1、STL初识
1.1STL的诞生
• 长久以来,软件界一直希望建立一种可重复利用的东西
•C++的面向对象和泛型编程思想,目的就是复用性的提升
• 大多情况下,数据结构和算法都未能有一套标准,导致被迫从事大量重复工作
• 为了建立数据结构和算法的一套标准,诞生了STL
1.2STL基本概念
• STL(Standard Template Library,标准模板库)
• STL从广义上分为:容器(container) 算法(algorithm)迭代器(iterator)
• 容器和算法之间通过迭代器进行无缝连接。
• STL几乎所有的代码都采用了模板类或者模板函数
1.3STL六大组件
STL大体分为六大组件,分别是:容器、算法、迭代器、仿函数、适配器(配接器)、空间配置器
1、容器:各种数据结构,如vector、list、deque、set、map等,用来存放数据。
2、算法:各种常用的算法,如sort、find、copy、for_each等
3、迭代器:扮演了容器与算法之间的胶合剂。
4、仿函数:行为类似函数,可作为算法的某种策略。
5、适配器:一种用来修饰容器或者仿函数或迭代器接口的东西。
6、空间配置器:负责空间的配置与管理。
1.4 STL中容器、算法、迭代器
容器:置物之所也
STL容器就是将运用最广泛的一些数据结构实现出来常用的数据结构:数组,链表,树,栈,队列,集合,映射表等
这些容器分为序列式容器和关联式容器两种:
序列式容器:强洞值的排序,序列式容器中的每个元素均有固定的位置。
关联式容器:二叉树结构,各元素之间没有严格的物理上的顺序关系
算法:问题之解法也
有限的步骤,解决逻辑或数学上的问题,这一门学科我们叫做算法(Algorithms)
算法分为:质变算法和非质变算法。
质变算法:是指运算过程中会更改区间内的元素的内容。例如拷贝,替换,删除等等
非质变算法:是指运算过程中不会更改区间内的元素内容,例如查找、计数、遍历、寻找极值等等
迭代器:容器和算法之间粘合剂
提供一种方法,便之能够依序寻访某个容品所含的各个元素,而又无需暴露该容器的内部表示方式。
每个容器都有自己专属的迭代器
迭代器使用非常类似于指针,初学阶段我们可以先理解迭代器为指针
迭代器种类:
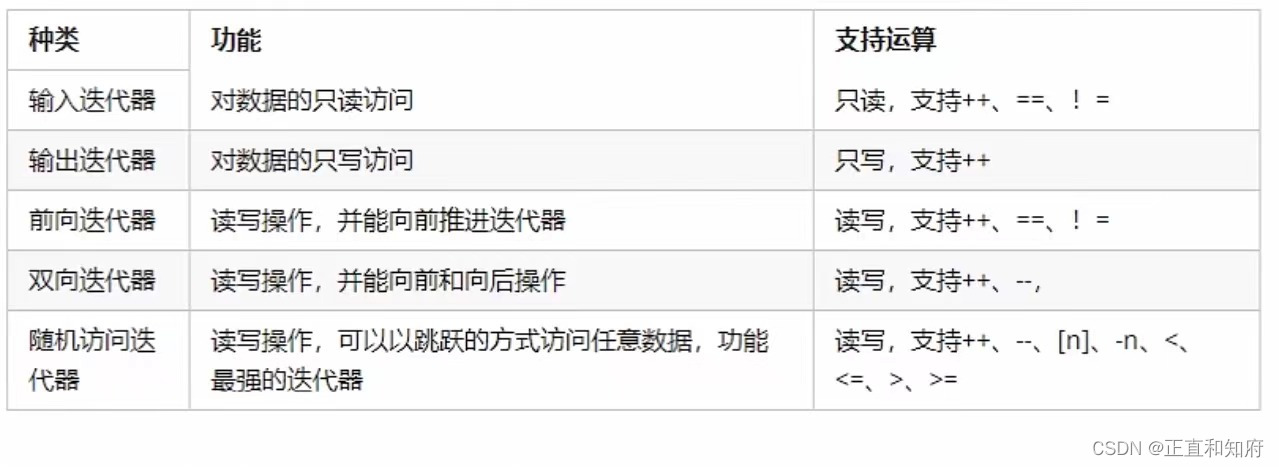
常用的容器中迭代器种类为双向迭代器,和随机访问迭代器
1.5容器算法迭代器初识
了解STL中容器、算法、迭代器概念之后,我们利用代码感受STL的魅力
STL中最常用的容器为Vector,可以理解为数组,下面我们将学习如何向这个容器中插入数据、并遍历这个容器
1.5.1vector存放内置数据类型
容器:
vector算法:
for_each迭代器:
vector<int>::iterator#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>//标准算法头文件
//vector容器存放内置数据类型
void myPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建了一个vector容器,数组
vector<int> v;
//向容器中插入数据
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
//通过迭代器访问容器中的数据
//起始迭代器 指向容器中第一个元素
vector<int>::iterator itBegin = v.begin();
//结束迭代器 指向容器中最后一个元素的下一个位置
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = v.end();
//第一种遍历方式
cout << "方式一遍历:" << endl;
while (itBegin != itEnd)
{
cout << *itBegin << endl;
itBegin++;
}
//第二种遍历方式
cout << "方式二遍历:" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
//第三种遍历方式 利用STL提供遍历算法
cout << "方式三遍历:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
方式一遍历:
10
20
30
40
方式二遍历:
10
20
30
40
方式三遍历:
10
20
30
40
请按任意键继续. . .1.5.2vector存放自定义数据类型
学习目标:vector存放自定义数据类型,并打印输出
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>//标准算法头文件
#include<string>
//vector存放自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
//创建了一个vector容器,数组
vector<Person> v;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
Person p5("eee", 50);
//向容器中插入数据
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
//遍历容器中的数据
cout << "测试一遍历:" << endl;
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//输出方式一
//it(可以理解为指针)解引用是Person的数据类型 所以用.
cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it).m_Age << endl;
//输出方式二
//迭代器使用非常类似于指针,初学阶段我们可以先理解迭代器为指针
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
//存放自定义数据类型 指针
void test02()
{
vector<Person*> v;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
Person p5("eee", 50);
//向容器中插入数据
v.push_back(&p1);
v.push_back(&p2);
v.push_back(&p3);
v.push_back(&p4);
v.push_back(&p5);
//遍历容器中的数据
cout << "测试二遍历:" << endl;
for (vector<Person*>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//it(可以理解为指针)解引用是Person* 是个指针 所以要用->
cout << "姓名:" << (*it)->m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it)->m_Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
测试一遍历:
姓名:aaa 年龄:10
姓名:aaa 年龄:10
姓名:bbb 年龄:20
姓名:bbb 年龄:20
姓名:ccc 年龄:30
姓名:ccc 年龄:30
姓名:ddd 年龄:40
姓名:ddd 年龄:40
姓名:eee 年龄:50
姓名:eee 年龄:50
测试二遍历:
姓名:aaa 年龄:10
姓名:bbb 年龄:20
姓名:ccc 年龄:30
姓名:ddd 年龄:40
姓名:eee 年龄:50
请按任意键继续. . .1.5.3vector容器嵌套容器
学习目标:容器中嵌套容器,我们将所有数据进行遍历输出
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
//#include<algorithm>//标准算法头文件
//#include<string>
//容器嵌套容器
void test01()
{
//创建了一个vector容器,数组
