EarthData
介绍
NASA:链接

数据下载
视频教程:Discover and Access Earth Science Data Using Earthdata Search
数据下载需要注册,已经被卡在邮箱验证上【2024-12-26】…

Essential Climate Variables——【The Global Climate Observing System(GCOS)
介绍
其是支持IPCC工作的重要数据源
ECV datasets provide the empirical evidence needed to understand and predict the evolution of climate, to guide mitigation and adaptation measures, to assess risks and enable attribution of climate events to underlying causes, and to underpin climate services. They are required to support the work of the UNFCCC and the IPCC. They address the needs for generating datasets for monitoring the climate system and its changes, for supporting climate applications, for underpinning assessments such as the IPCC, and for informing action by Parties to the UNFCCC.
 [2024-12-26]访问网站,显示无权限!!!!无法看具体每个变量的数值…
[2024-12-26]访问网站,显示无权限!!!!无法看具体每个变量的数值…

- Lake数据来源:其中的lake就是采用DAHITI (database for hydrological time series of inland water!)
The Global Climate Observing System (GCOS) lists the data base as an openly accessible data source for the Essential Climate Variable (ECV)
- **径流:**是由多方机构合成的,包括:
(1)Global River Discharge, 1807-1991, V[ersion]. 1.1 (RivDIS):月径流量。入口链接

(2)WMO Hydrological Observing System- 介绍:
In addition, it supports the WMO Unified Data policy, the Global Basic Observing Network (GBON), and Global Hydrological Status and Outlook System【HydroSOS (as a data platform)】.
- 数据面板:链接

- 数据按照2个阶段,先面板展示,后可以供用户下载使用:
第一阶段提供一个地图界面,与那些在网上提供实时和历史水文数据的国家气象和水文部门(nmhs)建立链接。第二阶段提供了一个面向服务的框架,通过一个水文信息系统将水文数据提供者和用户连接起来,该系统支持数据注册、数据发现和数据访问。位于南美洲拉普拉塔盆地(世卫组织-普拉塔)和北极区域(世卫组织-北极)的区域和国家世卫组织原型已进入最后实施阶段。有关世卫组织的更详细信息,请访问世卫组织社区网站。 - 使用时的说明:
WMO水文观测系统(以下简称:WHOS)的所有数据都是根据WMO数据政策提供的,该政策支持尽可能扩大和加强气象、水文、气候和相关环境数据和产品的自由和不受限制的国际交流。请注意,世卫组织不储存或存档任何数据。通过利用发现和访问代理技术,世卫组织对原始数据提供者通过其web服务发布的数据进行了协调、互操作和共享。通过访问世卫组织,用户接受下面规定的使用条款。用户接受使用世卫组织提供的数据可能发生的一切风险,并接受未经原始数据提供者事先同意不将数据用于商业目的,并注意到可能适用特定的使用条件和许可。用户不得复制世卫组织现有的内容以电子或任何其他格式创建数据库,也不得未经原始数据提供者事先同意公开使用和分发给第三方。用户将为科学出版物和业务产品和服务标明数据的来源。世界气象组织(以下简称:WMO)对因使用世卫组织数据而产生的任何直接或间接、意外、物质或非物质损害、损失或费用概不负责。使用世卫组织搜索、查看或下载的数据可以随时更新或修改,WMO对此类更改造成的任何损害不承担任何责任。WMO保留更改或修改使用WHOS的使用条款的权利,对此类更改可能造成的任何损害概不负责。
感想:其实我点进去,只有面板,没看到数据下载呢!!!!!!
(3)GRDC
其他介绍:
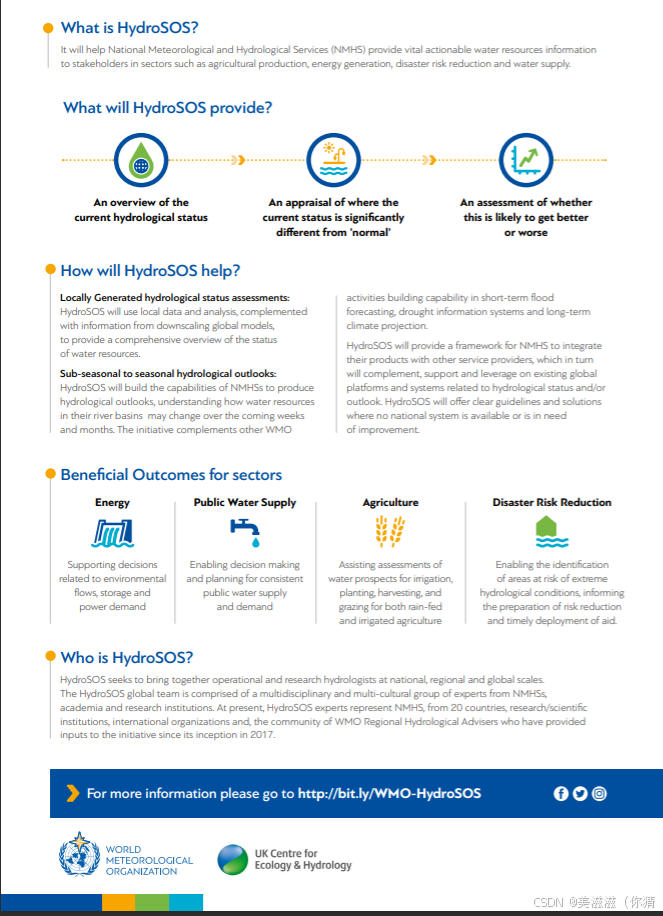
- The Global Hydrological Status and Outlook System (HydroSOS)
- 负责机构:世界气象组织(World Meteorological Organisation)

