目录
一、分数(2018)
题目描述
本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。
每项是前一项的一半,如果一共有 2020 项,求这个和是多少,结果用分数表示出来。

类似:3/2,当然,这只是加了前 2 项而已。分子分母要求互质。
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
题解
解题思路:等比数列
a 1 = 1 , q = 1 2 , s 8 = 2 20 − 1 2 19 a1=1,q=\frac{1}{2},s_8=\frac{2^{20}-1}{2^{19}} a1=1,q=21,s8=219220−1
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//在此输入您的代码..
int a = (int)(Math.pow(2, 20)) - 1;
int b = (a + 1) / 2;
System.out.println(a + "/" + b);
scan.close();
}
}
解题思路:模拟
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = 1; // 分子
int b = 1; // 分母
//在此输入您的代码..
for(int i = 2; i <= 20; i ++) {
a = a * 2 + 1;
b *= 2;
}
System.out.printf("%d/%d", a, b);
}
}
二、星期一(2018)
题目描述
本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。
整个 2020 世纪(19011901 年 11 月 11 日至 20002000 年 1212 月 3131 日之间),一共有多少个星期一?(不要告诉我你不知道今天是星期几)
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
题解
解题思路:EXCEL大法
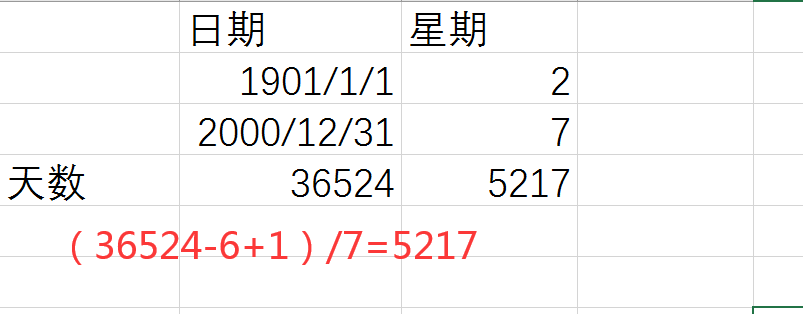
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//在此输入您的代码...
System.out.println("5217");
scan.close();
}
}
三、乘积尾零(2018)
题目描述
本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。
如下的 1010 行数据,每行有 1010 个整数,请你求出它们的乘积的末尾有多少个零?
5650 4542 3554 473 946 4114 3871 9073 90 4329
2758 7949 6113 5659 5245 7432 3051 4434 6704 3594
9937 1173 6866 3397 4759 7557 3070 2287 1453 9899
1486 5722 3135 1170 4014 5510 5120 729 2880 9019
2049 698 4582 4346 4427 646 9742 7340 1230 7683
5693 7015 6887 7381 4172 4341 2909 2027 7355 5649
6701 6645 1671 5978 2704 9926 295 3125 3878 6785
2066 4247 4800 1578 6652 4616 1113 6205 3264 2915
3966 5291 2904 1285 2193 1428 2265 8730 9436 7074
689 5510 8243 6114 337 4096 8199 7313 3685 211
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
-最大运行内存: 128M
题解
解题思路:大数计算
AC代码:
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main().init();
}
// 初始化
void init() {
String str = "5650 4542 3554 473 946 4114 3871 9073 90 4329 " +
"2758 7949 6113 5659 5245 7432 3051 4434 6704 3594 " +
"9937 1173 6866 3397 4759 7557 3070 2287 1453 9899 " +
"1486 5722 3135 1170 4014 5510 5120 729 2880 9019 " +
"2049 698 4582 4346 4427 646 9742 7340 1230 7683 " +
"5693 7015 6887 7381 4172 4341 2909 2027 7355 5649 " +
"6701 6645 1671 5978 2704 9926 295 3125 3878 6785 " +
"2066 4247 4800 1578 6652 4616 1113 6205 3264 2915 " +
"3966 5291 2904 1285 2193 1428 2265 8730 9436 7074 " +
"689 5510 8243 6114 337 4096 8199 7313 3685 211 ";
String[] strs = str.split(" ");
BigInteger res = new BigInteger("1");
for(String s : strs) {
BigInteger ss = new BigInteger(s);
res = res.multiply(ss);
