提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
Park & Unpark
基本使用
它们是 LockSupport 类中的方法
// 暂停当前线程
LockSupport.park();
// 恢复某个线程的运行
LockSupport.unpark(暂停线程对象)
先 park 再 unpark
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPark")
public class TestPark {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("start...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("park...");
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("resume...");
},"t1");
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
log.debug("unpark...");
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
}
}
11:25:19.102 [t1] DEBUG c.TestPark - start...
11:25:20.113 [t1] DEBUG c.TestPark - park...
11:25:21.113 [main] DEBUG c.TestPark - unpark...
11:25:21.114 [t1] DEBUG c.TestPark - resume...
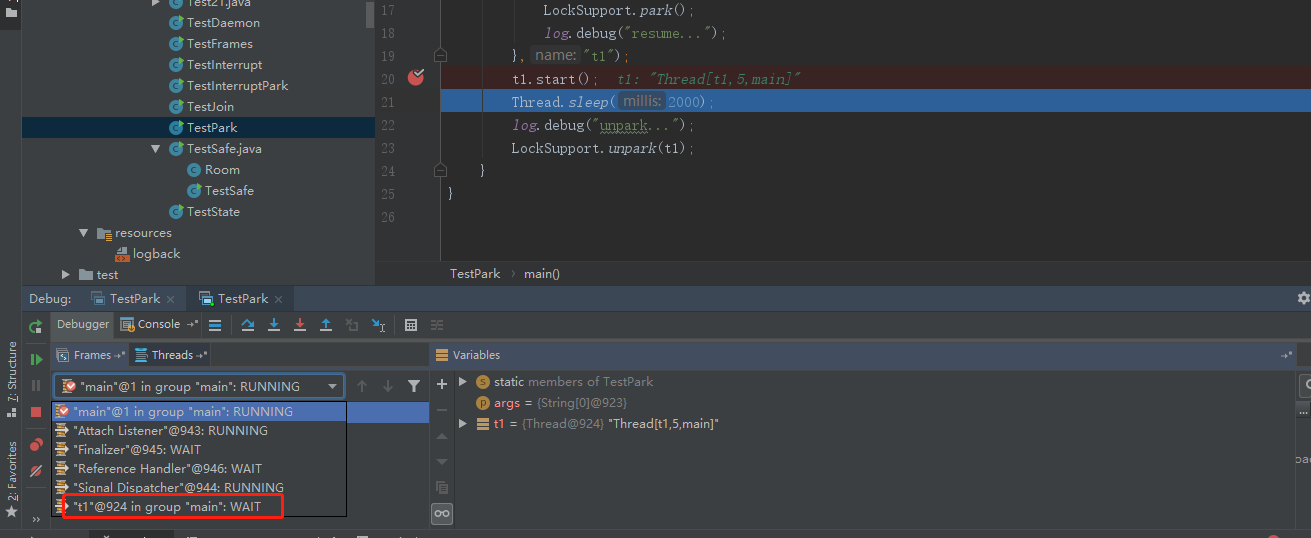
被park住的线程属于WAIT状态
先 unpark 再 park
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPark")
public class TestPark {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("start...");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("park...");
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("resume...");
},"t1");
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("unpark...");
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
}
}
11:26:29.448 [t1] DEBUG c.TestPark - start...
11:26:30.478 [main] DEBUG c.TestPark - unpark...
11:26:31.460 [t1] DEBUG c.TestPark - park...
11:26:31.460 [t1] DEBUG c.TestPark - resume...
