你好,我是沐爸,欢迎点赞、收藏和关注。个人知乎
要使用原生JS生成客户端路由器,需要借助HTML5 History API。这个API允许我们以一种不会重新加载页面的方式更改浏览器的URL。这主要通过history.pushState()和history.replaceState()方法以及popstate事件来实现。
下面是一个简单的客户端路由器实现,它将支持几个基本的路由,并在URL变化时更新页面内容,同时支持页面刷新。
一、效果预览
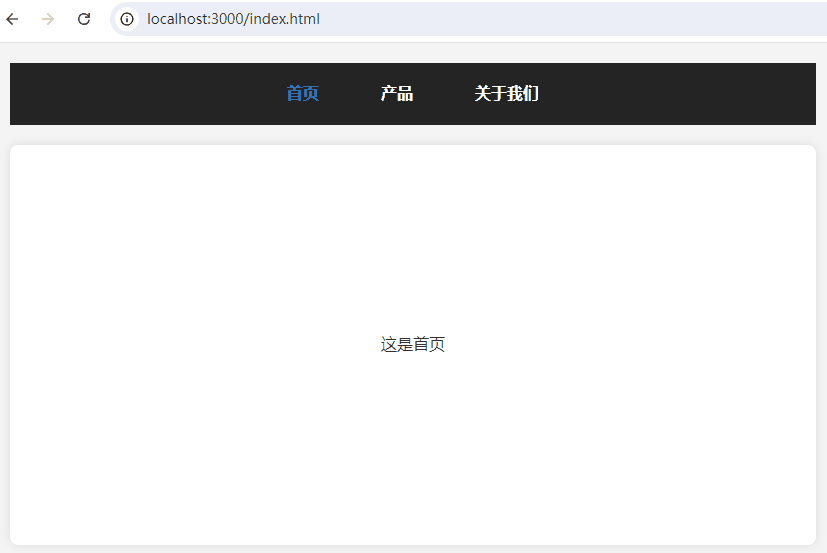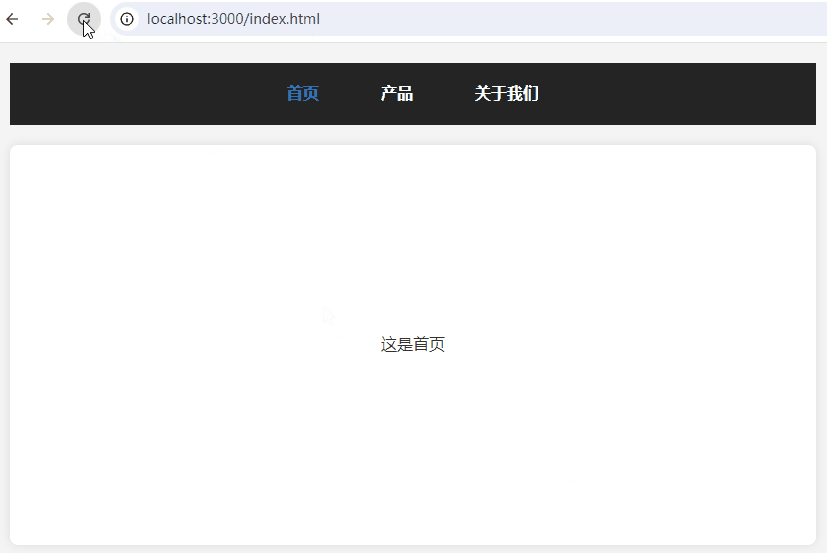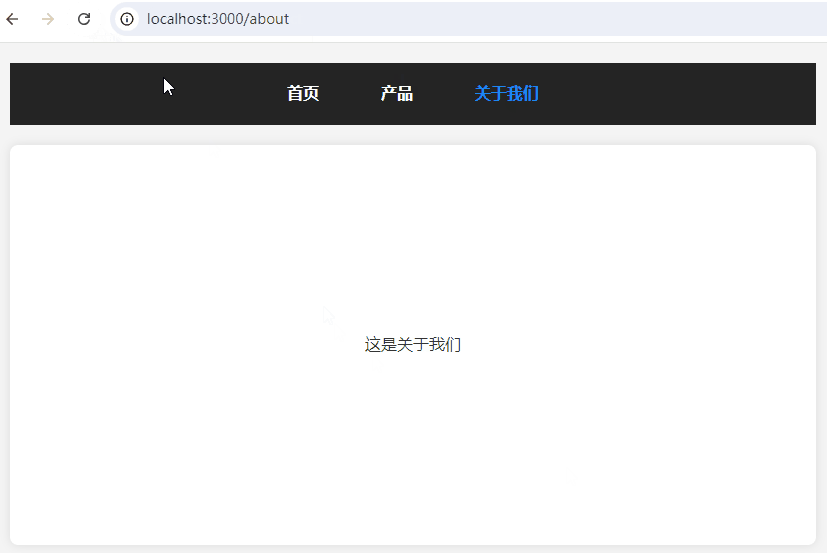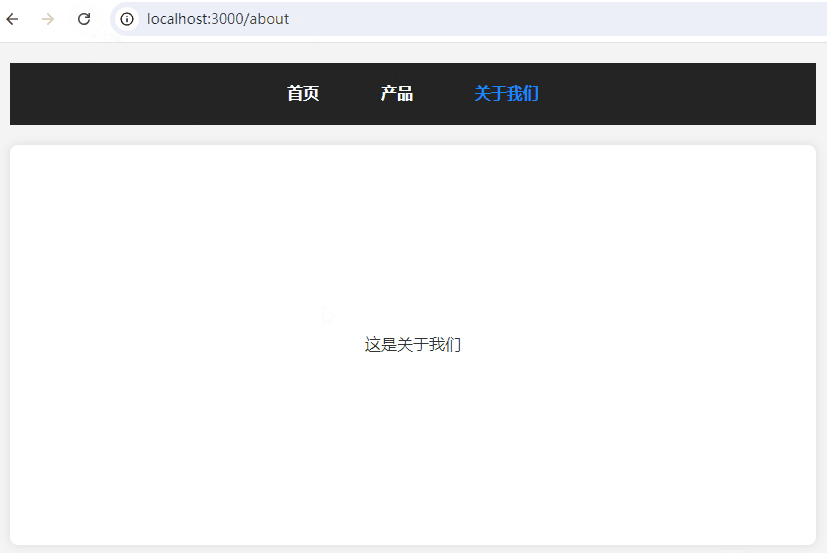
二、HTML 结构
index.html
<header>
<nav>
<ul id="nav-links">
<li><a href="/home" class="nav-link">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="/product" class="nav-link">产品</a></li>
<li><a href="/about" class="nav-link">关于我们</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
<main id="content">
<!-- 路由出口 -->
</main>
三、JavaScript 路由器
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function () {
let el = document.getElementById('content')
// 定义路由表
const routes = {
'/home': () => {
el.innerHTML = '<p>这是首页</p>'
updateActiveLink('/home')
},
'/product': () => {
el.innerHTML = '<p>这是产品页</p>'
updateActiveLink('/product')
},
'/about': () => {
el.innerHTML = '<p>这是关于我们</p>'
updateActiveLink('/about')
}
}
// 加载路由
function loadRoute(path) {
if (routes[path]) {
routes[path]()
updateActiveLink(path)
} else if (path === '/index.html' || path === '/') {
routes['/home']()
updateActiveLink('/home')
} else {
// 重定向404页面
el.innerHTML = '<p>404 Not Found</p>'
}
}
// 监听popstate事件以处理URL变化
window.addEventListener('popstate', function (event) {
loadRoute(location.pathname)
})
// 为导航链接绑定事件
const aTags = document.querySelectorAll('nav a')
aTags.forEach((a) => {
a.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
e.preventDefault() // 阻止链接的默认行为
const url = new URL(this.href)
history.pushState({ path: url.pathname }, '', url.href)
loadRoute(url.pathname)
})
})
// 更新链接的激活状态
function updateActiveLink(path) {
const navLinks = document.querySelectorAll('#nav-links .nav-link')
navLinks.forEach((link) => {
if (link.getAttribute('href') === path) {
link.classList.add('active')
} else {
link.classList.remove('active')
}
})
}
// 首次加载时加载路由
loadRoute(location.pathname)
})
代码注释详细,不再解读。
四、CSS 样式
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.6;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
color: #333;
}
header {
