目录
1.数组类封装目的
解决实际问题,训练构造函数,copy构造函数,为操作符重载做铺垫
2.步骤
2.1首先建立一个数组类:MyArray
2.2先大致确定模版内容
// 根据上述需求,可以大致确定类模板中的内容
类模板{
public:
无参构造
有参构造
拷贝构造函数
重载operator=
遍历函数
赋值函数
获得元素个数
析构函数
private:
指针
元素个数
}
2.3介绍几个基本的接口
- 无参构造
- 有参构造
- 析构函数
- 赋值函数
- 遍历函数
- 拷贝操作
- 访问数组长度的函数
- 重载operator=
2.4在头文件中声明以上函数接口
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyArray
{
public:
MyArray();
MyArray(int len);
~MyArray();
MyArray(const MyArray1& another);
int getLen();
void setData(int index, int data);
int getData(int index);
void operator=(const MyArray& another);
private:
int len;
int* space;
};2.4在.c文件中实现头文件中的函数并在首句引用头文件
#include "MyArray.h"
MyArray::MyArray()//无参构造
{
cout << "MyArray::MyArray()..." << endl;
this->len = 0;
this->space = NULL;
}
MyArray::MyArray(int len)//有参构造
{
if (len <= 0)
{
this->len = 0;
return;
}
else
{
this->len = len;
//给space开辟空间
this->space = new int[this->len];
cout << "MyArray::MyArray(int)..." << endl;
}
}
MyArray::MyArray(const MyArray& another)//拷贝构造
{
if (another.len >= 0)
{
this->len = another.len;
//深拷贝
this->space = new int[this->len];
for (int i = 0; i < this->len; i++)
{
this->space[i] = another.space[i];
}
cout << "MyArray::MyArray(const MyArray& another)..." << endl;
}
}
void MyArray::setData(int index, int data)//赋值函数
{
if (this->space != NULL)
{
this->space[index] = data;
}
}
int MyArray::getData(int index)//遍历返回数组值