特点
与 Object 的 wait & notify 相比
- wait,notify 和 notifyAll 必须配合 Object Monitor 一起使用,而 park,unpark 不必
- park & unpark 是以线程为单位来【阻塞】和【唤醒】线程,而 notify 只能随机唤醒一个等待线程,notifyAll 是唤醒所有等待线程,就不那么【精确】
- park & unpark 可以先 unpark,而 wait & notify 不能先 notify
park和unpark原理
每个线程都有自己的park对象,由三部分组成_counter,_cond和_mutex打个比喻
-
每个线程就像一个旅人,park就像他随身写带的背包,条件变量就好比背包中的帐篷,_conter就好比背包中的干粮(0为耗尽,1为充足)
-
调用park就是要看需不需要停下来休息
如果备用干粮耗尽,那就钻进帐篷里休息
如果备用干粮充足,那么不需要停留,继续前进 -
调用unpark就好比令干粮充足
如果这时线程还在帐篷,就唤醒让他前进
如果线程还在运行,那么下次他调用park时,仅是消耗备用干粮,不会停留,继续前进
因为背包空间有限,多次调用unpark仅会补充一份备用干粮
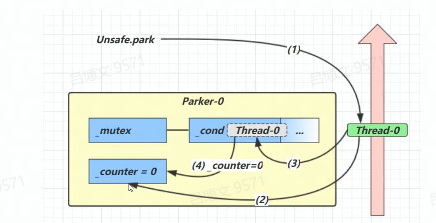
1、当前线程调用Unsafe.park()方法
2、检查_counter,本情况为0,这时,获得_mutex互斥锁、
3、线程进入_cond条件变阻塞
4、设置_counter=0
线程转换状态
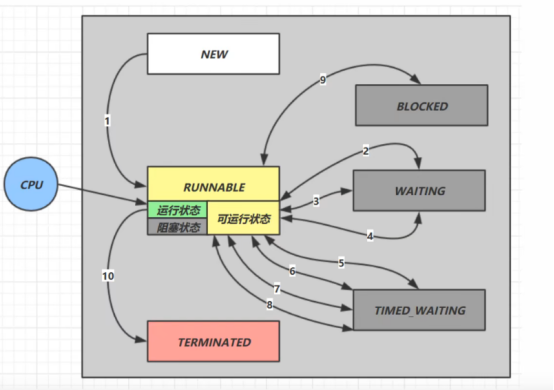
New:刚创建了线程对象,但是线程对象还未与操作系统中的线程关联
假设有线程Thread t1
情况1:new—>RUNNABLE
当调用t.start()方法时,由new—>RUNNABLE
情况2:RUNNABLE<—>WATING
t1线程用看synchronized(obj)获得了对象锁后
调用t.wait()方法时,t线程从RUNNABLE—>WATING
调用obj.notify(), obj.notifyAll , t.interrupt()方法时
- 竞争锁成功,t1线程从WATING—>RUNNABLE
- 竞争锁失败,t线程从WATING—>BLOCKED
情况3:RUNNABLE<—>WATING
当线程调用t1.join()方法时,当前线程从RUNNABLE—>WATING
注意是当前线程在t1线程对象的监视器上等待
t1运行结束,或调用了当前线程的interrupt()方法时,当前线程从WATING—>RUNNNABLE
情况4:RUNNABLE<—>WATING
当前线程调用LockSupport.park()方法会让当前线程从RUNNABLE—>WATING’
调用LockSuppport.unpark(目标线程)或调用了线程的interrupt(),会让目标线程从WATING—>RUNNABLE
情况5:RUNNABLE<—>TIMED_WATING
t1线程用看synchronized(obj)获得了对象锁后
调用t.wait(long n)方法时,t线程从RUNNABLE—>TIMED_WATING
t线程等待时间超过n毫秒,或调用obj.notify(), obj.notifyAll , t.interrupt()方法时
- 竞争锁成功,t1线程从TIMED_WATING—>RUNNABLE
- 竞争锁失败,t线程从TIMED_WATING—>BLOCKED
情况6:RUNNABLE<—>TIMED_WATING
当前线程调用t.join(long n)方法时,当前线程从RUNNABLE—>TIMED_WATING