vector<vector<int>> v;
//创建小容器
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
vector<int>v3;
vector<int>v4;
//向小容器中添加数据
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 1);
v2.push_back(i + 2);
v3.push_back(i + 3);
v4.push_back(i + 4);
}
//将小容器插入到大容器中
v.push_back(v1);
v.push_back(v2);
v.push_back(v3);
v.push_back(v4);
//通过大容器,把所有数据遍历一遍
for (vector<vector<int>>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//(*it)----容器vector<int>
for (vector<int>::iterator vit = (*it).begin(); vit != (*it).end(); vit++)
{
cout << *vit << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
1 2 3 4
2 3 4 5
3 4 5 6
4 5 6 7
请按任意键继续. . .2、string容器
2.1string基本概念
本质:string是C++风格的字符串,而string本质上是一个类
string和char*的区别:
char*是一个指针
string是一个类,类内部封装了char*,管理这个字符串,是一个char*型容器
特点:
string类内部封装了很多成员方法
例如:查找find,拷贝copy,删除delete,替换replace,插入insert
string管理char*所分配的内存,不用担心复制越界和取值越界,由类内部进行负责
2.2string构造函数
构造函数原型:
string(); //创建一个空的字符串 例如:string str;
string(const char* s); //使用字符串s初始化
string(const string& str); //使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象
string(int n, char c); //使用n个字符c初始化#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<string>
//string();//创建一个空的字符串 例如:string str;
//string(const char* s);//使用字符串s初始化
//string(const string& str);//使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象
//string(int n, char c);//使用n个字符c初始化
//string的构造函数
void test01()
{ //方式1
string s1;//默认构造
//方式2
const char* str = "hello world";
string s2(str);
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
//方式3
string s3(s2);
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
//方式4
string s4(10, 'a');
cout << "s4 = " << s4 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出结果:
s2 = hello world
s3 = hello world
s4 = aaaaaaaaaa
请按任意键继续. . .2.3string赋值操作
功能描述:给string字符串赋值
赋值的函数原型:
string& operator=(const char* s); //char*类型字符串 赋值给当前的字符串
string& operator=(const string& s); // 把字符串S赋给当前的字符串
string& operator=(char c); // 字符赋值给当前的字符串
string& assign(const char* s); //把字符串s赋给当前的字符串
string& assign(const char* s, int n); //把字符串S的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串
string& assign(const string& s); // 把字符串s赋给当前字符串
string& assign(int n, char c); // 用n个字符c赋给当前字符串#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<string>
//string赋值操作
//string& operator=(const char* s); //char*类型字符串 赋值给当前的字符串
//string& operator=(const string& s); // 把字符串S赋给当前的字符串
//string& operator=(char c); // 字符赋值给当前的字符串
//string& assign(const char* s); //把字符串s赋给当前的字符串
//string& assign(const char* s, int n); //把字符串S的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串
//string& assign(const string& s); // 把字符串s赋给当前字符串
//string& assign(int n, char c); // 用n个字符c赋给当前字符串
void test01()
{ //方式1
string str1;
str1 = "hello world";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
//方式2
string str2;
str2 = str1;
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
//方式3
string str3;
str3 = 'a';
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
//方式4
string str4;
str4.assign("hello C++");
cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
//方式5
string str5;
str5.assign("hello C++",4);
cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;
//方式6
string str6;
str6.assign(str5);
cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;
//方式7
string str7;
str7.assign(4, 'a');
cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出结果:
str1 = hello world
str2 = hello world
str3 = a
str4 = hello C++
str5 = hell
str6 = hell
str7 = aaaa
请按任意键继续. . .2.4string字符串拼接
功能描述:实现在字符串末尾拼接字符串
函数原型:
string& operator+=(const char* str); // 重载 += 操作符