- github上关于该平台的代码;网页链接。包含了如何整合实测和预测月径流,
Hydrological Status and Outlook System (HydroSOS). This repository contains code to facilitate common categorisation of status and forecast data for integration into the HydroSOS portal.
-
用来监测和预测全球淡水水文条件
-
使用数据包括:
- 局地尺度的地面数据:河流流量、土壤湿度、大湖水位和地下水深度,
- 全球/区域尺度遥感卫星数据:降水、土壤湿度、含水层和积雪/深度;
- 全球/区域天气和气候预报模式:降水和温度
- 全球/区域/流域尺度水文模型:河流流量、土壤湿度、地下水。

-
详细介绍链接
-

-
监测尺度:全球,但是目前数据点还是主要分布在南美、北美、欧洲、非洲呢!
-
英国的case是模型流量例子:
- 使用GR4J模型的“集成流预测(ESP)”方法建模
- 数据获取流程:

 感想:感觉和现在发展的流域平台类似,接入已有的数据或者模型预测的数据,就是一个数据可视化平台
感想:感觉和现在发展的流域平台类似,接入已有的数据或者模型预测的数据,就是一个数据可视化平台
Global Surface Water
介绍
全球地表水资源管理器是一个简单的网络地图工具,它显示了所有的水数据集,并允许用户在不安装任何软件的情况下浏览全球可视化的水数据集。它还允许用户通过点击地图查看37年来的完整水检测历史。该工具旨在作为数据查看器,不提供任何分析功能-如果您想对数据进行自己的分析,则使用data Download或谷歌Earth Engine访问数据。
数据内容包括:Occurrence、change、seasonality、recurrence、transitions、maximum extent。
数据下载
链接
The new dataset 1984-2021 is available to download
支持在线下载、用GEE查看、QGis、Arcgis中用Url查看【但是好像失效了QAQ】
 提供在线查看河流变化的平台:链接 如果查看某个河流这几十年形态是否变化,则可以将其作为一个基础。对重构水文要素、河流形态分析、水动力参数等等有很大帮助。
提供在线查看河流变化的平台:链接 如果查看某个河流这几十年形态是否变化,则可以将其作为一个基础。对重构水文要素、河流形态分析、水动力参数等等有很大帮助。