注意是当前线程在t线程对象上等待
当前线程等待时间超过n毫秒 或 t线程运行结束,或调用了当前线程的interrupt()方法时,当前线程从TIMED_WATING—>BLOCKED、
情况7:RUNNABLE<—>TIMED_WATING
当前线程调用Thread.sleep(long n)方法时,当前线程从RUNNABLE—>TIMED_WATING
当前线程等待时间超过n毫秒,当前线程从TIMED_WATING
情况8:RUNNABLE<—>TIMED_WATING
当前线程调用LockSupport.parkNacos(long nacos) 或 LockSupport.parkUntil(long millis)时,当前线程从RUNNABLE—>TIMED_WATING
调用LockSupport.unpark(目标线程)或调用了线程的interrupt(),或者等待超时,会让目标线程从TIMED_WATING—>BLOCKED
情况9:RUNNABLE<—>BLOCKED
t线程用synchronized(obj获取了对象锁时如果竞争失败,从RUNNABLE—>BLOCKED
持obj锁线程的同步代码块执行完毕,会唤醒该对象上所有BLOCKED的线程重新竞争,如果其中t线程竞争成功,会从BLOCKED—>TIMED_WATING,其他失败的线程仍然BLOCKED
情况10:RUNNABLE—>TERMNATED:当前线程所有代码运行完毕
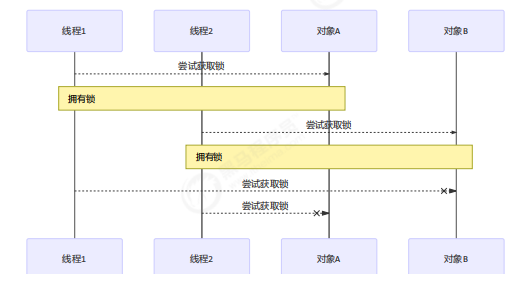
死锁
线程A和线程B各自持有锁,但又想获得对象的锁,就会放生死锁。
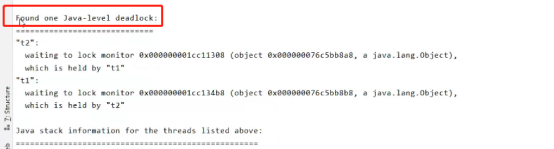
定位死锁:
方法1:
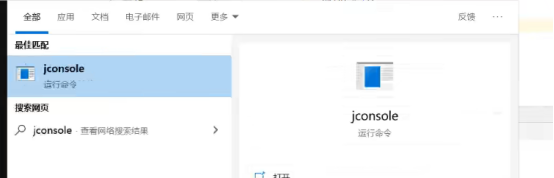
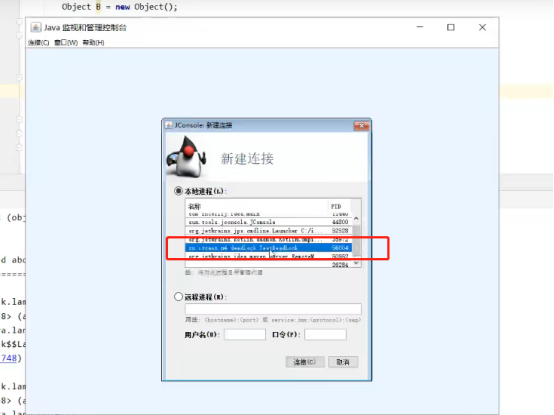
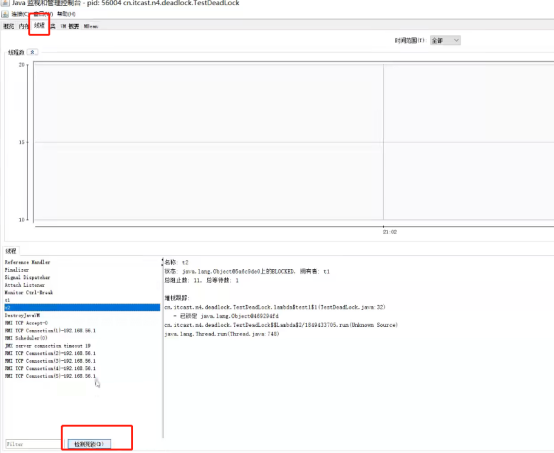
方法2:
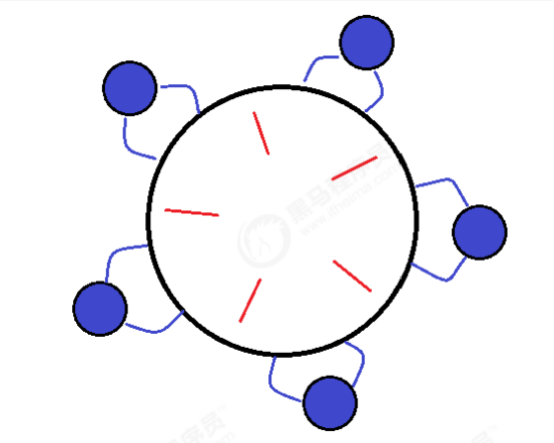
哲学家就餐问题

@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestDeadLock")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chopstick c1 = new Chopstick("1");
Chopstick c2 = new Chopstick("2");
Chopstick c3 = new Chopstick("3");
Chopstick c4 = new Chopstick("4");
Chopstick c5 = new Chopstick("5");
new Philosopher("苏格拉底", c1, c2).start();
new Philosopher("柏拉图", c2, c3).start();
new Philosopher("亚里士多德", c3, c4).start();
new Philosopher("赫拉克利特", c4, c5).start();
new Philosopher("阿基米德", c5, c1).start();
}
}
class Chopstick {
String name;
public Chopstick(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "筷子{" + name + '}';
