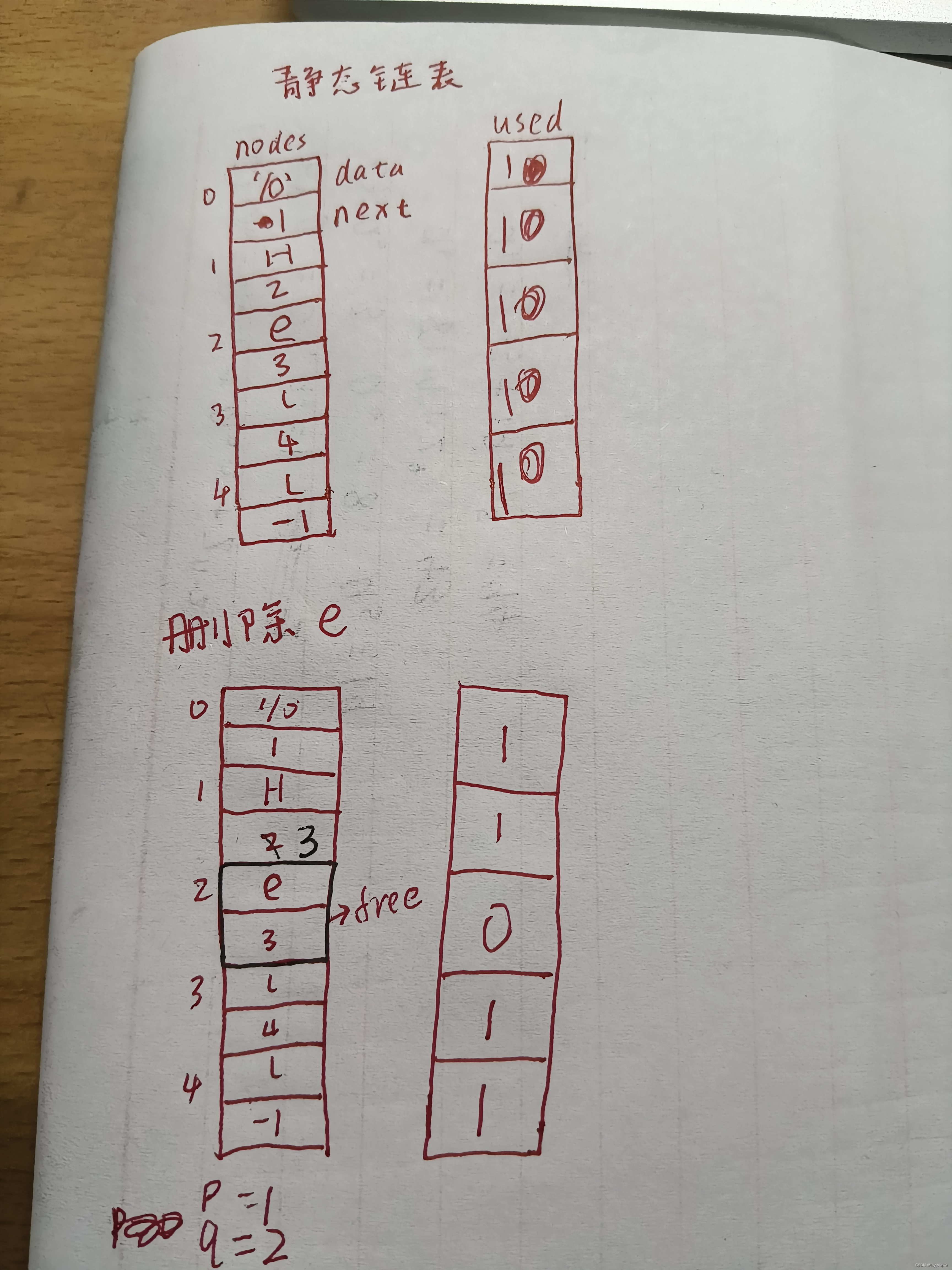
1.与动态链表相比,静态链表在内存使用上更为高效。因为静态链表是在数组的基础上实现的,所以其节点空间在程序运行前就已经分配好,不需要在运行时动态申请和释放内存
2.在deleteElement函数中,paraListPtr->used[q] = 0相当于释放了这一空间,以此来表示该节点是空闲的
运行结果
Space at 1 allocated.
linking
Space at 2 allocated.
linking
Space at 3 allocated.
linking
Space at 4 allocated.
linking
No space.
Hell
Deleting 'e'.
Deleting 'a'.
Cannot delete a
Deleting 'o'.
Cannot delete o
Hll
Space at 2 allocated.
linking
Hxll图示解说






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








