1.文件
文件的创建(三种放法)
public class FileCreate {
@Test
public void no1(){
//第一种方法:new File(String pathname);
File file = new File("e:\\new1.txt");
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("创建成功");
}
@Test
public void no2() throws IOException {
//第二种方法:new File(File parent,String child) 根据目录文件+子路径构造
File parentFile = new File("e:\\");
String childFile = "new2.txt";
//这里的file对象,在java程序中,只是一个对象
//只有执行了 createNewFile 方法,才会真正的,在磁盘创建文件
File file = new File(parentFile, childFile);
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功");
}
@Test
public void no3() throws IOException {
//第三种方法:new file(spring parent,String child) 根据父目录+子路径的结构
String parent = "e:\\";
String child = "new3.txt";
File file = new File(parent, child);
file.createNewFile();
}
}结果:
常用的文件操作:
public void means(){
File file = new File("e:\\new1.txt");
System.out.println("文件名字=" + file.getName());
System.out.println("文件的绝对路径=" + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件父级目录=" + file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件大小(字节)=" + file.length());
System.out.println("文件是否存在=" + file.exists());
System.out.println("是不是一个文件=" + file.isFile());
System.out.println("是不是一个目录=" + file.isDirectory());
}结果:

2.目录
目录创键:
public class Directory_ {
//判断 e:\\new1.txt 是否存在,如果存在就删除
@Test
public void m1(){
String filePath = "e:\\new1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()){
if (file.delete()){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
}else {
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
}
//判断 e:\\demo02 是否存在,存在就删除,否则提示不存在
@Test
public void m2(){
String filePath = "e:\\demo02";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()){
if (file.delete()){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
}else {
System.out.println("目录不存在");
}
}
//判断 e:\\demo\\a\\b\\c 目录是否存在,如果存在提示已经存在,否则就创建
@Test
public void m3(){
String filePath = "e:\\demo\\a\\b\\c";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()){
System.out.println("目录已经存在");
}else {
//mkdirs 创建多级的目录
//mkdir 创建一级的目录
file.mkdirs();
System.out.println("创建成功");
}
}
}
3.io的原理

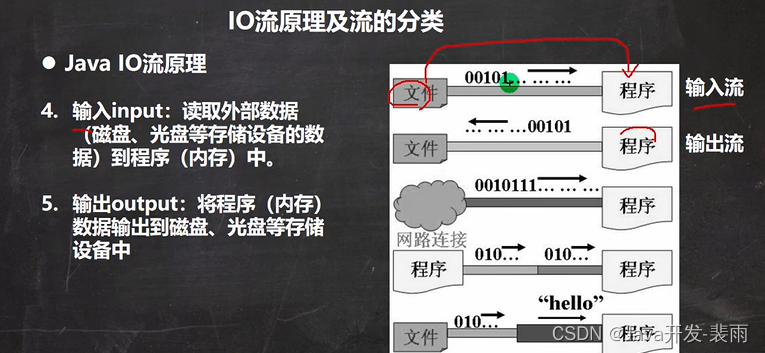
类图:
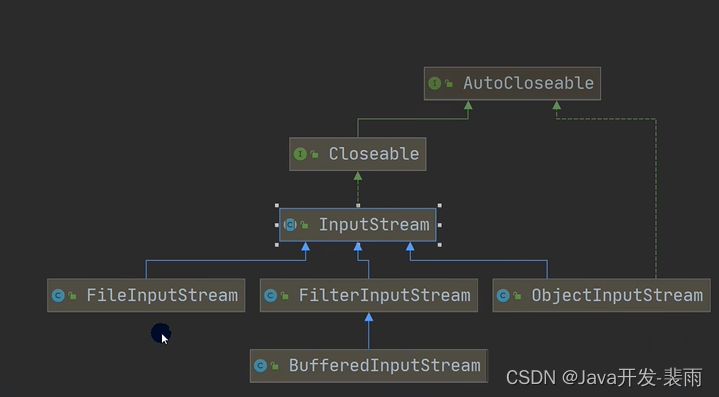
(1.)字节输入\输出流
FileInputStream:
**
* @author peiyu
* @version 1.0
* 演示FileInputStream的使用(字节流 文件--->程序)
*/
public class FileInputStream_ {
/**
* 演示读取文件
* 单个字节的读取,效率比较低 优化 ————> 使用 read(byte[] b)
*/
@Test
public void readFile(){
String filePath = "e:\\hello.txt";
int redaDate = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建 fileInputStream 对象 用于读取文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果输入可用,此方法将阻止
//如果结果返回 -1 表示读取完毕
while ((redaDate = fileInputStream.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)redaDate); //转成char类型
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭流释放资源
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
public void readFile02(){
String filePath = "e:\\hello.txt";
//字节数组
byte[] buf = new byte[8];
int readLen = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建 fileInputStream 对象 用于读取文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流最多读取 b.length 字节的数据到字节数组。此方法将阻塞,直到某些输入可用
//如果返回 -1 表示读取完毕
//如果读取正常,返回读取的字节长度
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1){
System.out.print(new String(buf,0,readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
FileOutStream:
public class FileOutPutStream_ {
/**
* 演示使用 FileOutStream 将数据写入到文件去
* 如果该文件不存在,则创建文件
*/
@Test
public void writeFile(){
String filePath = "e:\\a.txt";
//创建 FileOutStream 对象
FileOutputStream fileOutPutStrea







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 247
247











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








