目录
一、集合操作
定义两个集合,然后在集合中存储多个用户的名称,实现以下操作
1.第一个集合只保留姓名长度为3的成员
2.第一个集合筛选后只要前个人
3.第二个集合只要姓张的人
4.第二个集合筛选后不要前两个人
5.将两个集合并为一个
6.根据姓名创建Person对象
7.打印整个person的信息
public class StreamCaseTest21 {
/*1.第一个集合只保留姓名长度为2的成员
2.第一个集合筛选后只要前3个人
3.第二个集合只要姓张的人
4.第二个集合筛选后不要前1个人
5.将两个集合并为一个
6.根据姓名创建Person对象
7.打印整个person的信息*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("迪丽热巴", "古力娜扎","宋远桥", "苏星河", "老子", "庄子", "孔子", "洪七公");
List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("张无忌", "张三丰", "赵丽颖", "白百合", "张二狗", "张天爱", "林俊杰");
Stream<String> stream1 = list1.stream().filter(s -> s.length() == 3).limit(2);
//stream1.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("--------------------");
Stream<String> stream2 = list2.stream().filter(s -> s.contains("张")).skip(1);
//stream2.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("--------------------");
Stream.concat(stream1,stream2).map(Person::new).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}二、Stream-数据收集
2.1 结果收集到集合中
/**
* 将结果收集到集合中
*/
public class StreanResTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//收集到list中
List<String> list = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa").collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
//收集到Set集合中
Set<String> set = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa").collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(set);
//收集到具体的实现中,如ArrayList,HashSet
ArrayList<String> arrayList = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
//.collect(Collectors.toCollection(() -> new ArrayList<>()));
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
System.out.println(arrayList);
//收集到具体的实现中,如ArrayList,HashSet
HashSet<String> hashSet = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
//.collect(Collectors.toCollection(() -> new HashSet<>()));
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
System.out.println(hashSet);
}
}输出:
[aa, bb, cc, aa]
[aa, bb, cc]
[aa, bb, cc, aa]
[aa, bb, cc]
2.2结果收集到数组中
/**
* @author: 程序员Haris
* @description:将Stream结果收集到集合中
*/
public class StreanResTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] array = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa").toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));//返回数组中的内容是Object类型
//指定返回数组中的元素类型
String[] array1 = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa").toArray(String[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array1));
}
}三、Stream-聚合计算
当我们使用Stream流做数据处理后,可以向数据库的聚合函数一样将某个字段进行操作,比如获得最大值,最小值,求和,平均值,统计数量
四、Stream-分组计算
public class StreanResTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//求根据某一列分组
Map<String, List<Person>> map = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 16),
new Person("李四", 18),
new Person("张三", 20),
new Person("李四", 20),
new Person("张三", 20))
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getName));
map.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println("k=" + k + "\t" +"v=" + v ));
System.out.println("----------------------");
Map<String, List<Person>> map2 = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 16),
new Person("李四", 18),
new Person("张三", 20),
new Person("李四", 20),
new Person("张三", 20))
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(p -> p.getAge() >= 18 ? "成年" : "未成年"));
map2.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println("k=" + k + "\t" +"v=" + v ));
}
}输出:
k=李四 v=[Person{name='李四', age=18}, Person{name='李四', age=20}]
k=张三 v=[Person{name='张三', age=16}, Person{name='张三', age=20}, Person{name='张三', age=20}]
----------------------
k=未成年 v=[Person{name='张三', age=16}]
k=成年 v=[Person{name='李四', age=18}, Person{name='张三', age=20}, Person{name='李四', age=20}, Person{name='张三', age=20}]
多级分组
先根据name分,再根据age分
public class StreanResTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//多级分组
Map<String, Map<String, List<Person>>> map = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 16),
new Person("李四", 18),
new Person("张三", 15),
new Person("李四", 20),
new Person("张三", 22)
).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
Person::getName,
Collectors.groupingBy(p -> p.getAge() >= 18 ? "成年" : "未成年")
));
map.forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println(k);
v.forEach((k1,v1) -> {
System.out.println("\t" + k1 + "=" + v1);
});
});
}
}输出:
李四
成年=[Person{name='李四', age=18}, Person{name='李四', age=20}]
张三
未成年=[Person{name='张三', age=16}, Person{name='张三', age=15}]
成年=[Person{name='张三', age=22}]
五、Stream-分区和拼接操作
Collectors.partitionBy会根据值是否为true将集合中的数据分为两个列表,一个true列表,一个false列表
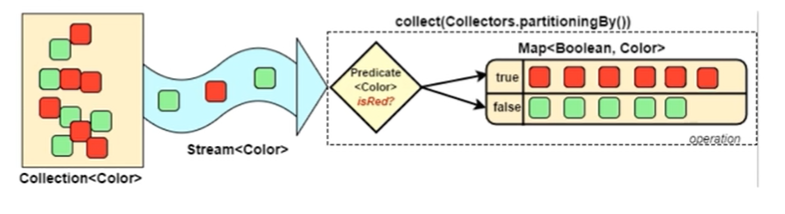
根据年龄是否大于18分区:
public class StreanResTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//分区
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> collect = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 16),
new Person("李四", 18),
new Person("张三", 15),
new Person("李四", 20),
new Person("张三", 22)
).collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.getAge() > 18));
collect.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println(k + "\t" +v));
}
}对流中的数据进行拼接:
不带分隔符:
public class StreanResTest07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//拼接
String collect = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 16),
new Person("李四", 18),
new Person("王五", 15)
).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println(collect);
}
}输出:
张三李四王五
带分隔符:
public class StreanResTest07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//拼接
String collect2 = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 16),
new Person("李四", 18),
new Person("王五", 15)
).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining("_"));
System.out.println(collect2);
}
}输出:
张三_李四_王五
带分隔符,前缀和后缀
public class StreanResTest07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//拼接
String collect3 = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 16),
new Person("李四", 18),
new Person("王五", 15)
).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining("_","***","###"));
System.out.println(collect3);
}
}输出:
***张三_李四_王五###























 107
107











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










