文章目录
优先级队列----堆
1.概念
如果有一个关键码的集合K = {k0,k1, k2,…,kn-1},把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储 在一个一维数组中,并满足:Ki <= K2i+1 且 Ki<= K2i+2 (Ki >= K2i+1 且 Ki >= K2i+2) i = 0,1,2…,则称为 小堆(或大堆)。将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
2.性质
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或者不小于其父节点的值;
- 对总是一棵完全二叉树
3.结构与存储
堆是一棵完全二叉树 ,因此可以层序的规则采用顺序的方式来高效存储
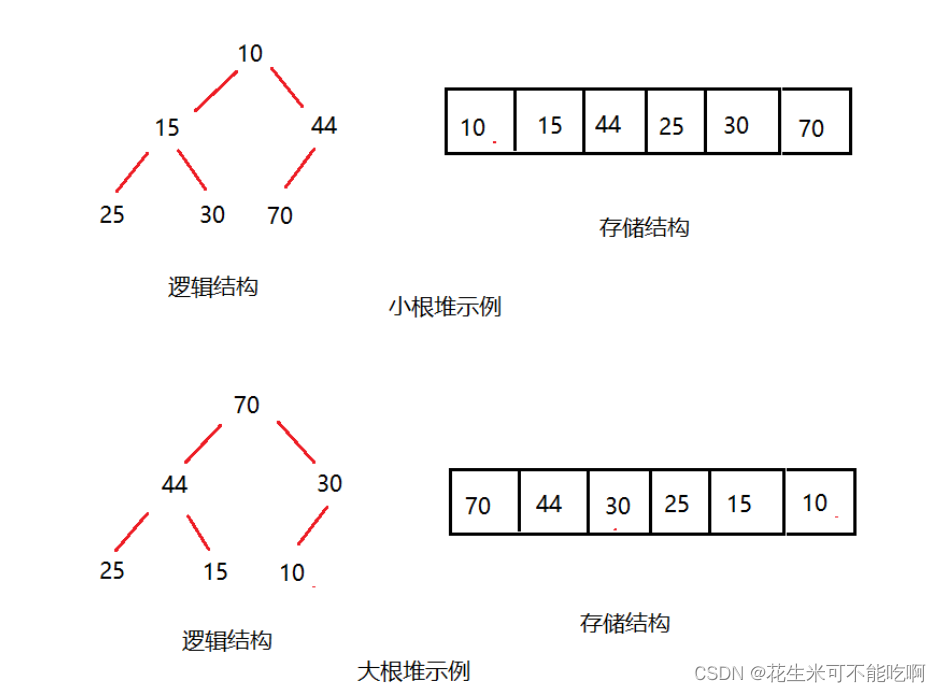
注意: 对于非完全二叉树 , 则不适用使用顺序方式进行存储 , 因为为了能够还原二叉树 , 空间中必须要存储空节点 , 就会导致空间利用率比较低
4.堆的创建
4.1 堆向下调整
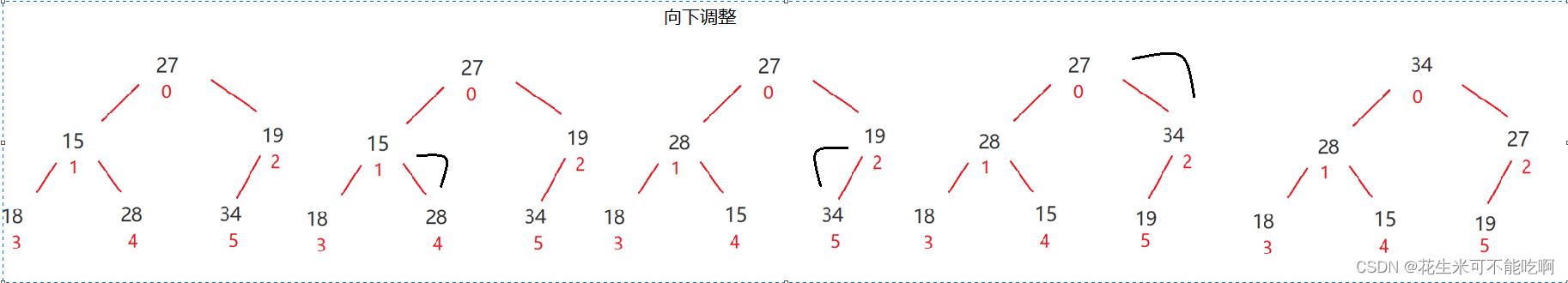
以大根堆为例 : 对于集合{ 27,15,19,18,28,34 }中的数据,如果将其创建成堆呢 ?