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);
padding: 10px 0;
text-align: center;
}
nav ul {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
nav ul li {
margin: 0 15px;
}
nav ul li a {
color: white;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
padding: 8px 16px;
display: inline-block;
border-radius: 4px;
transition: background-color 0.3s;
}
nav ul li .nav-link.active {
color: #1b87f3;
}
main {
background-color: white;
min-height: 400px;
padding: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
到这里,功能基本上就完成,切换路由能正常显示各路由对应页面。然而,这里有个致命问题,那就是刷新时页面丢失了,报404错误。
怎么解决呢?需要服务器配置。不通过服务器配置能解决这个问题吗?答案是不能。
不通过服务器直接解决SPA(单页面应用)的刷新404问题是不可能的,因为这个问题本质上是由前端路由和服务器路由之间的不匹配造成的。在SPA中,前端路由负责在客户端(浏览器)中处理URL的变化,并相应地更新页面内容,而不需要重新加载整个页面。然而,当用户直接访问一个非根URL并刷新页面时,浏览器会向服务器发送一个请求来加载该URL对应的资源。
如果服务器没有针对该URL配置相应的路由规则来返回SPA的入口文件(如index.html),那么服务器就会返回404错误,表示找不到请求的资源。
要解决这个问题,通常需要在服务器端进行配置,以确保所有路由请求都能返回SPA的入口文件,然后由前端路由来处理具体的页面渲染。这是因为SPA的页面渲染逻辑是完全在客户端执行的,服务器只负责提供静态资源和处理API请求。
五、服务器配置
以Express.js(Node.js)为例配置服务器来解决SPA的刷新404问题:
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public'))); // 假设你的SPA文件在public目录下
app.get('*', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'public', 'index.html'));
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
如果你使用的是Express.js作为后端,你可以设置一个中间件来捕获所有请求并返回 index.html。
六、完整代码
1.public/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>单页面路由示例</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.6;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
color: #333;
}
header {
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);
padding: 10px 0;
text-align: center;
}
nav ul {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
nav ul li {
margin: 0 15px;
}
nav ul li a {
color: white;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
padding: 8px 16px;
display: inline-block;
border-radius: 4px;
transition: background-color 0.3s;
}
nav ul li .nav-link.active {
color: #1b87f3;
}
main {
background-color: white;
min-height: 400px;
padding: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<nav>
<ul id="nav-links">
<li><a href="/home" class="nav-link">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="/product" class="nav-link">产品</a></li>