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
输出结果:
112142221918653666702449201125076321480831896827506427440731023870278025729017605653056978504625081950967446934475613782859722081655293509714201067451491601144000940085173776751705443818861349991600968912829674368417898694508188364854988187881792613763161458365648071883922054736261940944120399031297726871056069331318210560000000000000000000000000000000
提交代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("0000000000000000000000000000000".length());
}
}
四、第几个幸运数字(2018)
题目描述
本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。
到 X 星球旅行的游客都被发给一个整数,作为游客编号。
X 星的国王有个怪癖,他只喜欢数字 3,5 和 7。
国王规定,游客的编号如果只含有因子:3,5,73,5,7,就可以获得一份奖品。
我们来看前 1010 个幸运数字是:
3 5 7 9 15 21 25 27 35 453579152125273545
因而第 1111 个幸运数字是: 4949
小明领到了一个幸运数字 5908470958750559084709587505,他去领奖的时候,人家要求他准确地说出这是第几个幸运数字,否则领不到奖品。
请你帮小明计算一下,5908470958750559084709587505 是第几个幸运数字。
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
题解
解题思路:打表 || 枚举
因为3,5,7的公约数均为1,所以三次for循环能生成全部的幸运数。
AC代码:
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main().init();
}
// 初始化
void init() {
long num = 59084709587505L;
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 30; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 30; j ++) {
for(int k = 0; k < 30; k ++) {
if(Math.pow(3, i) * Math.pow(5, j) * Math.pow(7, k) <= num) {
count ++;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(count - 1); // 去除 1 * 1 * 1的情况
}
}
提交代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("1905");
}
}
五、打印图形(2018)
题目描述
本题为代码补全填空题,请将题目中给出的源代码补全,并复制到右侧代码框中,选择对应的编译语言(C/Java)后进行提交。若题目中给出的源代码语言不唯一,则只需选择其一进行补全提交即可。复制后需将源代码中填空部分的下划线删掉,填上你的答案。提交后若未能通过,除考虑填空部分出错外,还需注意是否因在复制后有改动非填空部分产生错误。
如下的程序会在控制台绘制分形图(就是整体与局部自相似的图形)。
当 n=1,2,3 的时候,输出如下: 请仔细分析程序,并填写划线部分缺少的代码。
n=1时:
o
ooo
o
copy
n=2n=2 时:
o
ooo
o
o o o
ooooooooo
o o o
o
ooo
o
n=3时:
o
ooo
o
o o o
ooooooooo
o o o
o
ooo
o
o o o
ooo ooo ooo
o o o
o o o o o o o o o
ooooooooooooooooooooooooooo
o o o o o o o o o
o o o
ooo ooo ooo
o o o
o
ooo
o
o o o
ooooooooo
o o o
o
ooo
o
源代码
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void show(char* buf, int w){
int i,j;
for(i=0; i<w; i++){
for(j=0; j<w; j++){
printf("%c", buf[i*w+j]==0? ' ' : 'o');
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void draw(char* buf, int w, int x, int y, int size){
if(size==1){
buf[y*w+x] = 1;
return;
}
int n = _________________________ ; //填空
draw(buf, w, x, y, n);
draw(buf, w, x-n, y ,n);
draw(buf, w, x+n, y ,n);
draw(buf, w, x, y-n ,n);
draw(buf, w, x, y+n ,n);
}
int main()
{
int N ;
scanf("%d",&N);
int t = 1;