- 先设定根节点为当前节点(通过下标获取,标记为cur),比较左右子树的值,找出更大的值,用child来标记。
- 比较child和cur的值,如果child比cur大,则不满足大堆的规则,需要进行交换。
- 如果child比cur小,满足大堆的规则,不需要交换,调整结束。
- 处理完一个节点之后,从当前的child出发,循环之前的过程
时间复杂度 : 树的高度
建堆时间复杂度 : O(N)
4.2 堆向上调整
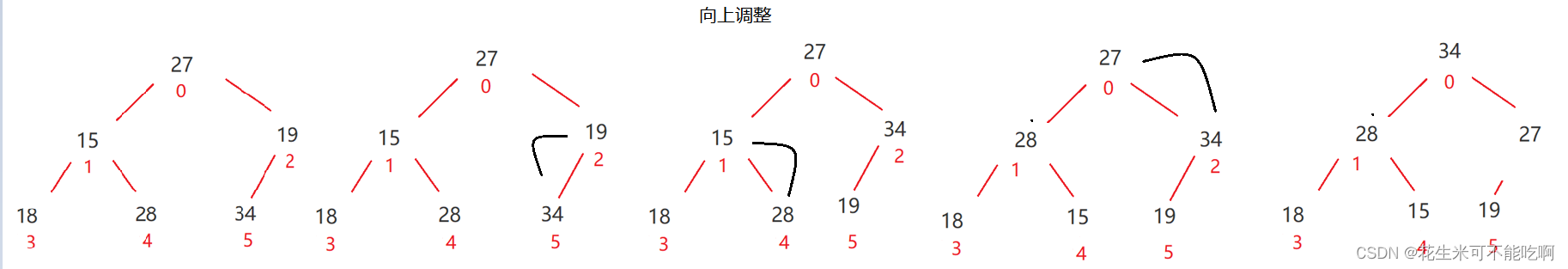
- 先设定倒数的第一个叶子节点为当前节点(通过下标获取,标记为cur),找出他的父亲节点,用parent来标记。
- 比较parent和cur的值,如果cur比parent大,则不满足大堆的规则,需要进行交换。
- 如果cur比parent小,满足大堆的规则,不需要交换,调整结束。
- 处理完一个节点之后,从当前的parent出发,循环之前的过程。
4.3 创建堆示例
/**
* 大根堆
*/
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
public void initElem(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
elem[i] = array[i];
usedSize++;
}
}
/**
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
*/
public void createHeap() {
for (int parent = (usedSize-1-1)/2;parent >= 0;parent--) {
shiftDown(parent,usedSize);
}
}
/**
* 父亲节点 和 每棵树的结束下标
*/
private void shiftDown(int parent,int len) {
int child = 2*parent + 1;
//最起码要有左孩子
while (child < len) {
//一定是有右孩子的情况下
if (child+1 < len && elem[child] < elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
//child下标 一定是左右孩子 最大值的下标
if (elem[child] > elem[parent]) {
int tmp = elem[child];
elem[child] = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
建堆的时间复杂度 : O(N)
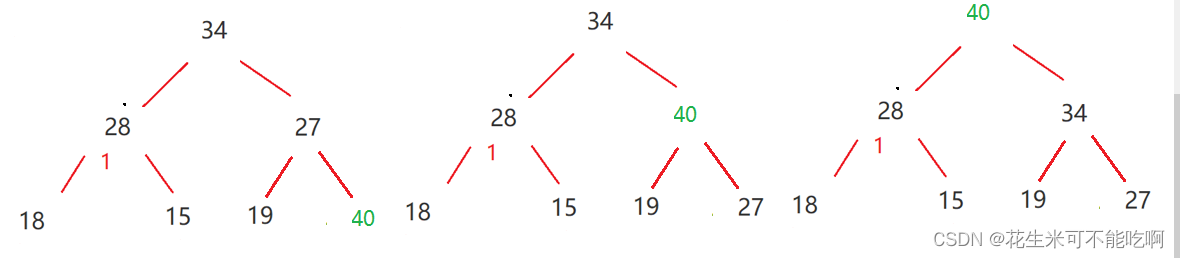
