一个例子
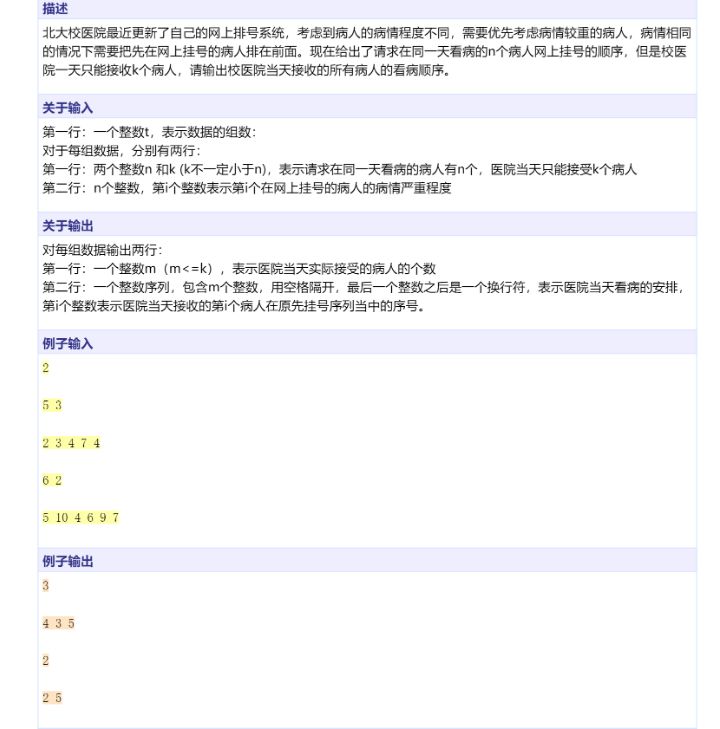
这是一道北大计院期末考试题,偶然看到,以下是我直观想法,使用TreeSet辅助实现功能
public class Person {
private int value;
private int rank;
public Person(int value, int rank) {
this.value = value;
this.rank = rank;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public int getRank() {
return rank;
}
}
Person的value代表病情严重程度,rank代表排队顺序
public class SortComparator implements Comparator<Person> {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
if (o1.getValue() > o2.getValue())
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
}
创建Person的比较器,病情严重程度大的应放在排序前面
public class PekingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (sc.hasNext()) {
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int m = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
SortComparator comparator = new SortComparator();
TreeSet<Person> treeSet = new TreeSet<Person>(comparator);
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
int swap = sc.nextInt();
Person p = new Person(swap, j);
treeSet.add(p);
}
System.out.println(k);
Iterator<Person> iterator = treeSet.iterator();
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
System.out.print(iterator.next().getRank() + " ");
}
}
}
}
}
TreeSet简介
TreeSet继承了AbstractSet,实现了NavigableSet, Cloneable, Serializable接口。
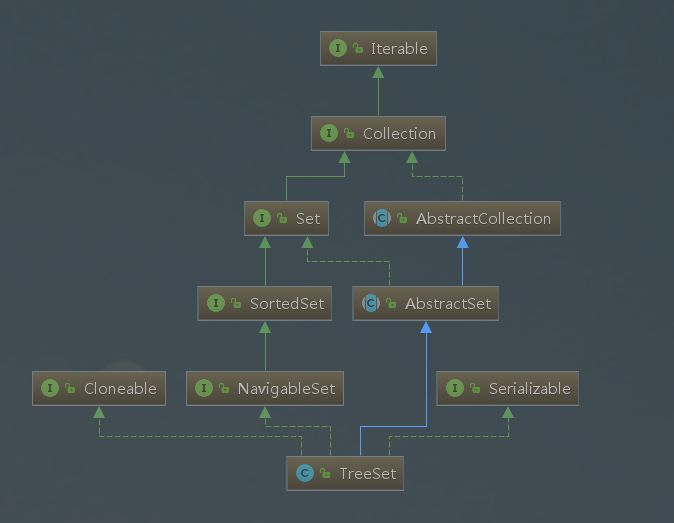
简要概括几个特点:
底层结构是TreeMap,采用红黑树结构;
equals相等的元素只会出现一次,不允许有null元素;
插入的数据必须实现Comparable接口,默认按照字典序排列;
可通过重写Comparable 或 Comparator改变排序规则;
基本操作(add、remove、contains)时间复杂度为log(n)
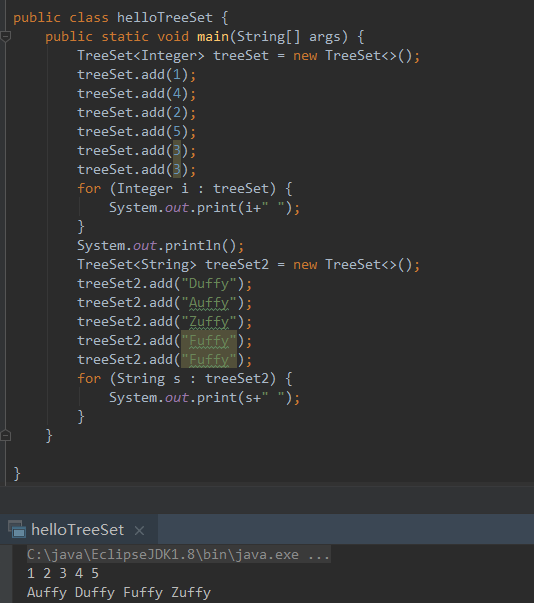
先通过一个例子感受下TreeSet基本功能,treeSet中元素为Integer类型,默认按照升序排序;treeSet2中元素为String类型,默认按照字典序排序
源码分析
基本构造函数
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
/**
* Constructs a set backed by the specified navigable map.
*/
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
public TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
this(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}常用函数
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return m.containsKey(o);
}
public void clear() {
m.clear();
}
public int size() {
return m.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return m.isEmpty();
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E first() {
return m.firstKey();
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E last() {
return m.lastKey();
}
/**
*Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in ascending order
* 以升序返回此集合中元素的迭代器
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return m.navigableKeySet().iterator();
}
/**
*Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in descending order
* 以降序返回此集合中元素的迭代器
*/
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return m.descendingKeySet().iterator();
}
可以发现TreeSet都是通过调用TreeMap的函数来实现的,在TreeMap的key位进行操作,value位用PRESENT填补,具体实现参考以下TreeMap源码。
TreeMap
/**
* 用于维护Tree Map的顺序,自然顺序下comparator为null
*/
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
/**
* 底层红黑树
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
private transient int size = 0;
private transient int modCount = 0;
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
红黑树
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
...
}
红黑树有以下几个属性:
1.节点是红色或黑色
2.根是黑色
3.所有叶子都是黑色,NIL节点
4.红色节点的每个子节点都是黑色,黑色节点子节点可为黑,且最长路径为红黑节点交替
5.从任一节点到其任一叶子节点,所有简单路径都包含相同数量的黑节点