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Philosopher")
class Philosopher extends Thread {
Chopstick left;
Chopstick right;
public Philosopher(String name, Chopstick left, Chopstick right) {
super(name);
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
private void eat() {
log.debug("eating...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 获得左手筷子
synchronized (left) {
// 获得右手筷子
synchronized (right) {
// 吃饭
eat();
}
// 放下右手筷子
}
// 放下左手筷子
}
}
}
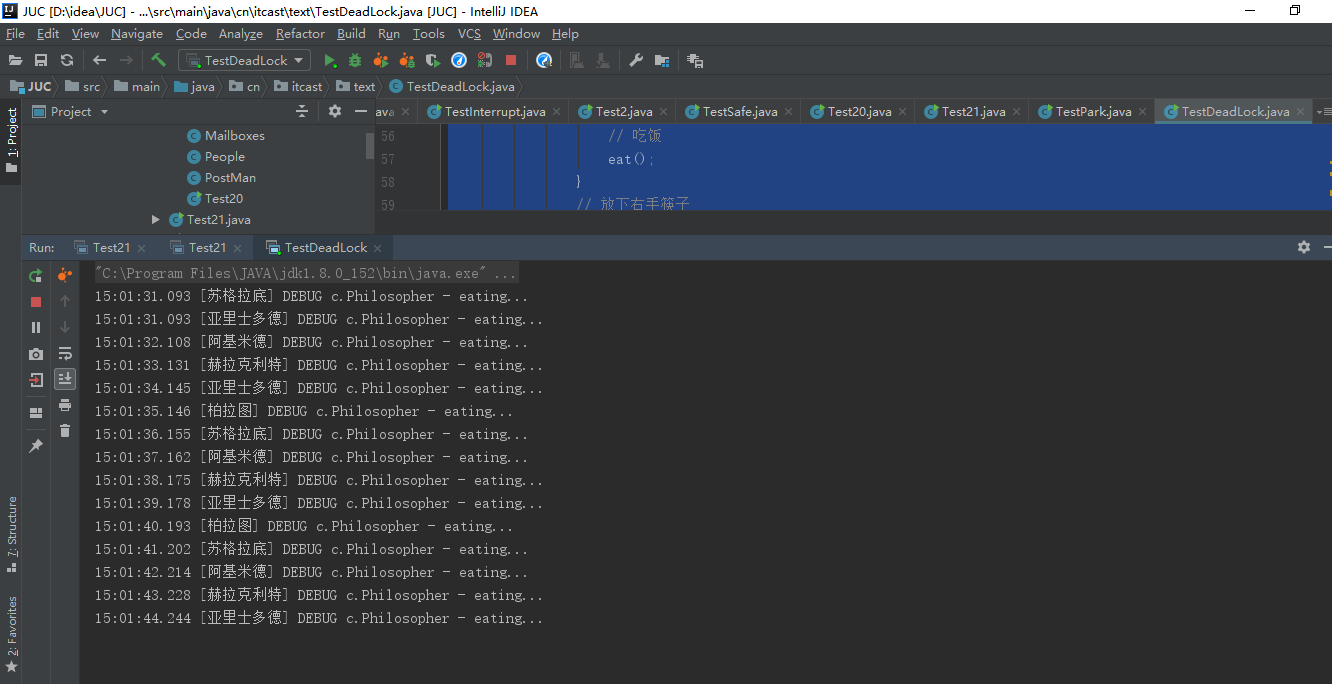
检测到死锁
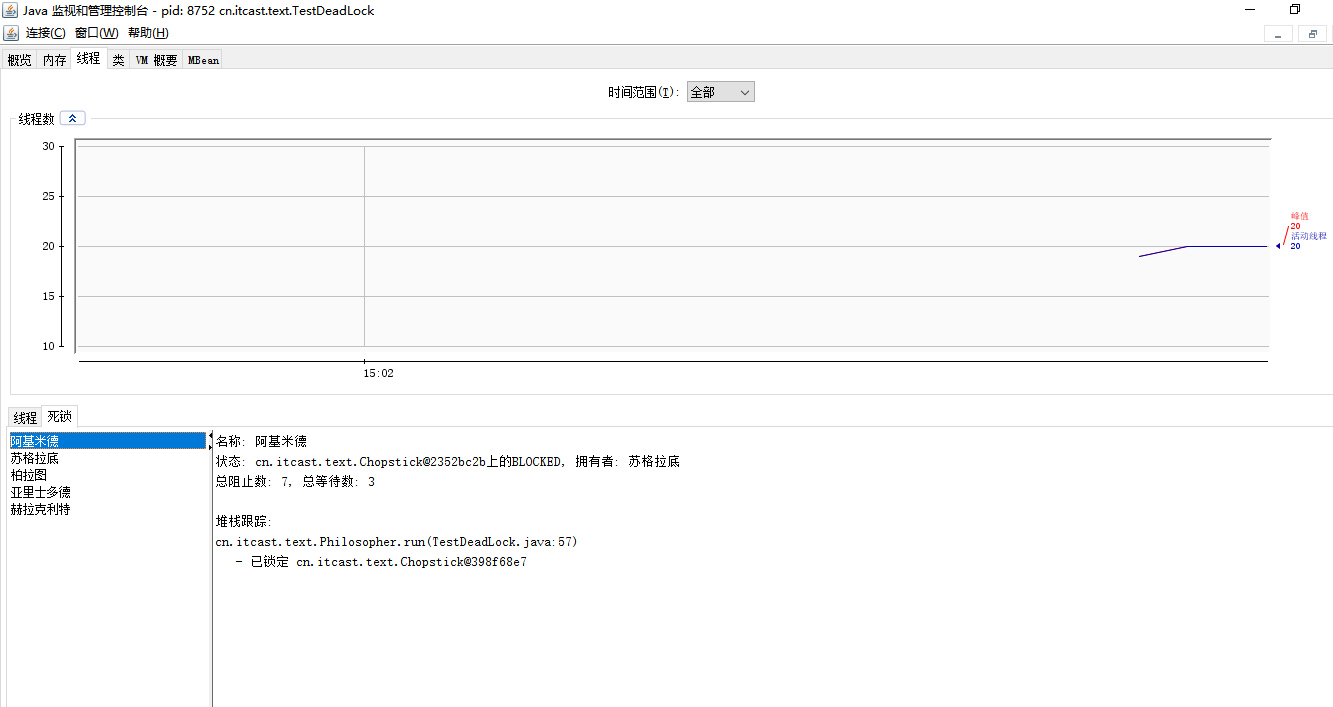
活锁
活锁出现在两个线程互相改变对方的结束条件,最后谁也无法结束,例如
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestLiveLock")
public class TestLiveLock {
static volatile int count = 10;
static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
// 期望减到 0 退出循环
while (count > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count--;
log.debug("count: {}", count);
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
// 期望超过 20 退出循环
while (count < 20) {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
log.debug("count: {}", count);
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
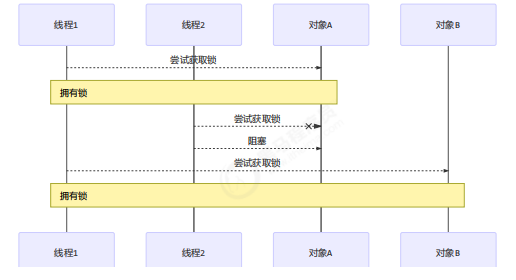
饥饿
很多教程中把饥饿定义为,一个线程由于优先级太低,始终得不到 CPU 调度执行,也不能够结束,饥饿的情况不易演示,讲读写锁时会涉及饥饿问题下面我讲一下我遇到的一个线程饥饿的例子,先来看看使用顺序加锁的方式解决之前的死锁问题
顺序加锁的解决方案
ReentrantLock
相对于 synchronized 它具备如下特点
- 可中断
- 可以设置超时时间
- 可以设置为公平锁
- 支持多个条件变量
与 synchronized 一样,都支持可重入
基本语法
// 获取锁
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
// 临界区
} finally {
// 释放锁
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
可重入
可重入是指同一个线程如果首次获得了这把锁,那么因为它是这把锁的拥有者,因此有权利再次获取这把锁
如果是不可重入锁,那么第二次获得锁时,自己也会被锁挡住