5.堆的插入
1 . 先将元素放入到底层空间中 , 看是否需要扩容
2 . 将最后新插入的节点向上调整 , 直至满足堆的性质
public void shiftUp(int child) {
int parent = (child-1)/2;
while (child > 0) {
if (elem[child] > elem[parent]) {
int tmp = elem[child];
elem[child] = elem[parent];
elem[parent] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child-1)/2;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
//向上调整建堆的时间复杂度: N*logN
public void offer(int val) {
if (isFull()) {
//扩容
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}
elem[usedSize++] = val;//11
//向上调整
shiftUp(usedSize-1);//10
}
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
向上调整建堆的时间复杂度为 : N*logN
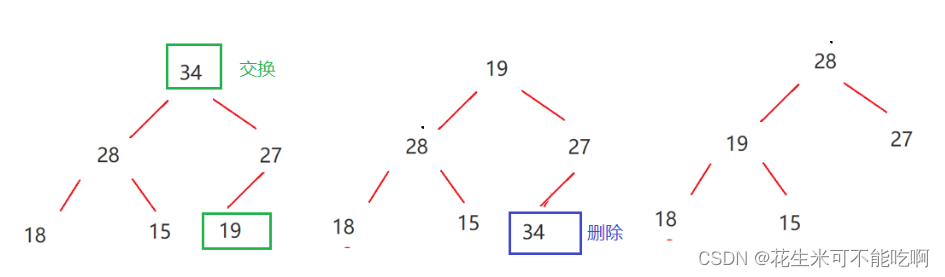
6.堆的删除
注意 : 堆的删除一定删除的是堆顶元素 .
1 . 将堆顶元素对堆中最后一个元素交换
2 . 将堆中有效数据个数减少一个
3 . 对堆顶元素进行向下调整
public void pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("堆为空");
}
swap(elem,0,usedSize-1);
usedSize--;
shiftDown(0,usedSize);
}
private void swap(int[] array,int i,int j) {
int tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = tmp;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}
7.常用接口
7.1 PriorityQueue的特性
Java集合框架中提供了 PriorityQueue 和 PriorityBlockingQueue 两种类型的优先级队列 , PriorityQueue 是线程不安全的 , PriorityBlockingQueue 是线程安全的.
