说是自实现vector,其实就是尽量模拟出vector所具有的操作。
1、类 应有的成员
1、三个成员变量:
elements,指向首元素first_free,指向实际存在元素之后的位置cap,指向分配的内存末尾之后的位置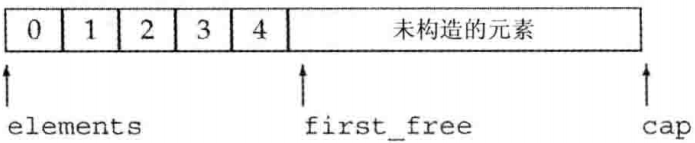
2、一个【静态alloctor成员】,用于给【所有】vector对象【分配内存空间】。
3、需要4个工具函数,管理每个vector的内存空间。
由于他们是用于实现这个类的,所以应该是私有的成员函数。
2、StrVec.h文件
#pragma once
#ifndef _STRVEC_H_
#define _STRVEC_H_
#include<string>
#include<memory>
#include<utility>
#include<initializer_list>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class StrVec
{
public:
StrVec() : elements(nullptr), first_free(nullptr), cap(nullptr) { }
StrVec(const StrVec&);
StrVec(const initializer_list<string>&);
StrVec& operator=(const StrVec&);
~StrVec();
void reserve(size_t);
size_t capacity() const;
void resize(size_t, char c = '0');
void push_back(const string&);
string* begin() const { return elements; }
string* end() const { return first_free; }
size_t size() { return first_free - elements; }
private:
string* elements;
string* first_free;
string* cap;
static allocator<string> alloc;
pair<string*, string*> alloc_n_copy(const string*, const string*); // 分配原始内存,并拷贝给定范围元素
void free(); // 销毁元素,释放内存
void reallocate(); // 内存用完时,重新分配内存
void chk_n_alloc(); // 保证至少有一个空间,否则调用 reallocate
inline void reallocate(size_t newcapacity);
};
#endif
inline void StrVec::reallocate(size_t newcapacity)
{
auto new_data = alloc.allocate(newcapacity);
auto dest = new_data;
auto elem = elements;
for (size_t i = 0; i != size(); ++i)
alloc.construct(dest++, std::move(*elem++));
free();
elements = new_data;
first_free = dest;
cap = new_data + newcapacity;
}
3、StrVec.cpp文件
#include "StrVec.h"
StrVec::StrVec(const StrVec& v)
{
auto new_data = alloc_n_copy(v.begin(), v.end());
elements = new_data.first;
first_free = new_data.second;
cap = new_data.second;
}
StrVec& StrVec::operator=(const StrVec& v)
{
auto new_data = alloc_n_copy(v.begin(), v.end());
free();
elements = new_data.first;
first_free = new_data.second;
cap = new_data.second;
return *this;
}
StrVec::~StrVec() { free(); }
pair<string*, string*> StrVec::alloc_n_copy(const string* b, const string* e)
{
auto new_data = alloc.allocate(b - e);
return { new_data, uninitialized_copy(b, e, new_data) }; // 这里很妙,用一个初始化列表初始化了pair,并返回
}
void StrVec::free()
{
while (first_free != elements)
alloc.destroy(--first_free);
alloc.deallocate(elements, cap - elements);
}
void StrVec::free()
{
for_each(elements, first_free, [](string& sp) { alloc.destroy(&sp); });
alloc.deallocate(elements, cap - elements);
}
void StrVec::reallocate()
{
auto newcapacity = size() ? size() * 2 : 1;// 记住,先要确定重新分配的策略,当容器不够用时,再多分配多大内存??
auto new_data = alloc.allocate(newcapacity); // 即使你后边用移动构造,也免不了要先老老实实分配内存
auto dest = new_data; // 指向新数组下一空位
auto elem = elements; // 指向旧数组下一个元素
for (size_t i = 0; i != size(); ++i)
alloc.construct(dest++, std::move(*elem++));// 开始构造了
free(); // 构造完了,原来的可以滚了
// 别忘了,更新成员指针哦
elements = new_data;
first_free = dest;
cap = elements + newcapacity;
}
void StrVec::chk_n_alloc()
{
if (size() == capacity()) // 注意这里的判断条件可不是 first_free == elements
reallocate();
}
void StrVec::push_back(const string& s)
{
chk_n_alloc();
//*first_free = s; 好好想想为什么这么写是错的!!!first_free指向的空间还是原始空间,必须先构造!!!
alloc.construct(first_free++, s);
first_free++;
}
void StrVec::reserve(size_t n) // 还需要另一个辅助函数的,你一个 reserve 怎么可能办得到
{
//alloc.allocate(n); 好好想想你这为啥错了??你这分配了一段八竿子打不着的内存,个这干啥呢??
// 你以为 allocate 能在原来结尾的地方,继续增加内存???想得美!
if (n > capacity())
reallocate(n); // 得重新写一个带参数的 reallocate
}
void StrVec::resize(size_t n, char c = '0')
{ // 这 TM 直接调用自己写好的 push_back 就行了,哪这么麻烦??????焯!!!
if (n == size() || n > capacity()) return;
if (n > size())
{
auto new_data = alloc.allocate(n);
uninitialized_copy(elements, elements + size(), new_data);
uninitialized_fill_n(new_data + size(), n - size(), c);
size_t tmp = capacity();
free();
elements = new_data;
first_free = new_data + n;
cap = new_data + tmp;
}
else
{
auto new_data = alloc.allocate(n);
uninitialized_copy(elements, elements + size(), new_data);
size_t tmp = capacity();
free();
elements = new_data;
first_free = new_data + n;
cap = elements + tmp;
}
}
size_t StrVec::capacity() const
{
return cap - elements;
}
StrVec::StrVec(const initializer_list<string>& sl)
{
auto new_data = alloc.allocate(sl.size());
first_free = uninitialized_copy(sl.begin(), sl.end(), new_data);
cap = first_free;
elements = new_data;
}
























 206
206











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