问:那么为什么要选用红黑树呢?
答:首先是元素保持有序的,而且确保在每次插入和删除后树的高度保持为ceil(log(n)),那么可以保证所有这些操作的时间复杂度为O(log(n))。
问:与AVL树比较呢?
答:与红黑树相比,AVL树更加平衡,但它们可能在插入和删除期间引起更多旋转。 因此,如果应用涉及频繁的插入和删除,那么应该首选红黑树。
put方法——对应TreeSet中的add方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
1.红黑树若为空,则创建,添加元素,结束
注意:key不能为null,否则抛出NullPointerException()
2.判断是否为默认比较器,若不是cpr != null,则cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key),如果为默认比较器,cmp = k.compareTo(t.key),输入的key值小于当前树节点t.key,在左子树上,大于则在右子树上,继续循环查找,等于则t.setValue(value)并返回
3.如果红黑树上没有,需要插入节点,根据大小对比决定是插入到左子树还是右子树
4.size增加1, modCount增加1
containsKey方法
// public boolean remove(Object o)
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null;
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
同样查找的时候,输入的key不能为null,否则抛出NPE异常
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key)判断key是在左子树还是右子树上,如果找到则返回对应的红黑树节点,否则返回null
remove方法
// TreeSet:public boolean remove(Object o)
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} //
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
1.getEntry(key)树中寻找此节点,若没有返回null,结束
2.存在删除的key值,则先保存key对应的value,执行deleteEntry(p),结构性变动次数modCount增1,size减1
3.p 左子树和右子树都不为空情况,通过successor得到p的位置替代者;若果左子树或右子树为空,不做处理
4.1替代节点不为null,判断被替换节点p在父节点的位置,然后用replacement替换,如果原本p是黑色的,可能需要改变颜色并进行左/右旋转操作
4.2被替代节点p的父节点为null,说明树中只有此一个节点
4.3p无孩子情况,判断p若为黑,则需要改变颜色和左/右旋转操作;判断p是父节点的左孩子还是右孩子,然后设置为null
//public E first()
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
//public E last()
final Entry<K,V> getLastEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
return p;
}
TreeSet的first方法调用getFirstEntry()返回最左子树元素,last方法调用getLastEntry()返回最后子树元素
比较器
public class Person implements Comparable {
private int value;
private int rank;
public Person(int value, int rank) {
this.value = value;
this.rank = rank;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public int getRank() {
return rank;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Person p = (Person) o;
int v = this.getValue() - p.getValue();
if (v > 0) return -1;
else return 1;
}
}Person类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(Object o)方法
public class SortComparator implements Comparator<Person> {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
if (o1.getValue() > o2.getValue())
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
}
例子中是使用的是创建SortComparator类实现Comparator接口,重写compare方法
或者用以下方式:
TreeSet<Person> treeSet = new TreeSet<Person>(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
if (o1.getValue() > o2.getValue())
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
});
与HashSet比较
1.HashSet调用HashMap方法,底层为数组+链表/红黑树结构,HashMap可以参考之前文章,【Java基础干货】HashMap源码剖析;TreeSet调用TreeMap方法,底层是红黑树
2.HashSet中元素时无序的,适合去重的场景;TreeSet中元素是按一定规则排序的,适合需要排序的场景
3.HashSet可以存入null值;TreeSet不能存入null值
同一系列文章:【Java基础干货】ArrayList源码剖析
























 720
720











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