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test22")
public class Test22 {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
}
public static void method1() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("execute method1");
method2();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void method2() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("execute method2");
method3();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void method3() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("execute method3");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
15:11:21.996 [main] DEBUG c.Test22 - execute method1
15:11:22.004 [main] DEBUG c.Test22 - execute method2
15:11:22.005 [main] DEBUG c.Test22 - execute method3
可打断
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test23")
public class Test23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("启动...");
try {
//如果没有竞争,那么此线程就会获取到锁
//如果有竞争就进入阻塞队列,可以被其他线程用interrupt打断
lock.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("等锁的过程中被打断");
return;
}
try {
log.debug("获得了锁");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
log.debug("获得了锁");
t1.start();
try {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t1.interrupt();
log.debug("执行打断");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
15:18:08.268 [main] DEBUG c.Test23 - 获得了锁
15:18:08.274 [t1] DEBUG c.Test23 - 启动...
java.lang.InterruptedException
at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.doAcquireInterruptibly(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:898)
at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.acquireInterruptibly(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:1222)
at java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.lockInterruptibly(ReentrantLock.java:335)
at cn.itcast.text.Test23.lambda$main$0(Test23.java:16)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
15:18:09.278 [main] DEBUG c.Test23 - 执行打断
15:18:09.280 [t1] DEBUG c.Test23 - 等锁的过程中被打断
注意如果是不可中断模式,那么即使使用了 interrupt 也不会让等待中断
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test23")
public class Test23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("启动...");
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("获得了锁");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
log.debug("获得了锁");
t1.start();
try {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t1.interrupt();
log.debug("执行打断");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
log.debug("释放了锁");
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
15:20:19.347 [main] DEBUG c.Test23 - 获得了锁
15:20:19.353 [t1] DEBUG c.Test23 - 启动...
15:20:20.355 [main] DEBUG c.Test23 - 执行打断 // 这时 t1 并没有被真正打断, 而是仍继续等待锁
15:20:21.368 [main] DEBUG c.Test23 - 释放了锁
15:20:21.368 [t1] DEBUG c.Test23 - 获得了锁
锁超时
立刻失败-tryLock()
public class Test23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("启动...");
if (!lock.tryLock()) {
log.debug("获取立刻失败,返回");
return;
}
try {
log.debug("获得了锁");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
log.debug("获得了锁");
t1.start();
try {
sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
15:23:12.173 [main] DEBUG c.Test23 - 获得了锁
15:23:12.180 [t1] DEBUG c.Test23 - 启动...