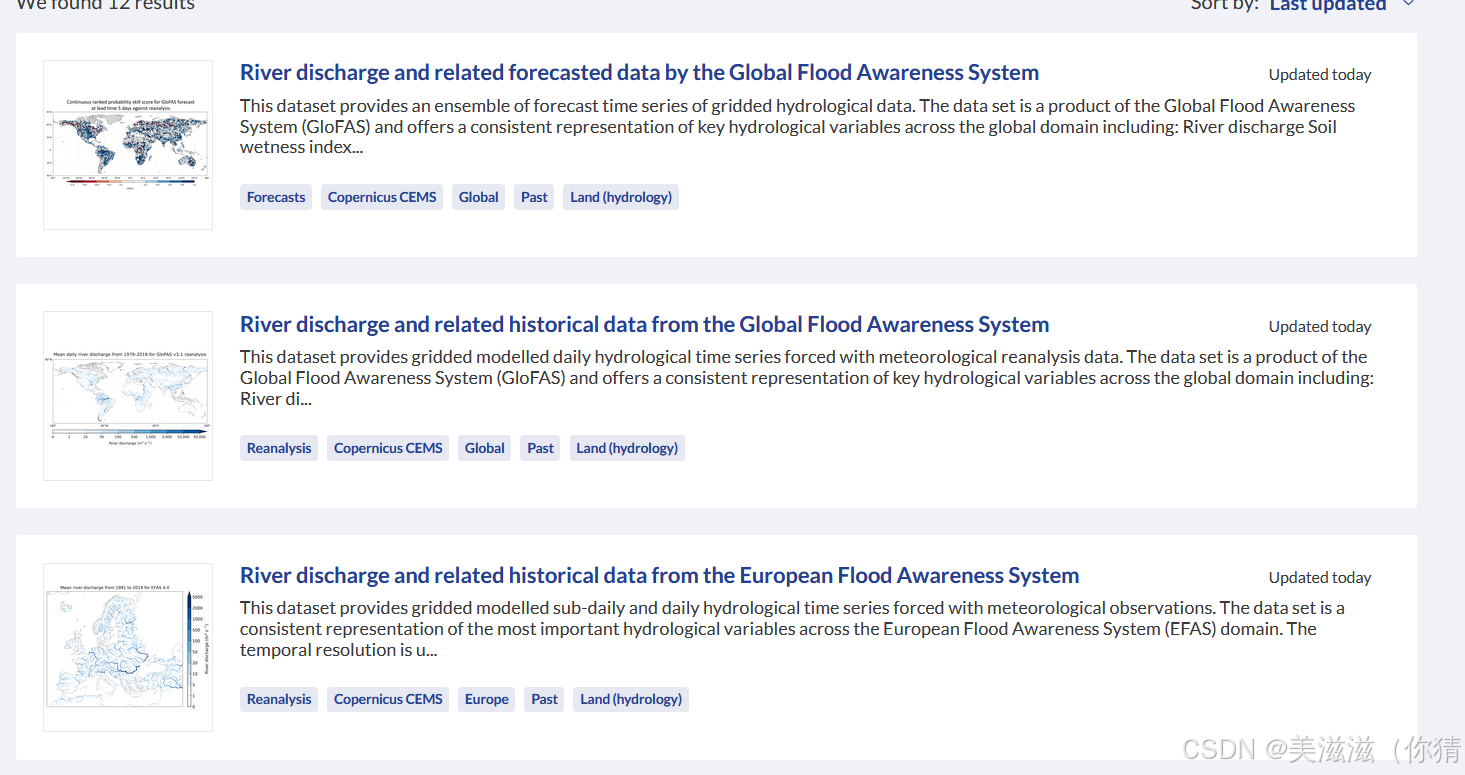
River discharge and related forecasted data by the Global Flood Awareness System (就是那个GloFAS生成的河流流量)
数据介绍
包括近24h的流量、径流通量(地表+地下)、雪水当量、土壤湿度指数。提供1979年起的历史流量数据和预报流量数据。
 数据描述:
数据描述:

数据来源
主要通过the open-source LISFLOOD hydrological model,结合气象预报得到的。
This dataset was produced by forcing the open-source LISFLOOD hydrological model with ERA5 meteorological reanalysis data, interpolated to the GloFAS resolution, produced at a 24-hourly timestep. Two variations of the ERA5 forcing data are used, resulting in two types of hydrological data: intermediate and consolidated. Intermediate hydrological data is produced using ERA5 Near Real Time (ERA5T) data and is updated daily, whilst consolidated hydrological data is produced using the consolidated ERA5 reanalysis and is updated monthly.【2020年版本提到】
This dataset was produced by forcing the open-source LISFLOOD hydrological model with input from the European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) ensemble forecast combined with the ECMWF extended-range ensemble forecast up to 30 days.【2024年版本提到】
数据下载
官网链接
不幸的是也要注册和登录!!!QAQ

