互斥锁的概念和使用
临界资源:只允许一个任务访问的资源。
例如外设打印机,打印的时候只能由一个程序使用。
mutex互斥锁:用来访问临界资源。
任务访问资源前申请锁,访问完后释放锁。
举例:(无互斥锁)
代码讲解:
代码中有两个线程会无限循环地向同一个文件(1.txt)写入内容。但这两个线程都在没有同步的情况下写入同一个文件,所以会遇到数据交错的问题,即一个线程写入的内容可能会被另一个线程写入的内容打断。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
// pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
FILE *fp;
void *func2(void *arg){
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
printf("This func2 thread\n");
char str[]="I write func2 line\n";
char c;
int i=0;
while(1){
// pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while(i<strlen(str)){
c = str[i];
fputc(c, fp);
usleep(1);
i++;
}
// pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
i=0;
usleep(1);
}
pthread_exit("func2 exit");
}
void *func(void *arg){
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
printf("This is func1 thread\n");
char str[]="You read func1 thread\n";
char c;
int i=0;
while(1){
// pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while(i<strlen(str)){
c = str[i];
fputc(c, fp);
usleep(1);
i++;
}
// pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
i=0;
usleep(1);
}
pthread_exit("func1 exit");
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid,tid2;
void *retv;
int i;
fp = fopen("1.txt", "a+");
if(fp==NULL){
perror("fopen");
return 0;
}
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, func2, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, func, NULL);
while(1){
sleep(1);
}
}
结果:
无互斥锁
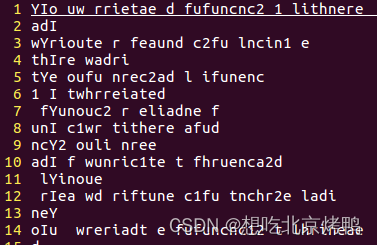
有互斥锁结果(将代码中注释部分取消即可)
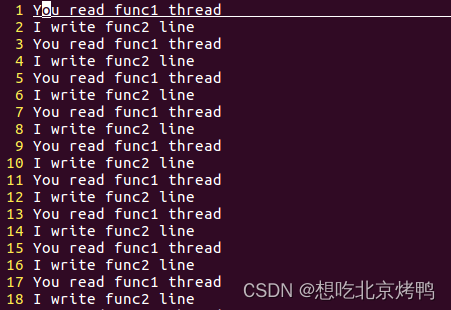





















 4632
4632

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