{
return this->space[index];
}
int MyArray::getLen()//
{
return this->len;
}
MyArray::~MyArray()
{
if (this->space != NULL)
{
delete[] space;
this->space = NULL;
}
this->len = 0;
cout << "MyArray::~MyArray()..." << endl;
}
void MyArray::operator=(const MyArray& another)//重载=
{
if (another.len >= 0)
{
this->len = another.len;
//深拷贝
this->space = new int[this->len];
for (int i = 0; i < this->len; i++)
{
this->space[i] = another.space[i];
}
cout << "MyArray::MyArray::operator=(const MyArray& another)..." << endl;
}
}2.5最后实现main函数
#include<iostream>
#include"MyArray.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
MyArray array1(10);//调用有参构造,开辟十个元素的数组
//赋值操作
for(int i=0;i<array1.getLen();i++)
{
array1.setData(i,i+10);
array[i]=i+10;
}
cout<<"array1:"<<endl;
//遍历操作
for(int i=0;i<array1.getLen();i++)
{
cout<<array1.getData(i)<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
//拷贝操作
MyArray array2=array1;//调用拷贝函数
cout<<"array2:"<<endl;
//遍历array2数组
for(int i=0;i<array2.getLen();i++)
{
cout<<array2.getData(i)<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
//等号操作符
MyArray array3;
array3=array1;
//遍历array3数组
for(int i=0;i<array3.getLen();i++)
{
cout<<array3.getData(i)<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}3.增加强度:操作符重载
- 等号操作符重载
- 下标引用操作符重载
- 左移操作符重载
- 右移操作符重载
MyArray& MyArray::operator=(const MyArray& another)