The Global Flood Awareness System(GloFAS)
介绍
全球洪水预警系统(The Global Flood Awareness System,GloFAS)是哥白尼应急管理服务( the Copernicus Emergency Management Service,CEMS)的一个组成部分。它的目的是支持世界范围内,特别是大型跨国河流流域的洪水事件的准备措施。为了提供即将发生和正在发生的洪水事件的信息,GloFAS结合了来自卫星、模型和现场测量的信息,产生:GloFAS中期洪水预报、GloFAS季节性预报、GloFAS快速风险评估。因此涉及气象模型、水文模型和灾害评估等等。
相关链接
PS:看在线地图需要账号登录!
- GloFAS官网主页
- Product查阅
- Case study(Ps要是能实现精准化和普及化的话,也是很智慧了)
- 关于模型和算法

关于3层数据:
水文模型性能:它显示了GloFAS可获得日流量数据的站点的修正克林-古普塔效率(KGE)及其组成部分(弹出式表格说明了当前操作版本中站点的校准位置)。模型校准的方法、数据和结果在相关操作版本的页面中给出(一个例子是GloFAS v4.0校准方法、数据和结果;请始终在GloFAS版本控制页面中验证最新的操作版本)。
中期预测技能表示最大提前期(以天为单位):最多提前30天,当GloFAS河流流量预测技能(CRPSS);连续排序概率技能得分(Continuous ranking Probability Skill Score)大于0.5,以河流流量再分析为参考,对持续性和气候学基准预测进行评估。
当GloFAS季节性河流流量预测技能(CRPSS;连续排名概率技能得分(Continuous ranking Probability Skill Score)大于0.5,是根据每周以河流流量再分析为参考的气候基准预测来评估的
相关模型
- 气象预报
GloFAS的预报是利用欧洲气象中心综合预报系统(IFS)最新的数值天气预报(NWP)集合而成。中期和大范围集合输出用于GloFAS预报,而长期的SEAS5集合用于GloFAS季节预报。ECMWF- ens是ECMWF的整体预报,由51个成员组成,分辨率约为9公里,持续15天,从第16天到第30天增加到36公里。在GloFAS 30天中,从第1天到第15天每天使用00:00 UTC的IFS中期运行的输出,并从第16天到第30天使用最新可用的IFS扩展范围运行。SEAS5是ECMWF(自2017年11月5日开始运行)的整体季节预报,是哥白尼气候变化服务的季节预报模式之一。它由51个成员组成,水平分辨率约为36公里。基于SEAS5, GloFAS季节性预报提供水文前景,显示未来16周内一个地区和GloFAS河网的高流量或低流量的可能性,每月一次。关于GloFAS气象预报的更详细的描述可从CEMS-Flood Wiki的这个页面获得。
GloFAS forecasts are produced using the latest ensemble of Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) forecasts of the ECMWF Integrated Forecast System (IFS). The medium- and extended-range ensemble outputs are used for GloFAS forecasts, and the long-range SEAS5 ensemble is used for GloFAS Seasonal forecast.
ECMWF-ENS is the ensemble forecast of ECMWF and consists of 51 members at ~9 km resolution up to 15 days, increasing to 36 km from day 16 to 30. In GloFAS 30-day, the outputs of the 00:00 UTC IFS medium-range runs are used daily for day 1 to 15, and the latest available IFS extended range runs used for day 16 to 30.
SEAS5 is the ensemble seasonal forecast of ECMWF (operational since 5 November 2017), and one of the seasonal forecast models of the Copernicus Climate Change Service. It consists of 51 members at ~36 km horizontal resolution. Based on SEAS5, GloFAS Seasonal forecasts provide hydrological outlooks which show the likelihood of high or low flows within the coming sixteen weeks in a region and the GloFAS river network once a month.
A more detailed description of GloFAS meteorological forecasts is available from this page of the CEMS-Flood Wiki.
- 水文模型
通过一组方程模拟水文陆地过程,将气象强迫预报转化为水文预报。从GloFAS v3.1(2021年5月)开始,利用开源LISFLOOD水文模型生成GloFAS中期和季节性预报。开源LISFLOOD (OS LISFLOOD)是自1997年以来由欧盟委员会联合研究中心(JRC)开发的空间分布式、基于物理的水文模型(De Roo et al., 2000)。数值模拟由气象强迫数据(降水、温度和潜在蒸散)驱动,模型求解每个时间步长和每个格元的水分平衡。一组显示地形形态、土壤特性、土地覆盖和土地利用特征以及水需求的栅格地图,使我们能够模拟不同气候和社会经济背景下的水文循环。OS LISFLOOD源代码,模型文档,用户指南和辅助工具(包括校准脚本)可以通过OS LISFLOOD页面访问。GloFAS OS LISFLOOD实现使用每日时间步长;模型空间分辨率在GloFAS v3.5前为0.1°,在GloFAS v4.0(2023年7月)时提高到0.05°(赤道约5 km)。有关OS LISFLOOD栅格图的信息可从以下页面获得:地表实现图。每个操作版本的技术描述可以从CEMS GloFAS版本控制系统中访问,该页提供最新操作版本的信息。
A hydrological model transforms the meteorological forcing forecasts into hydrological forecasts by mimicking the hydrological land processes by a set of equations. The hydrological model Open Source LISFLOOD has been used to generate GloFAS medium- and seasonal-range forecasts starting from GloFAS v3.1 (May 2021).