string & operator+=(const char c); //重载 += 操作符
string & operator+=(const string & str); // 重载 += 操作符
string & append(const char* s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
string& append(const char* s, int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
string & append(const string & s); //同operator+=(const string& str)
string& append(const string& s, int pos, int n); //字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string字符串拼接
//string& operator+=(const char* str); // 重载 += 操作符
//string& operator+=(const char c); //重载 += 操作符
//string& operator+=(const string& str); // 重载 += 操作符
//string& append(const char* s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
//string& append(const char* s, int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
//string& append(const string &s); //同operator+=(const string& str)
//string& append(const string &s, int pos, int n); //字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
void test01()
{
string str1 = "我";
str1 += "爱玩游戏";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
str1 += ':';
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2 = "王者荣耀 英雄联盟";
str1 += str2;
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str3 = "I";
str3.append(" LOVE ");
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append("game: abcd", 5);//注意空格也占用一个字符
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append(str2);
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append(str2, 9, 8);//一个汉字是2个字符
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
str1 = 我爱玩游戏
str1 = 我爱玩游戏:
str1 = 我爱玩游戏:王者荣耀 英雄联盟
str3 = I LOVE
str3 = I LOVE game:
str3 = I LOVE game:王者荣耀 英雄联盟
str3 = I LOVE game:王者荣耀 英雄联盟英雄联盟
请按任意键继续. . .2.5string查找和替换
功能描述:
查找:查找指定字符串是否存在
替换:在指定的位置替换字符串
函数原型:
int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const; // 查找str第一次出现位置 从pos开始查找
int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const; // 查找s第一次出现位置 / pos开始查找
int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const; // Mpos位置查找s的n个字符第一次位置
int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const; // 查找字符c第一次出现位置
int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const; // 查找str最后一次位違,从pos开始查找
int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const; // 查找s最后一次出現位置.从pos开始查找1
int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const; //从pos查找s的前;个字符最后一次位置
int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const; // 查找字符c最后一 - 次出现位置
string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str); // 替换从PPs开始n个字符为字符串str
string& replace(int pos, int n, const char* s); // 替换从pos开始的n个字符为字符串s#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string字符串查找和替换
//int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const; // 查找str第一次出现位置 从pos开始查找
//int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const; // 查找s第一次出现位置 / pos开始查找
//int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const; // Mpos位置查找s的n个字符第一次位置
//int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const; // 查找字符c第一次出现位置
//int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const; // 查找str最后一次位違,从pos开始查找
//int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const; // 查找s最后一次出現位置.从pos开始查找1
//int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const; //从pos查找s的前;个字符最后一次位置
//int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const; // 查找字符c最后一 - 次出现位置
//string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str); // 替换从PPs开始n个字符为字符串str
//string& replace(int pos, int n, const char* s); // 替换从pos开始的n个字符为字符串s
//1、查找
void test01()
