da1、定义
队列:只允许在一端进行数据插入操作,在另一端进行数据删除操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出的原则。
入队列:进行数据插入操作的一端称为队尾;
出队列:进行数据删除操作的一端成为队首;

2、队列的使用
在java中,Queue是一个接口,底层通过链表来实现

Queue是一个接口,在实例化时必须要实例化LinkedList的对象 ,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
3、队列的使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
System.out.println(queue);
queue.poll();
System.out.println(queue);
}4、队列代码模拟实现
public class MyQueue {
//定义一个节点的类
private static class ListNode{
//节点的值
int value;
//上一个节点的引用
ListNode prev;
//下一个节点的引用
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//头节点
public ListNode head;
//尾节点
public ListNode tail;
public int size;
public void offer(int e){
ListNode node =new ListNode(e);
if(head==null){
head=node;
}else {
tail.next = node;
node.prev = tail;
}
tail=node;
size++;
}
public int poll(){
//判断队列是否为空,如果为空返回null
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,出队异常");
}
//记录出队列的值
int headvalue=head.value;
//向后移动下一个
head.next=head;
if(head!=null) {
//处理前驱节点
head.prev.next = null;
//处理head的prev
head.prev = null;
}
//调整size的值
size--;
//返回出队的值
return headvalue;
}
public int peek(){
if(head==null){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,出队异常");
}
return head.value;
}
public Boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
public int size(){
ListNode current=head;
int count=0;
while(current!=null){
count++;
current=current.next;
}
return count;
}
public void display(){
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
ListNode current=head;
while(current!=null){
sb.append(current.value);
if(current.next!=null){
sb.append(",");
}
current=current.next;
}
sb.append("]");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
public class TestQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue myqueue = new MyQueue();
myqueue.offer(12);
myqueue.offer(23);
myqueue.offer(34);
myqueue.offer(45);
myqueue.offer(56);
myqueue.offer(67);
System.out.println(myqueue.size());
myqueue.display();
System.out.println(myqueue.peek());
}
}
运行结果:

5、循环队列:底层还是一个数组,指定一个队列的大小,入队时当队列已满时,就不能再往进放了;出队时当队列为空时,就不能出队了
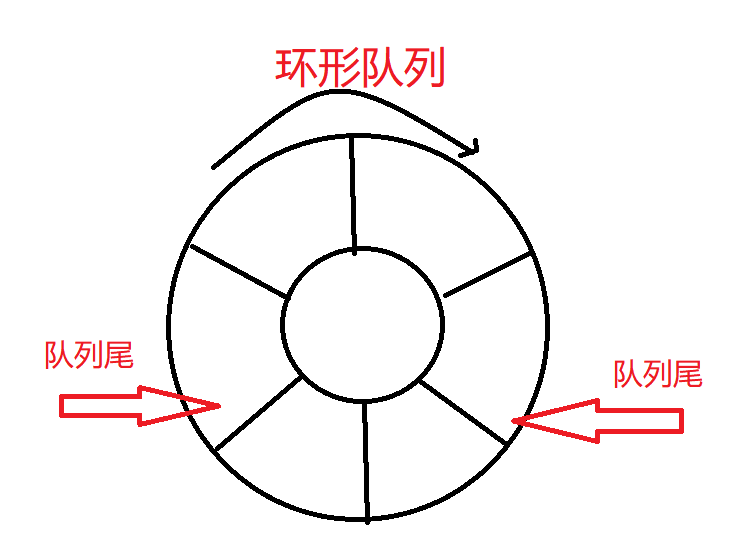
5.1、当数组为空的时候,front=rear;入队元素的时候,再rear添加元素,然后让rear++;用size记录元素数的时候,当ront==rear是,size==0则,队列为空,否则队列为满。