15:23:12.181 [t1] DEBUG c.Test23 - 获取立刻失败,返回
超时失败
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test23")
public class Test23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("启动...");
try {
if (!lock.tryLock(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
log.debug("获取等待 1s 后失败,返回");
return;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
log.debug("获得了锁");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
log.debug("获得了锁");
t1.start();
try {
sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
15:24:10.167 [main] DEBUG c.Test23 - 获得了锁
15:24:10.176 [t1] DEBUG c.Test23 - 启动...
15:24:11.182 [t1] DEBUG c.Test23 - 获取等待 1s 后失败,返回
使用 tryLock 解决哲学家就餐问题
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestDeadLock")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chopstick c1 = new Chopstick("1");
Chopstick c2 = new Chopstick("2");
Chopstick c3 = new Chopstick("3");
Chopstick c4 = new Chopstick("4");
Chopstick c5 = new Chopstick("5");
new Philosopher("苏格拉底", c1, c2).start();
new Philosopher("柏拉图", c2, c3).start();
new Philosopher("亚里士多德", c3, c4).start();
new Philosopher("赫拉克利特", c4, c5).start();
new Philosopher("阿基米德", c1, c5).start();
}
}
class Chopstick extends ReentrantLock {
String name;
public Chopstick(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "筷子{" + name + '}';
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Philosopher")
class Philosopher extends Thread {
Chopstick left;
Chopstick right;
public Philosopher(String name, Chopstick left, Chopstick right) {
super(name);
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 尝试获得左手筷子
if (left.tryLock()) {
try {
// 尝试获得右手筷子
if (right.tryLock()) {
try {
eat();
} finally {
right.unlock();
}
}
} finally {
left.unlock();
}
}
}
}
private void eat() {
log.debug("eating...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
15:27:46.882 [柏拉图] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:46.891 [赫拉克利特] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:47.929 [柏拉图] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:47.932 [赫拉克利特] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:48.939 [赫拉克利特] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:48.939 [苏格拉底] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:49.955 [亚里士多德] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:49.956 [苏格拉底] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:50.968 [苏格拉底] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:50.968 [赫拉克利特] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:51.983 [柏拉图] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:51.983 [阿基米德] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:52.991 [赫拉克利特] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:52.991 [苏格拉底] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:53.999 [柏拉图] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:53.999 [赫拉克利特] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:55.018 [柏拉图] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:55.018 [赫拉克利特] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:56.025 [阿基米德] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:56.025 [亚里士多德] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
15:27:57.031 [柏拉图] DEBUG c.Philosopher - eating...
...
公平锁
ReentrantLock 默认是不公平的
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test23")
public class Test23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(false);
lock.lock();
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running...");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t" + i).start();
}
// 1s 之后去争抢锁
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " start...");
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running...");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "强行插入").start();
lock.unlock();
}
}
强行插入,有机会在中间输出
注意:该实验不一定总能复现
t39 running...
t40 running...
t41 running...
t42 running...
t43 running...
强行插入 start...
强行插入 running...
t44 running...
t45 running...
t46 running...
t47 running...
t49 running...
改为公平锁后
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
强行插入,总是在最后输出
t465 running...
t464 running...
t477 running...
t442 running...
t468 running...
t493 running...
t482 running...
t485 running...
t481 running...
强行插入 running...