{
string str1 = "abcdefgde";
int pos = str1.find("de");
if (pos == -1)
{
cout << "未找到字符串" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到字符串,pos = " << pos << endl;
}
//rfind 和 find的区别
//rfind从右往左查找 find从左往右查找
pos = str1.rfind("de");
cout << "找到字符串,pos = " << pos << endl;
}
//2、替换
void test02()
{
string str1 = "abcdefgde";
//从1号位置起 3个字符 替换为1111
str1.replace(1, 3, "1111");
cout << "str1= " << str1 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
找到字符串,pos = 3
找到字符串,pos = 7
str1= a1111efgde
请按任意键继续. . .总结:
• find查找是从左往后,rfind从右往左
• find找到字符串后返回查找的第一个字符位置,找不到返回-1
• replace在替换时,要指定从哪个位置起,多少个字符,替换成什么样的字符串
2.6string字符串比较
功能描述:字符串之间的描述
比较方式:字符串比较是按字符的ASCII码进行对比:
= 返回 0
> 返回 1
< 返回 -1
函数原型:
int compare(const string& s) const; //与字符串s比较
int compare(const char* s) const; //与字符串s比较#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string字符串比较
//int compare(const string& s) const; //与字符串s比较
//int compare(const char* s) const; //与字符串s比较
void test01()
{
string str1 = "hello";
string str2 = "hello";
if (str1.compare(str2) == 0)
{
cout << "str1 等于 str2" << endl;
}
else if (str1.compare(str2) > 0)
{
cout << "str1 大于 str2" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "str1 小于 str2" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
str1 等于 str2
请按任意键继续. . .2.7string字符存取
string中单个字符存取方式有两种:
char& operator[](int n); //通过[]方法获取字符
char& at(int n); //通过at方法获取字符#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string字符存取
//char& operator[](int n); //通过[]方法获取字符
//char& at(int n); //通过at方法获取字符
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
//cout << "str =" << str << endl;
//1、通过[]访问单个字符
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//2、通过at方式访问单个字符
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//修改单个字符:[]方式
str[0] = 'x';
//xello
cout << "str =" << str << endl;
//修改单个字符:at方式
str.at(1) = 'x';
cout << "str =" << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
h e l l o
h e l l o
str =xello
str =xxllo
请按任意键继续. . .2.8string插入和删除
功能描述:对string字符串进行插入和删除字符操作
函数原型:
string& insert(int pos, const char* s); //插入字符串
string& insert(int pos, const string& str);//插入字符串
string& insert(int pos, int n, char c); //在指定位置插入n个字符c
string& erase(int pos, int n = npos); //删除从Pos开始的n个字符#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string插入和删除
//string& insert(int pos, const char* s); //插入字符串
//string& insert(int pos, const string& str);//插入字符串
//string& insert(int pos, int n, char c); //在指定位置插入n个字符c
//string& erase(int pos, int n = npos); //删除从Pos开始的n个字符
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
//插入
str.insert(1, "111");
cout << "str =" << str << endl;
//删除
str.erase(1, 3);
cout << "str =" << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
str =h111ello
str =hello
请按任意键继续. . .2.9string子串
功能描述:从字符串中获取想要的子串
函数原型:
string substr(int pos = 0, int n = npos)const; //返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//#include<vector>
#include<string>
//string求子串
//string substr(int pos = 0, int n = npos)const; //返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
void test01()
{
string str = "helloworld";
string substr = str.substr(2, 2);
cout << "substr =" << substr << endl;
}
//实用操作
void test02()
{
string email = "jack@sina.com";
//从邮件的地址中 获取用户名信息
int pos = email.find("@");
string username = email.substr(0, pos);
cout << "username =" << username << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出结果:
substr =ll
username =jack
请按任意键继续. . .总结:很实用






















 221
221











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