Open Source LISFLOOD (OS LISFLOOD) is a spatially distributed, physically based hydrological model which has been developed by the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission since 1997 ( De Roo et al., 2000). The numerical simulation is driven by meteorological forcing data (precipitation, temperature, and potential evapo-transpiration): the model solves the water balance at every time step and for each grid cell. A set of raster maps showing terrain morphology, soil properties, land cover and land use features, and water demand, enables the modelling of the hydrological cycle in different climates and socio-economic contexts. The OS LISFLOOD source code, model documentation, user guide, and ancillary tools (including calibration scripts) can be accessed via the OS LISFLOOD page.
GloFAS OS LISFLOOD implementation uses daily time steps; model spatial resolution was 0.1° up to GloFAS v3.5, it was increased to 0.05° (approximately 5 km at the Equator) with GloFAS v4.0 (July 2023). Information about OS LISFLOOD raster maps is available from the following page: land surface implementation maps. Technical description of each operational release can be accessed from CEMS GloFAS versioning system, with this page providing information on the latest operational release.
ML4Floods
介绍
ML4Floods 是一个用于洪水范围估计的端到端机器学习管道。该项目从数据预处理、模型训练、模型部署到可视化,提供了一整套解决方案。通过利用先进的机器学习技术,ML4Floods 能够高效地处理和分析卫星图像数据,从而准确地估计洪水范围,为灾害管理和应急响应提供有力支持。其集成了 WorldFloods 数据库,包含 509 对 Sentinel-2 图像和洪水分割掩码,数据量达 300GB。
代码链接和介绍
ESA组织的一系列流量反演计划
RIDESAT – RIver flow monitoring and Discharge Estimation by integrating multiple SATellite data
介绍
ESA发起的
Period: 2018 – 2019 (12 months)
Partners: The consortium is based on a close collaboration between 2 partners:
- IRPI CNR: Istituto di Ricerca per la Protezione Idrogeologica (Prime contractor)
- DTU: Technical University of Denmark (Subcontractor) 丹麦技术大学
目的是:理解光学和热红外传感器使用过程背后的物理意义及其应用领域的研究;融合不同传感器获得的不同水文要素(水位、坡度、河宽、流速)的物理方法来实现流量反演。
RIDESAT project has the purpose to develop a new methodology for the joint exploitation of three sensors (altimeter, optical and thermal) for river flow monitoring and discharge estimation. The intention is:
1) to better understand the use of optical and thermal sensors through the study of the physical meaning behind the process and their field of applicability;
2) to develop a procedure of merging the three different satellite data through a physically based method that uses hydraulic variables obtained by satellites (e.g. water height, slope, width, flow velocity).
相关链接
数据下载
 **要谷歌邮箱哦!!!!**QAQ
**要谷歌邮箱哦!!!!**QAQ
Satellite-based Run-off Evaluation And Mapping(STREAM)
介绍
ESA近年来的计划,采用简单的概念模型反演流量,目的是用卫星数据构建水文循环和建模,时间周期为2019年-2020年,实验开展区域包括five basins (Mississippi, Amazon, Danube, Niger and Murray-Darling)。
In this context, the STREAM project aimed at:
①Investigate the possibility to use satellite data for the hydrological cycle modeling;
②and developing a conceptual hydrological model, STREAM, directly ingesting satellite observation of soil moisture (SM), precipitation § and terrestrial water storage anomalies (TWSA).
开发者:
- IRPI CNR: instituto di Ricerca per la Protezione idroge(总承包商)
- 斯图加特大学大地测量研究所(https://www.gis.uni-stuttgart.de/, GIS,分包商)
基于模型
STREAM项目将开发一个概念水文模型,用于根据卫星土壤湿度、降水和陆地蓄水异常情况估算径流。STREAM背后的基本假设是对径流形成的关键机制和过程的了解,例如土壤湿度在决定流域对降水输入的响应中的作用,这已经在十多年的文献研究中得到了充分的证明。
结果
在为期一年的欧空局项目中,开发了一个简单而通用的概念水文模型STREAM。该模型能够通过对降水、土壤湿度和陆地储水量的卫星观测,准确估算全球5个试点流域(密西西比河、亚马逊河、多瑙河、墨累-达令河和尼日尔河)的河流流量和径流。例如,下面的动画代表了模拟径流图和每月在密西西比河(第一个动画)和多瑙河(第二个动画)流域出口段的观测/模拟河流流量数据。尽管获得了良好的结果,但对于特定的案例研究(例如人类影响较大的流域或植被茂密的地区),STREAM模型被发现无法准确地再现观测到的河流流量。
相关介绍链接
- 官网总结链接SaTellite-based Run-off Evaluation And Mapping
(STREAM) - 具体项目情况
- 文章链接:SYNERGY BETWEEN SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS OF SOIL MOISTURE AND WATER STORAGE ANOMALIES
FOR GLOBAL RUNOFF ESTIMATION