5.2、加一个冗余位置,当rear+1=front时也可以判断队列为满.
改变数组下标用一个公式来处理(index+x)%array.length=正确下标

5.3、再rear位置先添加元素,再移动rear下标
(rear+1)%elementData.length

5.4、出队操作:
从队首front下标出队,front向后移动,处理下标;
当front==rear时,队列为空;
空队列不能再出队
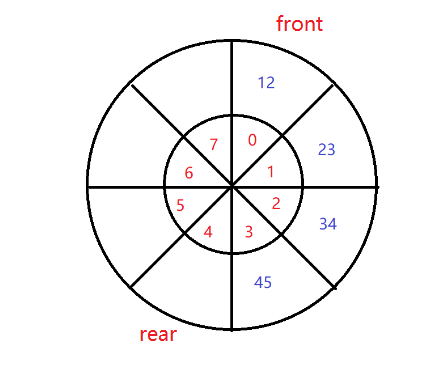
5.5、取队首元素:
队首元素:直接返回front下标的元素;
队尾元素:直接返回rear-1下标元素;
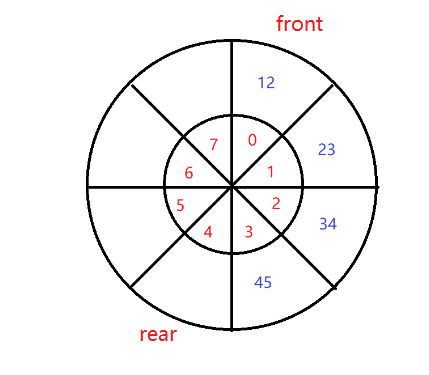
5.6、注意:
rear不是0下标的情况下rear-1,没有问题,但是rear在数组下标为0时,rear-1就会出现数组越界的问题,所以获取队尾元素:
//从队尾获取元素 int index=(rear-1+elementData.length)%elementData.length;
6、模拟实现循环队列:
class MyCircularQueue {
//定义一个数组
private int[] elementData;
//定义队头
private int front;
//定义队尾
private int rear;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
//初始化队列长度
//使用冗余原理来完成循环队列,这时使k+1,数组大小不变
elementData=new int[k+1];
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
//入队
//先判断队列是否满了
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
//队列不为空,入队
elementData[rear]=value;
//rear往后移动
rear=(rear+1)%elementData.length;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
//出队
//首先判断队列是否为空
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
//不为空出队
front=(front+1)%elementData.length;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
//从队首获取元素
return elementData[front];
}
public int Rear() {
//从队尾获取元素
int index=(rear-1+elementData.length)%elementData.length;
return elementData[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
//判断队列是否为空
return rear==front;
}
public boolean isFull() {
//判断队列是否满了
return (rear+1)%elementData.length==front;
}
}7、用队列实现栈
7.1、首先定义两个队列,一个用来入栈,一个用来出栈;
入栈的时候先入栈到那个为空的队列里面,再把那个不为空的队列中的元素全部出队并入队到当前入栈的队列中;
出栈时,直接出那个不为空的队列队头元素;
每次入完栈,把inQueue和outQueue做一个互换,保证inQueue一直为空
7.1、代码模拟实现:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class ExchangeQueue {
//定义两个队列
Queue<Integer> inQueue;
Queue<Integer> outQueue;
public ExchangeQueue() {
//初始化队列
inQueue=new LinkedList<>();
outQueue=new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
//直接入栈
inQueue.offer(x);
//把outQueue队列中的元素全部出队到inQueue队列中
while(outQueue.isEmpty()) {
inQueue.offer(outQueue.poll());
}
//inQueue和outQueue队列互换
Queue<Integer> temp=outQueue;
outQueue=inQueue;
inQueue=temp;
//执行后的结果就是元素x被压入栈内,inQueue还是为空
}
public int pop() {
//首先判断栈是否为空
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
int popvalue=0;
//出队元素
popvalue=outQueue.poll();
return popvalue;
}
public int top() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
return outQueue.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
//inQueue在每个元素入栈时候,inQueue一直为空,所以只需要判断outQueue是否为空就可以
return outQueue.isEmpty();
}
}







 文章介绍了队列的基本概念,包括先进先出的原则,以及在Java中如何通过LinkedList实现Queue接口进行队列操作。此外,文章详细讨论了循环队列的实现,包括满队列和空队列的判断,以及如何通过数组模拟循环队列。最后,提到了如何用队列实现栈的功能。
文章介绍了队列的基本概念,包括先进先出的原则,以及在Java中如何通过LinkedList实现Queue接口进行队列操作。此外,文章详细讨论了循环队列的实现,包括满队列和空队列的判断,以及如何通过数组模拟循环队列。最后,提到了如何用队列实现栈的功能。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