公平锁一般没有必要,会降低并发度,后面分析原理时会讲解
条件变量
synchronized 中也有条件变量,就是我们讲原理时那个 waitSet 休息室,当条件不满足时进入 waitSet 等待
ReentrantLock 的条件变量比 synchronized 强大之处在于,它是支持多个条件变量的,这就好比
- synchronized 是那些不满足条件的线程都在一间休息室等消息
- 而 ReentrantLock 支持多间休息室,有专门等烟的休息室、专门等早餐的休息室、唤醒时也是按休息室来唤
醒
使用要点:
- await 前需要获得锁
- await 执行后,会释放锁,进入 conditionObject 等待
- await 的线程被唤醒(或打断、或超时)需重新竞争 lock 锁
- 竞争 lock 锁成功后,从 await 后继续执行
例子:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test25")
public class Test25 {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static Condition waitCigaretteQueue = lock.newCondition();
static Condition waitbreakfastQueue = lock.newCondition();
static volatile boolean hasCigrette = false;
static volatile boolean hasBreakfast = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
while (!hasCigrette) {try {
waitCigaretteQueue.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("等到了它的烟");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
while (!hasBreakfast) {
try {
waitbreakfastQueue.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("等到了它的早餐");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}).start();
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
sendBreakfast();
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
sendCigarette();
}
private static void sendCigarette() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("送烟来了");
hasCigrette = true;
waitCigaretteQueue.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private static void sendBreakfast() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("送早餐来了");
hasBreakfast = true;
waitbreakfastQueue.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
15:37:57.901 [main] DEBUG c.Test25 - 送早餐来了
15:37:57.920 [Thread-1] DEBUG c.Test25 - 等到了它的早餐
15:37:58.954 [main] DEBUG c.Test25 - 送烟来了
15:37:58.954 [Thread-0] DEBUG c.Test25 - 等到了它的烟
同步模式之顺序控制
比如必须先2后1打印
wait notify版
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test26")
public class Test26 {
static final Object lock = new Object();
static Boolean t2runned = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
if (!t2runned) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("1");
}
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
log.debug("2");
t2runned = true;
lock.notify();
}
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
ReentrantLock
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test26")
public class Test26 {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static Condition waitT1Set = lock.newCondition();
static Boolean t2Runned =false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
lock.lock();
if (!t2Runned){
try {
waitT1Set.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("1");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
lock.lock();
log.debug("2");
t2Runned=true;
waitT1Set.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t2").start();
}
}
park unpark版
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test26")
public class Test26 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("1");
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
log.debug("2");
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
线程同步之交替输出
线程1 输出a5次,线程2 输出b5次,线程3输出c5次,现在要求输出abcabcabcabcabc
wait notify版
public class Test28 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WaitNotify wn = new WaitNotify(1,5);
new Thread(()->{
wn.print("a",1,2);
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
wn.print("b",2,3);
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
wn.print("c",3,1);
}).start();
}
}
class WaitNotify{
// 打印 a 1 2
public void print(String str,int waitFlag,int nextFlag){
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
synchronized (this){
while (flag!=waitFlag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.print(str);
flag=nextFlag;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
//等待标记
private int flag=1;
//循环次数
private int loopNumber;
public WaitNotify(int flag, int loopNumber) {
this.flag = flag;
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
}
ReentrantLock
public class Test29 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
AwaitSingle awaitSingle = new AwaitSingle(5);
Condition a = awaitSingle.newCondition();
Condition b = awaitSingle.newCondition();
Condition c = awaitSingle.newCondition();
new Thread(()->{
awaitSingle.print("a",a,b);
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
awaitSingle.print("b",b,c);
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
awaitSingle.print("c",c,a);
}).start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
awaitSingle.lock();
try {
System.out.println("开始");
a.signalAll();
}finally {
awaitSingle.unlock();
}
}
}
class AwaitSingle extends ReentrantLock{
private int loopNumber;
public AwaitSingle(int loopNumber) {
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
public void print(String str,Condition current,Condition next){
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
lock();
try {
current.await();
System.out.println(str);
next.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
}
}
park unpark
public class Test30 {
static Thread t1;
static Thread t2;
static Thread t3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParkUnpark parkUnpark = new ParkUnpark(5);
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
parkUnpark.print("a",t2);
});
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
parkUnpark.print("a",t3);
});
t3 = new Thread(() -> {
parkUnpark.print("a",t1);
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
}
}
class ParkUnpark{
private int loopNumber;
public ParkUnpark(int loopNumber) {
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
public void print(String str,Thread next){
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
LockSupport.park();
System.out.print(str);
LockSupport.unpark(next);
}
}
}






















 281
281











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