STREAMRIDE——SaTellite based Runoff and River Discharge Estimation
介绍
RIDESAT、STREAM计划的合并,开展计划的时间是2021年-2022年。
- 参与者:
- IRPI CNR: Istituto di Ricerca per la Protezione Idrogeologica (Prime contractor)
- Institute of Geodesy at the University of Stuttgart (https://www.gis.uni-stuttgart.de/, GIS, Subcontractor)
- Technical University of Denmark (https://www.dtu.dk/english, DTU, Subcontractor)
- 目标:
结合上述两个技术计划,提高流量反演精度:
refine the satellite-based approaches developed into STREAM and RIDESAT projects. New modules and formulations will be added to the original approaches to include elements which allow to overcome the limitations highlighted within the two projects.
integrate the two approaches to enhance the river discharge estimation. For the specific case studies, a merging configuration will be selected to optimally integrate the river discharge estimates obtained by STREAM and RIDESAT. The impact of the integration will be established through the comparison with in situ observations and the evaluation of the river discharge accuracy.
相关链接
为什么发布这个计划?【2023年的研究报道中记录】ESA这样说:
River discharge is typically obtained by using hydrological or land-surface models, which require accurate observations of precipitation and evaporation. But these models may need approximations that can introduce uncertainties into model predictions.
Hydrologists are always looking for ways of reducing uncertainties so as to improve runoff and river discharge predictions.
提炼下就是直接用遥感数据来减少传统水文模型或者陆面模型反演的不确定性。那么有什么改进呢?ESA这样说:
Through these ESA projects, the Hydrology Group of the Italian National Research Council has developed an innovative approach using satellite observations of terrestrial water storage, soil moisture and precipitation to predict runoff and river discharge – with the results published in the EGU Geoscientific Model Development journal.
Their research included using soil moisture data from ESA’s Climate Change Initiative and total water storage data from NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment, GRACE, mission.
“From space, we can obtain information on soil moisture content and terrestrial water storage that is not available from ground-based monitoring networks. By using these observations in a newly-designed hydrological model, we have been able to develop a robust and reliable system for predicting runoff and river discharge.”
MAGIC (Simulation studies for a Mass change And Geosciences International Constellation)质量变化和地球科学国际星座 【目前还没运行呢…】
介绍
质量变化和地球科学国际星座(MAGIC)是计划中的**美国国家航空航天局(NASA)和欧洲航天局(ESA)**的合资企业。该任务将由四颗卫星组成,成对运行,并将在诸如重力场和稳态海洋环流探测器(GOCE)任务、重力恢复和气候实验(GRACE)及其后续任务GRACE- fo等类似任务的成功基础上,测量地球重力场的波动。