int i;
for(i=0; i<N; i++) t *= 3;
char* buf = (char*)malloc(t*t);
for(i=0; i<t*t; i++) buf[i] = 0;
draw(buf, t, t/2, t/2, t);
show(buf, t);
free(buf);
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
static void show(byte[][] buf){
for(int i=0; i<buf.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<buf[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(buf[i][j]==0? ' ' : 'o');
}
System.out.println();
}
}
static void draw(byte[][] buf, int x, int y, int size){
if(size==1){
buf[y][x] = 1;
return;
}
int n = ________________________ ; // 填空
draw(buf, x, y, n);
draw(buf, x-n, y ,n);
draw(buf, x+n, y ,n);
draw(buf, x, y-n ,n);
draw(buf, x, y+n ,n);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = scan.nextInt();
int t = 1;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) t *= 3;
byte[][] buf = new byte[t][t];
draw(buf, t/2, t/2, t);
show(buf);
}
}
运行限制
最大运行时间:1s
最大运行内存: 256M
题解
解题思路:代入法=分别带入n=1,n=2,n=3验证
思路:
- 先看Main方法:填充byte数组0,1,然后根据byte数组画图(如果1就画
o) - 看draw方法,咦,发现是个递归,递归出口是size==1结束递归,后面的方法最后一个参数都传进n,说明这个n一定与size有关,且一定是每次n减少。
- 大概看看这几个方法,设坐标(x,y),然后将这个坐标和上下左右搞点什么,我们带入n=1,比对比对题目给的图形:
o ooo o - size=3,需要n=1,所以猜测n=size/3;然后把代码再编辑器跑跑n=2,n=3,诶嘿,果然是。
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
static void show(byte[][] buf){
for(int i=0; i<buf.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<buf[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(buf[i][j]==0? ' ' : 'o');
}
System.out.println();
}
}
static void draw(byte[][] buf, int x, int y, int size){
if(size==1){
buf[y][x] = 1;
return;
}
int n = size / 3 ; // 填空
draw(buf, x, y, n);
draw(buf, x-n, y ,n);
draw(buf, x+n, y ,n);
draw(buf, x, y-n ,n);
draw(buf, x, y+n ,n);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = scan.nextInt();
int t = 1;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) t *= 3;
byte[][] buf = new byte[t][t];
draw(buf, t/2, t/2, t);
show(buf);
}
}
六、航班时间(2018)
题目描述
小 h 前往美国参加了蓝桥杯国际赛。小 h 的女朋友发现小 h 上午十点出发,上午十二点到达美国,于是感叹到"现在飞机飞得真快,两小时就能到美国了"。
小 h 对超音速飞行感到十分恐惧。仔细观察后发现飞机的起降时间都是当地时间。由于北京和美国东部有 12 小时时差,故飞机总共需要 14 小时的飞行时间。
不久后小 h 的女朋友去中东交换。小 h 并不知道中东与北京的时差。但是小 h 得到了女朋友来回航班的起降时间。小 h 想知道女朋友的航班飞行时间是多少。
对于一个可能跨时区的航班,给定来回程的起降时间。假设飞机来回飞行时间相同,求飞机的飞行时间。
输入描述
一个输入包含多组数据。
输入第一行为一个正整数 TT,表示输入数据组数。
每组数据包含两行,第一行为去程的 起降 时间,第二行为回程的 起降 时间。
起降时间的格式如下
h1:m1:s1 h2:m2:s2
或
h1:m1:s1 h3:m3:s3 (+1)
或
h1:m1:s1 h4:m4:s4 (+2)
表示该航班在当地时间 h1 时 m1 分 s1 秒起飞,
第一种格式表示在当地时间 当日 h2 时 m2 分 s2 秒降落
第二种格式表示在当地时间 次日 h3 时 m3 分 s3 秒降落。
第三种格式表示在当地时间 第三天 h4 时 m4 分 s4 秒降落。
对于此题目中的所有以 hⓂ️s 形式给出的时间, 保证 ( 0 \leq h \leq 23, 0 \leq m,s \leq 590≤h≤23,0≤m,s≤59).