{
if (this == &another)
{
return *this;
}
if (this->space != NULL)
{
delete[] this->space;
this->space = NULL;
this->len = 0;
}
if (another.len >= 0)
{
this->len = another.len;
//深拷贝
this->space = new int[this->len];
for (int i = 0; i < this->len; i++)
{
this->space[i] = another.space[i];
}
cout << "MyArray::MyArray operator(const MyArray& another)..." << endl;
}
return *this;
}
int& MyArray::operator[](int index)const
{
return this->space[index];
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const MyArray& array)//该函数只是用来遍历整个数组的,不希望数组中的值被改变,所以array应该加const修饰,但是当array数组加const修饰后,该数组中的成员函数也要用const修饰
{
os << "遍历整个数组" << endl;
array.getLen();//getLen(&array);
for (int i = 0; i < array.getLen(); i++)
{
os << array[i] << " ";//array.operator[](&array,i)
}
os << endl;
os << "调用的<<操作符重载" << endl;
return os;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, MyArray& array)
{
cout << "请输入" << array.getLen() << "个数" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < array.getLen(); i++)
{
cin >> array[i];
}
return is;
}大家可以根据操作符重构函数自己想一想main函数和.c文件中的变化
4.文件截图
main函数:
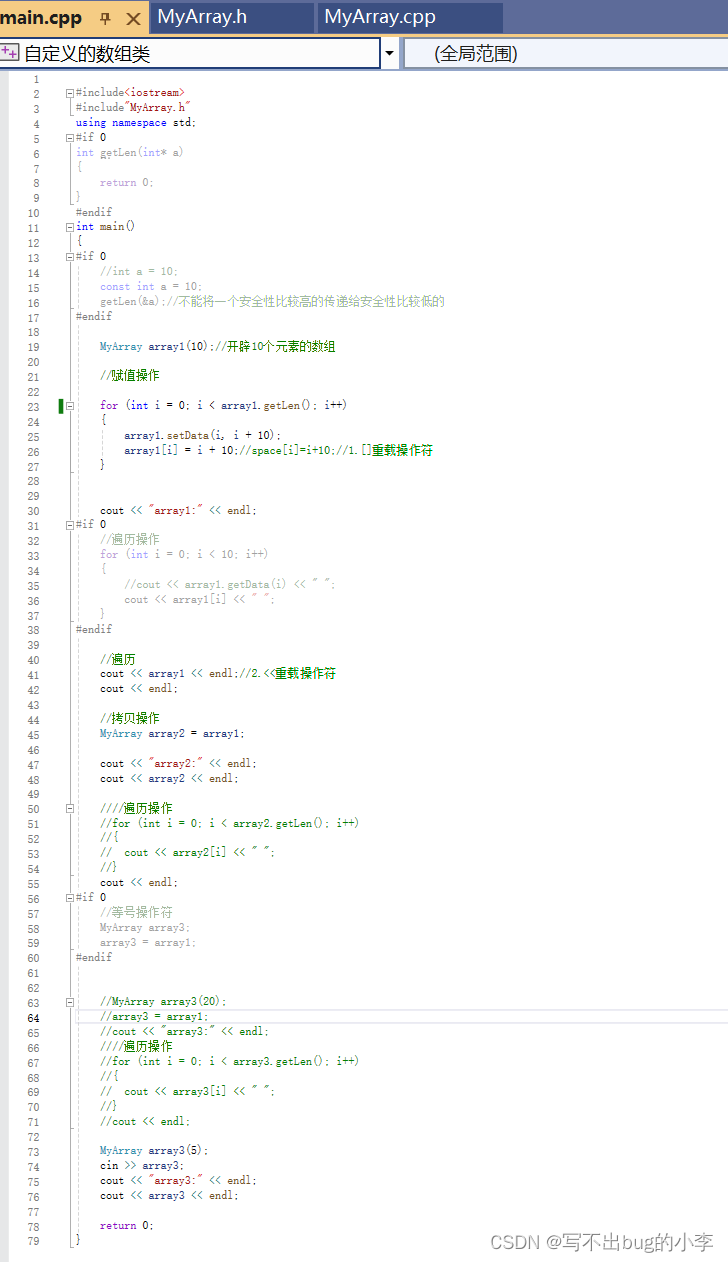
头文件:

.c文件:

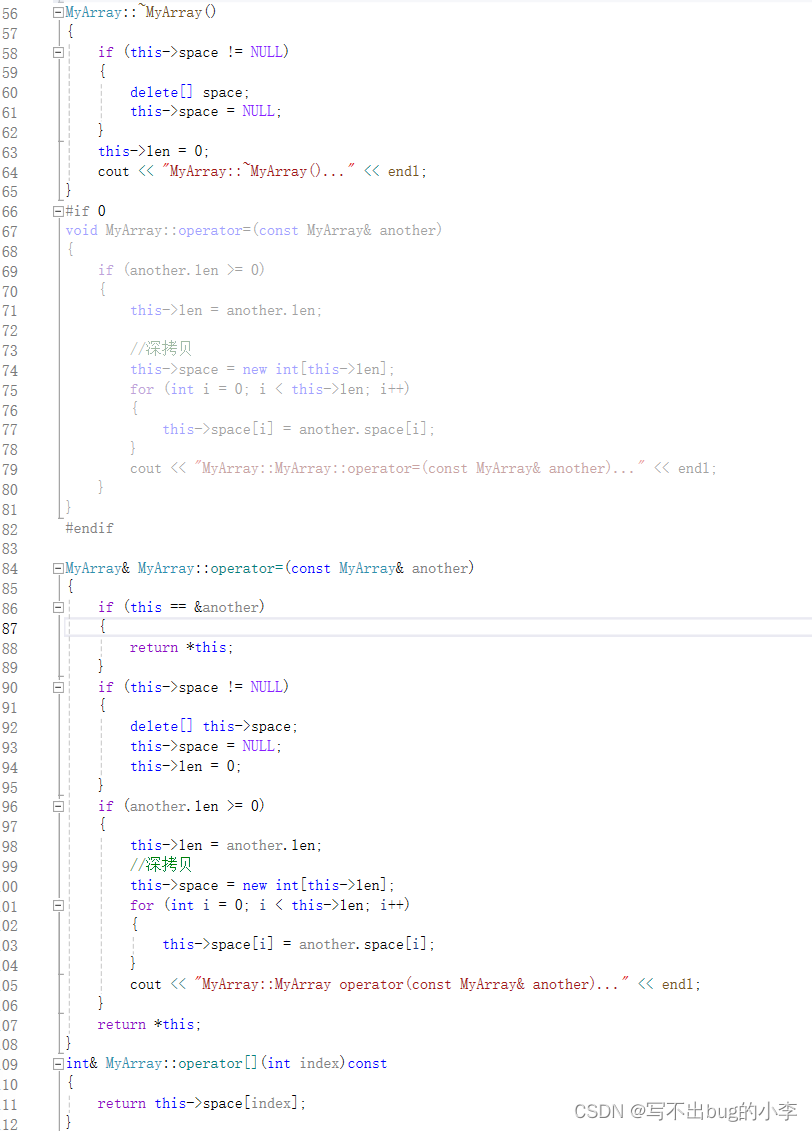
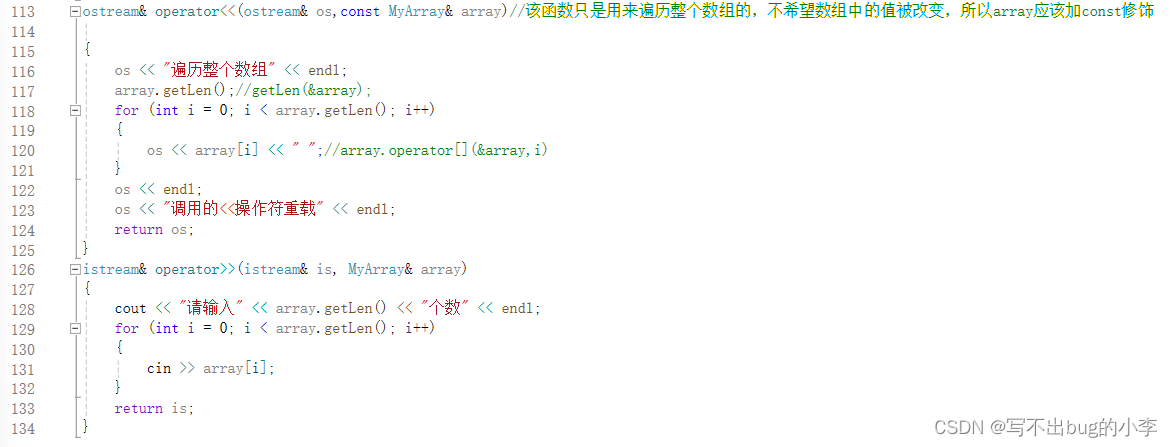
以上就是关于数组类的c++实现























 1786
1786











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