目前状态
2020年11月:欧航局部长级理事会决定在a阶段研究下一代重力任务(NGGM),作为未来地球观测计划的第一个机会任务。
2021年10月1日:ESA的下一代重力任务(NGGM)是ESA - nasa在质量变化和地球科学国际星座(MAGIC)框架下合作的候选机会任务。该任务的目的是在较长的时间间隔(低至3天)长期监测地球重力场的时间变化,并提高空间分辨率(高至100公里。
2022年10月13日:ESA和NASA宣布,他们的联合“下一代重力任务”正在质量变化和地球科学国际星座内进行初始阶段的设计活动。
2022年11月23日:欧空局部长级理事会决定为欧空局的地球观测计划额外拨款27亿欧元,并批准启动下一个欧空局地球探测器、和谐号和MAGIC任务。
2023年3月:gracc - KDP-A于03年3月16日报告成功通过。
2023年4月25日:欧空局宣布,NGGM阶段A正在进行延长阶段(8个月),直到卫星设计的三角洲初步需求审查(2023年7月至9月),这是由两个竞争联盟提出的。
2023年6月:欧空局批准在基于仪器优先方法的B1阶段开始采购下一代重力任务(NGGM)。Microstar加速计、激光跟踪仪EM和EQM的采购与B1阶段系统研究一起启动。
相关链接
MAGIC (Mass-Change and Geosciences International Constellation)

※※:所有EO missions and sensors的介绍!!!:链接
Discover more about past, operational and future missions in the Satellite Missions database, which offers an extensive list of articles about spaceborne EO missions and sensors, as well as other space missions.

GRDC(Global Runoff Database Center)
介绍
世界气象组织下的数据集。
The Global Runoff Data Centre (GRDC) is an international data centre operating under the auspices of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Established in 1988 to support the research on global and climate change and integrated water resources management, it holds the most substantive collection of quality assured river discharge data on global scale.
其中的流量数据来自各个国家提交的数据(WMO所有成员国的国家水文部门)。数据中心作为一个国际数据中心,协调和传播关于国家数据持有和数据获取的信息。【可以理解为是各个国家的实测径流????】
官网链接:https://grdc.bafg.de/
历史和地位:
The initial demand for the construction of an observational global runoff data set came from the WMO/ICSU Global Atmospheric Research Programme’s First GARP Global Experiment (FGGE).
Since 1988 the GRDC database has grown continuously becoming the most comprehensive quality checked global discharge dataset.
数据下载
(1)流量数据下载链接
- 不支持使用API下载数据。
- 下载数据前可以选择按照:①分区(subregion);②水文站(station); PS:在GRDC Station Catalogue中详细罗列了各个水文站的基本信息(见图),可以先下载下来后再判断哪些好用!
 


(2)其他可下载数据

(3)数据使用条款:
全球径流数据中心(GRDC)是在世界气象组织(WMO)主持下运作的一个国际数据中心。本网站提供的所有水文数据均由GRDC管理,并获得数据所有者(通常是创建数据的国家水文部门)的许可。所有水文数据均为所有者的财产,仅可用于研究目的。不允许将水文数据用于商业用途。不允许将下载的水文数据部分或全部重新分发给未经授权的人、第三方或公众(包括通过电子媒体)。允许对水文数据进行分析和进一步处理以及使用统计数据产品,并适当注明数据来源:“全球径流数据中心,56068 Koblenz,德国”。与您的数据请求有关的问题应直接发送至grdc(at) bagg .de
其余提到的,后续再检索
NOAA National Weather Service数据: 美国国家海洋和大气管理局(NOAA)提供了有关天气、降水和河流水位等信息的数据,这些数据可用于洪水预测研究。你可以在NOAA的网站上找到这些数据。
USGS河流流量数据: 美国地质调查局(USGS)提供了有关美国各地河流的流量数据。这些数据可用于监测河流水位和流量,从而帮助预测洪水。
CAMELS数据集: CAMELS(Catchment Attributes and Meteorology for Large-sample Studies)数据集包含了来自美国境内的多个流域的水文和气象数据,可用于水文模型和洪水预测的研究。
European Space Agency(ESA)的Sentinel卫星数据: ESA的Sentinel卫星提供了全球范围内的地表覆盖和气象数据,这些数据可用于监测洪水事件。
国际洪水数据库(International Flood Database): 国际洪水数据库包含了世界各地的洪水事件历史数据,可以用于研究洪水的频率和影响。
国际水文气象数据和地球观测系统(International Hydro-Meteorological Observatory System): 这个系统提供了全球范围内的水文和气象观测数据,包括降雨、温度、湿度等,有助于洪水预测和监测。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45410037/article/details/133364215



























 5280
5280

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