保证输入时间合法,飞行时间不超过 24 小时。
输出描述
对于每一组数据输出一行一个时间 hh:mm:ss,表示飞行时间为 hh 小时 mm 分 ss 秒。
注意,当时间为一位数时,要补齐前导零。如三小时四分五秒应写 03:04:05。
输入输出样例
示例
输入
3
17:48:19 21:57:24
11:05:18 15:14:23
17:21:07 00:31:46 (+1)
23:02:41 16:13:20 (+1)
10:19:19 20:41:24
22:19:04 16:41:09 (+1)
输出
04:09:05
12:10:39
14:22:05
运行限制
最大运行时间:1s
最大运行内存: 256M
题解
解题思路:初中生解方程
设航行时间为
x
,时差为
y
,
a
1
,
b
1
,
a
2
,
b
2
分别为去回程的起降时间,则
\text{设航行时间为}x\text{,时差为}y,a_1,b_1,a_2,b_2\text{分别为去回程的起降时间,则}
设航行时间为x,时差为y,a1,b1,a2,b2分别为去回程的起降时间,则
{
a
1
+
x
+
y
=
b
1
a
2
+
x
−
y
=
b
2
\left\{ \begin{array}{l} a_1+x+y=b_1\\ a_2+x-y=b_2\\ \end{array} \right.
{a1+x+y=b1a2+x−y=b2
解得:
x
=
(
b
1
−
a
1
)
+
(
b
2
−
a
2
)
2
\text{解得:}x=\frac{\left( b_1-a_1 \right) +\left( b_2-a_2 \right)}{2}
解得:x=2(b1−a1)+(b2−a2)
AC代码:
import java.text.*;
import java.util.*;
// 1:无需package
// 2: 类名必须Main, 不可修改
public class Main {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
int n = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
long t1 = getTime();//第一次a->b 的时间差
long t2 = getTime();//往返时b->a 的时间差
long t = (t1+t2)/2; //两次的时间差相加 / 2
System.out.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n",t/3600,t/60%60,t%60);//输出时分秒。%2d表共两位,不足就补0
}
}
private static long getTime() throws ParseException {
String line = sc.nextLine();//输入起飞时间 到达时间
String[] split = line.split(" "); //获取起飞时间、到达时间、间隔天数的数组
SimpleDateFormat sd = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");//日期格式化显示(10:02:03)
Date t1 = sd.parse(split[0]); //将一个字符串类型的日期 转化为上述格式的日期
Date t2 = sd.parse(split[1]);
int day=0;//记录跨越的天数
if(split.length==3) {//存在天数的跨度
day = Integer.parseInt(split[2].substring(2, 3));//包括2不包括3(2、3均表示下标,下标从0开始)
}
return day*24*60*60 + t2.getTime()/1000 - t1.getTime()/1000;//返回往返相差的总秒数。getTime方法返回的是毫秒单位的long型数据。
}
}
七、三体攻击(2018)
题目描述
三体人将对地球发起攻击。为了抵御攻击,地球人派出 A × B × C 艘战舰,在太空中排成一个 A 层 B 行 C 列的立方体。其中,第 i 层第 j 行第 k 列的战舰(记为战舰 (i, j, k))的生命值为 d(i, j, k)。
三体人将会对地球发起 m 轮"立方体攻击",每次攻击会对一个小立方体中的所有战舰都造成相同的伤害。具体地,第 t 轮攻击用 7 个参数 lat, rat, lbt, rbt, lct, rct, ht 描述;
所有满足 i ∈ [lat, rat],j ∈ [lbt, rbt],k ∈ [lct, rct]的战舰 (i, j, k)会受到 ht 的伤害。如果一个战舰累计受到的总伤害超过其防御力,那么这个战舰会爆炸。
地球指挥官希望你能告诉他,第一艘爆炸的战舰是在哪一轮攻击后爆炸的。
输入描述
输入格式:
从标准输入读入数据。
第一行包括 4 个正整数 A, B, C, m;
第二行包含 A × B × C 个整数,其中第 ((i − 1)×B + (j − 1)) × C + (k − 1)+1 个数为 d(i, j, k);
第 3 到第 m + 2 行中,第 (t − 2) 行包含 7 个正整数 lat, rat, lbt, rbt, lct, rct, ht。
输出描述
输出描述
输出第一个爆炸的战舰是在哪一轮攻击后爆炸的。保证一定存在这样的战舰。
输入输出样例
示例
| 输入
2 2 2 3
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 2 1 2 1 1 1
1 1 1 2 1 2 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 2
| 输出
2
运行限制
最大运行时间:2s
最大运行内存: 256M
题解
解题思路:暴力
AC代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = sc.nextInt();
int B = sc.nextInt();