使用 PriorityQueue的使用要注意 :
-
使用时必须导入 PriorityQueue 所在的包 ,
import java.util.PriorityQueue; -
PriorityQueue中放置的元素要能够比较大小 , 不能插入无法比较的对象 , 否则会抛出
-
不能插入null对象 , 否则会抛出 NullPointerException
-
没有容量限制 , 可以插入任意多个元素 , 其内部可以自动扩容
-
插入和删除元素的时间复杂度为O(logN)
-
PriorityQueue 底层使用了堆数据结构
-
PriorityQueue 默认情况下是小堆—即每次获取到的元素都是最小的元素
7.2 PriorityQueue常用接口介绍
1.优先级队列的构造
| 构造器 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| PriorityQueue() | 创建一个空的优先级队列 , 默认容量是11 |
| PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) | 创建一个初始容量为initialCapacity优先级队列,initialCapacity 不能小于1,否则会抛illegalArgumentException异常 |
| PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E>c) | 用一个集合来创建优先级队列 |
7.3 比较器
用户自己定义比较器 : 直接实现 Comparator 接口 , 然后重写接口中的compare 方法即可
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
public int age;
public String name;
public Student(String name,int age) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(age, name);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
class NameComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.name.compareTo(o2.name);
}
}
class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.age - o2.age;
}
}
public class TestCompare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("zhangsan",10);
Student student2 = new Student("zhangsan",20);
System.out.println(student1 == student2);
System.out.println(student1.equals(student2));
System.out.println(student1.compareTo(student2));
System.out.println("======姓名比较器=====");
NameComparator nameComparator = new NameComparator();
int ret = nameComparator.compare(student1,student2);
System.out.println(ret);
System.out.println("=======年龄比较器=======");
AgeComparator ageComparator = new AgeComparator();
int ret2 = ageComparator.compare(student1,student2);
System.out.println(ret2);
}
}
7.4插入/删除/获取优先级最高元素
从源码当中分析
1 . boolean offer(E e)
插入元素e , 插入成功返回 true , 如果 e 对象为空 , 抛出 空指针异常 , 空间不够时候进行扩容
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
2 . E peek()
获取优先级最高的元素 , 如果优先级队列为空 , 返回 null
public E peek() {
return (size == 0) ? null : (E) queue[0];
}
3 . E poll()
移除优先级最高的元素并返回 , 如果优先级队列为空 , 返回 null
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0];
E x = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);
return result;
}
4 . int size()
获取有效元素个数
public int size() {
return size;
}
5 . void clear()
清空
public void clear() {
modCount++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
queue[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
6 . boolean isEmpty()
检测优先级队列是否为空 , 空返回 true
7.5 PriorityQueue 的扩容方式
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
- 如果容量小于 64 时 , 按照 oldCapacity 的 2 倍 进行扩容
- 如果容量大于等于 64 , 按照 oldCapacity 的 1.5 倍 进行扩容
- 如果容量超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,按照MAX_ARRAY_SIZE来进行扩容
PriorityQueue 的应用 ----top-k 问题
top-k问题:最大或者最小的前k个数据。比如:世界前500强公司
1 . 用数据集合中前 K 个元素来建堆
① 前 K 个最大的元素 , 则建小堆
②前 K 个最小的元素 , 则建大堆
2 . 用剩余的 N-K 个元素依次与堆顶元素来比较 , 不满足则替换堆顶元素
将剩余N-K个元素依次与堆顶元素比完之后,堆中剩余的K个元素就是所求的前K个最小或者最大的元素。
一 . 设计一个算法,找出数组中最小的k个数。以任意顺序返回这k个数均可
public int[] smallestK(int[] arr, int k) {
int[] ret = new int[k];
if (arr == null || k == 0) {
return ret;
}
//O(N*logN)
Queue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(arr.length);
for (int x : arr) {
minHeap.offer(x);
}
//K*logN
for (int i = 0;i < k;i++) {
ret[i] = minHeap.poll();
}
return ret;
}
二 . 找前K个最大的元素
1.将数组前K个元素建立小根堆 , 剩下的元素依次和堆顶元素进行比较
2.小根堆的堆顶元素就是小根堆的最小元素 , 剩下元素比堆顶元素小,则不入堆
3.剩下元素比堆顶元素大,则将堆顶元素放到堆尾删除, 将剩余元素放入堆顶,再 进行排序,使新堆变成小根堆
4.以此往复 ,直到将数组元素比较结束
public int[] maxK2(int[] arr, int k) {
int[] ret = new int[k];
if (arr == null || k == 0) {
return ret;
}
Queue<Integer> minHeap2 = new PriorityQueue<>(k);
//1.遍历数组的前k 个元素 放到堆中 O(K*logK)
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
minHeap2.offer(arr[i]);
}
//2.遍历剩下的 k-1 个 , 每次和堆顶元素进行比较
// 当堆顶元素小的时候 , 就出堆 O(N-K)*logK
for (int i = k; i < arr.length; i++) {
int val = minHeap2.peek();
if (val < arr[i]) {
minHeap2.poll();
minHeap2.offer(arr[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ret[i] = minHeap2.poll();
}
return ret;
}





















 1042
1042











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