<li><a href="/about" class="nav-link">关于我们</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
<main id="content">
<!-- 路由出口 -->
</main>
<script>
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function () {
let el = document.getElementById('content')
// 定义路由表
const routes = {
'/home': () => {
el.innerHTML = '<p>这是首页</p>'
updateActiveLink('/home')
},
'/product': () => {
el.innerHTML = '<p>这是产品页</p>'
updateActiveLink('/product')
},
'/about': () => {
el.innerHTML = '<p>这是关于我们</p>'
updateActiveLink('/about')
}
}
// 加载路由
function loadRoute(path) {
if (routes[path]) {
routes[path]()
updateActiveLink(path)
} else if (path === '/index.html' || path === '/') {
routes['/home']()
updateActiveLink('/home')
} else {
// 重定向404页面
el.innerHTML = '<p>404 Not Found</p>'
}
}
// 监听popstate事件以处理URL变化
window.addEventListener('popstate', function (event) {
loadRoute(location.pathname)
})
// 为导航链接绑定事件
const aTags = document.querySelectorAll('nav a')
aTags.forEach((a) => {
a.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
e.preventDefault() // 阻止链接的默认行为
const url = new URL(this.href)
history.pushState({ path: url.pathname }, '', url.href)
loadRoute(url.pathname)
})
})
// 更新链接的激活状态
function updateActiveLink(path) {
const navLinks = document.querySelectorAll('#nav-links .nav-link')
navLinks.forEach((link) => {
if (link.getAttribute('href') === path) {
link.classList.add('active')
} else {
link.classList.remove('active')
}
})
}
// 首次加载时加载路由
loadRoute(location.pathname)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.index.js
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public'))); // 假设你的SPA文件在public目录下
app.get('*', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'public', 'index.html'));
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
3.package.json
{
"name": "demo",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"serve": "node index.js"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "yourname",
"license": "ISC",
"description": "",
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.19.2"
}
}
将上面三个文件放在同一目录下,然后分别执行 npm install, npm run serve即可,接着就可以在浏览器打开 http://localhost:3000 访问页面了。
好了,分享结束,欢迎点赞,下期再见!


























 195
195

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










