More complex feature-based meta-analyses
之前下载的dataset.pkl直接读取
dataset链接
import neurosynth as ns
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Core functionality for managing and accessing data
from neurosynth import Dataset
# Analysis tools for meta-analysis, image decoding, and coactivation analysis
from neurosynth import meta, decode, network
dataset = Dataset.load('dataset.pkl')
You will have a set of Nifti-format brain images on your drive that display various meta-analytic results. The image names are somewhat cryptic; see documentation elsewhere for details. It’s important to note that the meta-analysis routines currently implemented in Neurosynth aren’t very sophisticated; they’re designed primarily for efficiency (most analyses should take just a few seconds), and take multiple shortcuts as compared to other packages like ALE or MKDA. But with that caveat in mind (and one that will hopefully be remedied in the near future), Neurosynth gives you a streamlined and quick way of running large-scale meta-analyses of fMRI data. Of course, all of the images you could generate using individual features are already available on the Neurosynth website, so there’s probably not much point in doing this kind of thing yourself unless you’ve defined entirely new features.
Fortunately, we’re not constrained to using single features in our meta-analyses. Neurosynth implements a parsing expression grammar, which is a fancy way of saying you can combine terms according to syntactic rules–in this case, basic logical operations.For example, suppose we want to restrict our analysis to studies of emotion that do NOT use the terms ‘reward’ or ‘pain’, which we might construe as somewhat non-prototypical affective states. Then we could do the following:
冒号前是感兴趣的对象,冒号后是根据经验总结的相关关键词
terms = pd.DataFrame({'social attention':['social & attention', 'social_attention'],
'joint attention':['(joint & attention) | (gaze & (following | cue))', 'joint_attention'],
'eye gaze':['gaze &~ (cue | following)' , 'gaze_without_cue_or_following']})
然后开始批量搜索
# 简单的都可以批量搜索
for i in range(0,terms.shape[1]):
studies= dataset.get_studies(expression= terms.iloc[0,i], frequency_threshold=0.01);
ma= meta.MetaAnalysis(dataset, studies);
ma.save_results('./test', terms.iloc[1,i]);
print(terms.iloc[1,i] + ' saved successfully! study number is ' + str(len(studies)))

RSA
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import nibabel as nib
categories = [];
for j in range(0,terms.shape[1]):
categories.append(terms.iloc[1,j])
ncon = len(categories)
nx, ny, nz = (91, 109, 91)
data_for_corr = pd.DataFrame()
for k in range(0, terms.shape[1]):
file = ("./test/"+ terms.iloc[1,k] +"_association-test_z.nii.gz")
data = nib.load(file).get_fdata().reshape(902629).tolist()
data_for_corr[terms.iloc[1,k]]=data
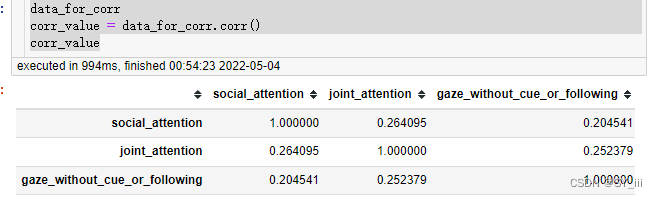
data_for_corr
corr_value = data_for_corr.corr()
corr_value
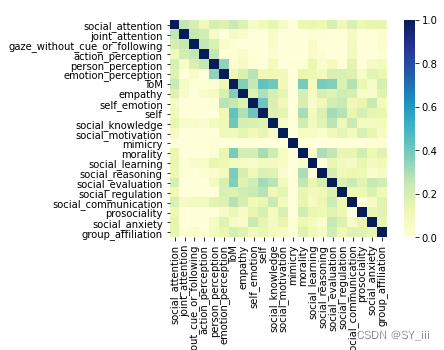
sns.heatmap(corr_value,annot=False, vmax=1,vmin = 0, xticklabels= True, yticklabels= True, square=True, cmap="YlGnBu")




















 1959
1959











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