int C = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
// 战舰生命值
int[][][] martix = new int[A + 1][B + 1][C + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= A; i ++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= B; j ++) {
for(int k = 1; k <= C; k ++) {
martix[i][j][k] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
}
// 进行m轮攻击
boolean flag = false;
for(int t = 1; t <= m; t ++) {
int lat = sc.nextInt();
int rat = sc.nextInt();
int lbt = sc.nextInt();
int rbt = sc.nextInt();
int lct = sc.nextInt();
int rct = sc.nextInt();
int ht = sc.nextInt();
if(flag) continue;
for(int i = lat; i <= rat; i ++) {
for(int j = lbt; j <= rbt; j ++) {
for(int k = lct; k <= rct; k ++) {
martix[i][j][k] -= ht;
if(martix[i][j][k] < 0) {
System.out.println(t);
flag = true;
}
}
}
}
}
//在此输入您的代码...
sc.close();
}
}
八、全球变暖(2018)
题目描述
你有一张某海域 NxNNxN 像素的照片,".“表示海洋、”#"表示陆地,如下所示:
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
..####.
...###.
.......
其中"上下左右"四个方向上连在一起的一片陆地组成一座岛屿。例如上图就有 2 座岛屿。
由于全球变暖导致了海面上升,科学家预测未来几十年,岛屿边缘一个像素的范围会被海水淹没。具体来说如果一块陆地像素与海洋相邻(上下左右四个相邻像素中有海洋),它就会被淹没。
例如上图中的海域未来会变成如下样子:
.......
.......
.......
.......
....#..
.......
.......
请你计算:依照科学家的预测,照片中有多少岛屿会被完全淹没。
输入描述
第一行包含一个整数 (1≤N≤1000)。
以下 N 行 N 列代表一张海域照片。
照片保证第 1 行、第 1 列、第 N 行、第 N 列的像素都是海洋。、
输出一个整数表示答案。
输入输出样例
示例
| 输入
7
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
..####.
...###.
.......
|输出
1
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 256M
题解
解题思路:dfs
AC代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int MAX = 1005;
static char[][] map = new char[MAX][MAX]; // 岛屿
static boolean[][] vis = new boolean[MAX][MAX]; // 访问标记
static int num = 0, ans = 0, N; // 总岛屿数, 未被淹没的岛屿, 输入N
static int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}; // 方向
static boolean flag; // 是否被淹没
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++) map[i] = sc.next().toCharArray();
sc.close();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; j ++) {
if(map[i][j] == '#' && !vis[i][j]) {
num ++;
flag = true; // 假设岛屿可被淹没
dfs(i, j);
if(!flag) {
ans ++;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(num - ans);
}
static void dfs(int x, int y) {
vis[x][y] = true;
if(x+1>=0 && x+1<N && x-1>=0 && x-1<N && y+1>=0 && y+1<N && y-1>=0 && y-1<N) {
if(map[x+1][y]=='#' && map[x-1][y]=='#' && map[x][y+1]=='#' && map[x][y-1]=='#')
flag = false; // 存在一个不被淹没的点,标记该岛屿不可被淹没
}
// 四个方向dfs
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){
int xx = x + dir[i][0];
int yy= y + dir[i][1];
if(xx<0 || xx>=N || yy<0 || yy>=N || map[xx][yy]!='#' || vis[xx][yy])
continue;
dfs(xx,yy);
}
}
}






















 6618
6618











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








